Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells | Biology | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the fundamental differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles, such as a nucleus and mitochondria, while prokaryotes do not. Eukaryotic DNA is organized in multiple strands, whereas prokaryotic DNA is circular. Examples of eukaryotes include animals, plants, fungi, and protists, while bacteria and archaea are prokaryotes. The video also highlights the evolutionary theory that mitochondria may have originated as symbiotic prokaryotes. It concludes with an overview of life's three domains: bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Eukaryotes and prokaryotes are the two main categories of life forms.
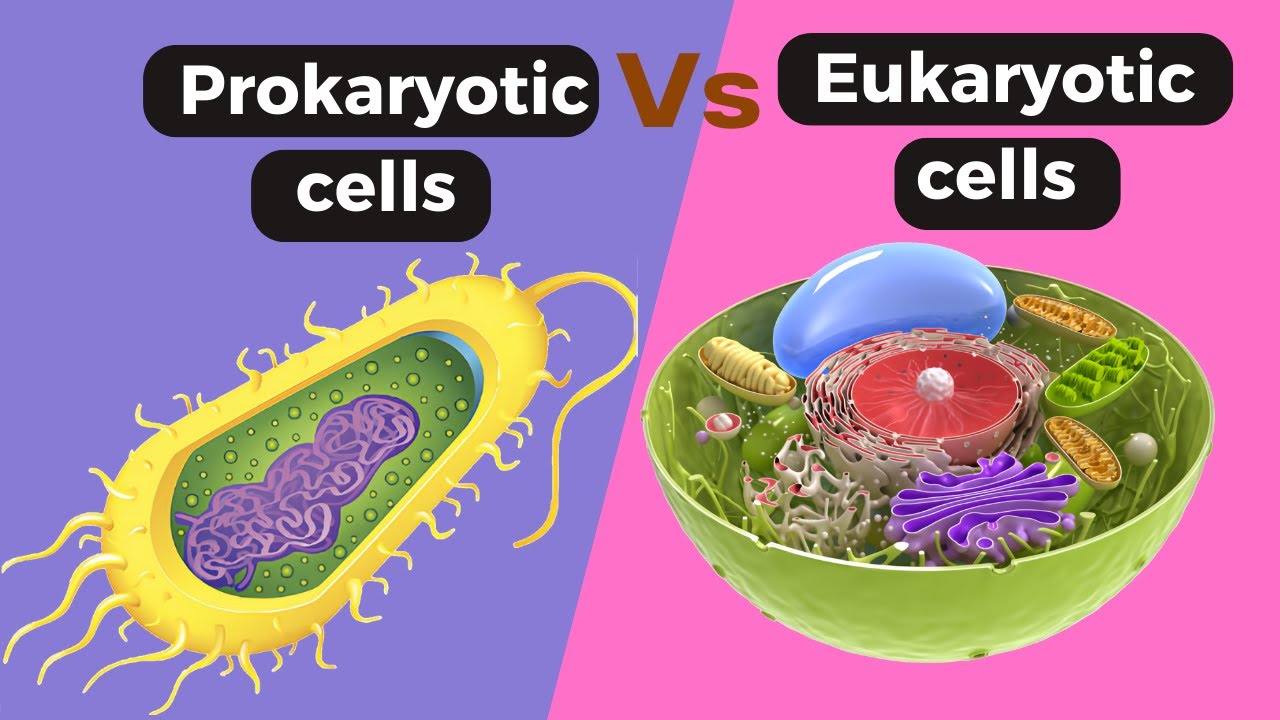
- 🔬 The key difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes is the presence of membrane-bound structures in eukaryotes, including a membrane-bound nucleus.
- 🧪 In eukaryotic cells, DNA is contained within a membrane-bound nucleus, while in prokaryotic cells, DNA is found in a nucleoid region without a membrane.
- 📜 Eukaryotes have other membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria and the Golgi apparatus, which are absent in prokaryotes.
- ⚛️ Mitochondria may have originated from prokaryotic organisms that lived in symbiosis with larger eukaryotic cells.
- 🔗 Eukaryotic DNA is linear and organized in multiple strands, while prokaryotic DNA is circular.
- 🌱 Eukaryotes include multicellular organisms like animals, plants, fungi, and protists.
- 🦠 Prokaryotes include bacteria and archaea, the latter being a distinct domain of life often found in extreme environments.
- 🌍 Eukaryotes are typically larger and more complex than prokaryotes, which tend to be smaller and simpler.
- 🔬 Prokaryotes (like bacteria) and archaea are distinct domains, while eukaryotes include organisms we encounter daily, like animals and plants.
Q & A
What is the main distinction between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
-The main distinction is that eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound structures, including a nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not. Eukaryotic cells have their genetic material enclosed within a membrane-bound nucleus, while prokaryotic cells have their DNA in a nucleoid region without a membrane.
What does the term 'eukaryote' mean, and how does it relate to cell structure?
-The term 'eukaryote' comes from the Greek word for 'nut' or 'kernel,' referring to the membrane-bound nucleus in these cells. This contrasts with prokaryotes, where 'pro' means 'before,' indicating the lack of a membrane-bound nucleus.
What are some other membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells besides the nucleus?
-Other membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells include mitochondria, which are involved in energy production, and the Golgi apparatus, which packages proteins.
What is the function of the nucleolus in a eukaryotic cell?
-The nucleolus, located within the nucleus, is responsible for producing ribosomal RNA (rRNA), which forms part of the structure of ribosomes, essential for protein synthesis.
How does the structure of DNA differ between eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
-In eukaryotes, the DNA is organized into multiple linear strands, whereas in prokaryotes, the DNA is typically circular.
What is a key theory about the origin of mitochondria in eukaryotic cells?
-A key theory is that mitochondria evolved from prokaryotic organisms that entered into a symbiotic relationship with larger eukaryotic cells.
What are some examples of eukaryotic organisms?
-Examples of eukaryotic organisms include animals, plants, fungi, and protists. These organisms can be multicellular, such as animals and plants, or unicellular, like certain protists.
What are some examples of prokaryotic organisms?
-Examples of prokaryotic organisms include bacteria and archaea. Archaea are often found in extreme environments and were once thought to be a type of bacteria.
How are archaea different from bacteria?
-Although archaea were initially thought to be a type of bacteria, they are now classified as a separate domain of life. Archaea often live in extreme conditions and differ from bacteria at a molecular level.
What are the three core distinctions between eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
-The three core distinctions are: (1) eukaryotes have a membrane-bound nucleus, while prokaryotes do not, (2) eukaryotes contain other membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria and the Golgi apparatus, which prokaryotes lack, and (3) eukaryotic DNA is organized into multiple linear strands, while prokaryotic DNA is circular.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes

Comparing prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells | High school biology | Khan Academy
Prokaryotic cell Vs Eukaryotic cells|| Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell

Citologia 1/2: Estrutura Básica das Células | Anatomia e etc

Sel: Prokariotik vs Sel Eukariot | Biologi | Alternatifa

Perbedaan Sel Prokariotik & Sel Eukariotik | Pembelajaran Daring - Dunia Biologi
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
