Mole Conversions Made Easy: How to Convert Between Grams and Moles
Summary
TLDRThis video, presented by Ketzbook, offers an easy guide to mole conversions in chemistry. It explains what a mole is and its significance in measuring atoms, molecules, and compounds. The video covers how to calculate molar mass using the periodic table, convert between grams and moles, and perform mole conversions for both elements and compounds. With clear examples, such as lithium, carbon monoxide, and magnesium nitrate, the video simplifies complex concepts, making it ideal for learners. The host also provides step-by-step problems to ensure mastery of mole conversions.
Takeaways
- 📏 The mole in chemistry is a large number, equal to 6 x 10^23, similar to how a dozen is 12.
- 🔬 Moles are used to count atoms and molecules because atoms are incredibly small.
- 📊 One mole of any element has a mass equal to its atomic weight in grams, making it a useful conversion factor between grams and moles.
- 🧮 The molar mass of lithium is 6.94 grams per mole, so 25 grams of lithium equals 3.6 moles.
- 🔄 Mole conversions use molar mass as a conversion factor, such as when converting between grams and moles.
- ⚖️ The molar mass of a molecule is calculated by adding the molar masses of each element in the compound, like carbon monoxide (28.01 g/mol).
- 🥼 For diatomic elements like nitrogen (N2), the molar mass is doubled because there are two atoms in each molecule.
- 🧪 For ionic compounds, such as magnesium nitrate, the molar mass is the sum of all atoms in the formula, which for magnesium nitrate is 148.3 grams per mole.
- 📐 Mole conversion problems can go both ways, from grams to moles or from moles to grams, depending on the given and the conversion factor.
- 👍 The video encourages engagement by asking for likes and comments and offers additional resources through the creator's website.
Q & A
What is a mole in chemistry?
-In chemistry, a mole is a large number of things, similar to a dozen but much larger. One mole equals 6 times 10 to the 23rd things, which is approximately 600 billion trillion.
Why is the number of things in a mole so large?
-The number is so large because atoms are incredibly small. For example, one cup of water contains about 15 trillion, trillion hydrogen atoms, which would be counted as only 25 moles.
What is the significance of the number 6 times 10 to the 23rd in chemistry?
-The number 6 times 10 to the 23rd is significant because it represents both Avogadro's number, the number of entities in one mole, and the number of atomic mass units in one gram.
What is the molar mass of lithium according to the script?
-The molar mass of lithium is 6.94 grams per mole, which is also its atomic weight.
How many moles of lithium are in 25 grams of lithium?
-There are 3.6 moles of lithium in 25 grams of lithium.
What is the mass of 11.5 moles of lithium?
-The mass of 11.5 moles of lithium is 79.8 grams.
How does one calculate the molar mass of a compound?
-To calculate the molar mass of a compound, you add up the molar masses of all the atoms in the molecule.
What is the molar mass of carbon monoxide?
-The molar mass of carbon monoxide is 28.01 grams per mole, calculated by adding the molar mass of carbon (12.01 g/mol) and oxygen (16 g/mol).
How is the molar mass of a diatomic molecule like nitrogen (N2) calculated?
-The molar mass of nitrogen (N2) is calculated by multiplying the atomic mass of nitrogen (14.01 g/mol) by 2, resulting in a molar mass of 28.02 grams per mole.
What is the molar mass of carbon dioxide?
-The molar mass of carbon dioxide is 44.01 grams per mole, calculated by adding the molar mass of carbon (12.01 g/mol) and twice the molar mass of oxygen (16 g/mol * 2).
How does one convert grams of a compound to moles using the molar mass?
-To convert grams to moles, divide the mass of the compound by its molar mass. For example, to convert 6.35 grams of magnesium nitrate to moles, divide 6.35 by the molar mass of magnesium nitrate (148.3 g/mol).
What is the mass of 0.369 moles of magnesium nitrate?
-The mass of 0.369 moles of magnesium nitrate is 54.7 grams, calculated by multiplying 0.369 moles by the molar mass of magnesium nitrate (148.3 g/mol).
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Stoichiometry - clear & simple (with practice problems) - Chemistry Playlist
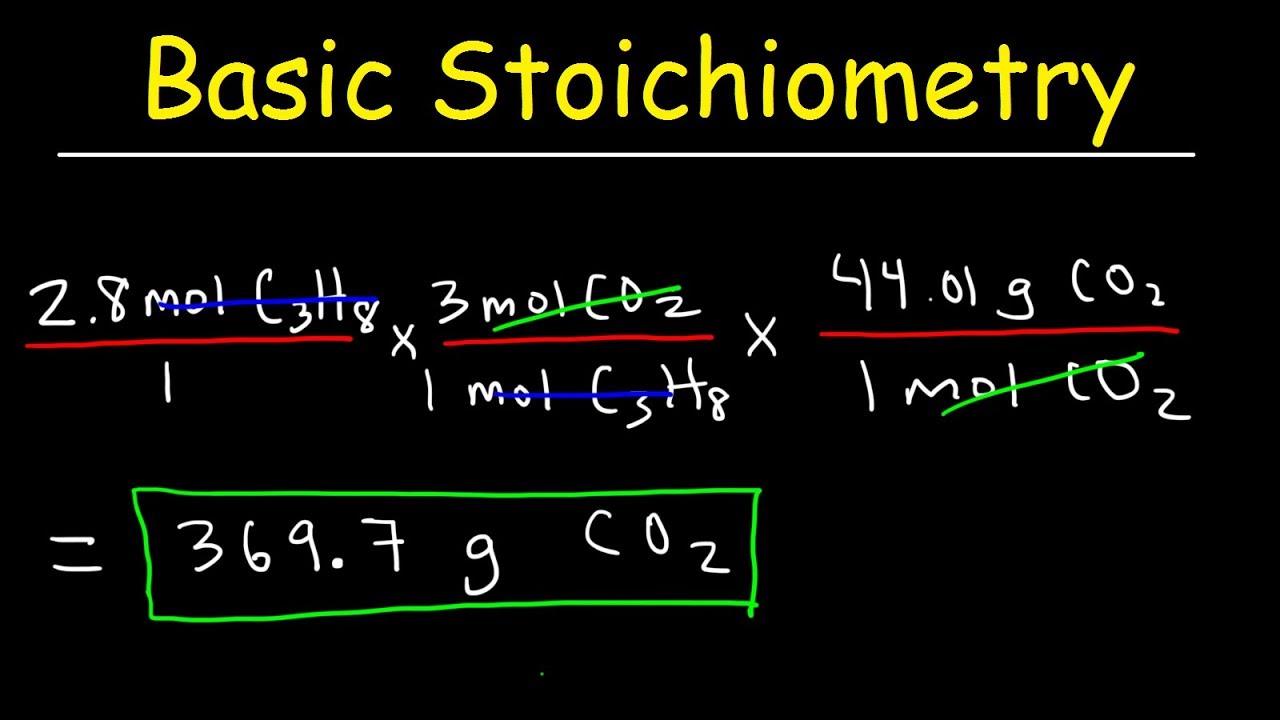
Stoichiometry Basic Introduction, Mole to Mole, Grams to Grams, Mole Ratio Practice Problems

S9Q2W7 | THE MOLE

GCSE Chemistry - The Mole (Higher Tier) #25

Boost Your Class 12th Exam | The Catalyst
Stoikiometri Larutan || Larutan Asam dan Basa || Materi Kimia SMA Kelas XI || Hikmah nor
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
