Peluang (Part 2) | Kejadian Majemuk | Saling Lepas, Tidak Saling Lepas, Saling Bebas, dan Bersyarat
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Deni from Metland channel discusses various concepts of probability, focusing on dependent and independent events. The tutorial covers how to calculate the probability of simultaneous dice rolls resulting in specific sums, explains the difference between mutually exclusive and non-mutually exclusive events, and introduces conditional probability. Examples include rolling dice and flipping coins to illustrate these concepts, making the content engaging and easy to understand.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video discusses the concept of compound events in probability theory.
- 🎯 The first topic covered is 'mutually exclusive events', where events A and B cannot occur at the same time.
- 📊 A visual representation using a Venn diagram is used to explain mutually exclusive events.
- 👉 The formula for the probability of mutually exclusive events is P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B).
- 🎲 An example is given involving the roll of two dice to illustrate the calculation of mutually exclusive events.
- 🤔 The concept of 'not mutually exclusive events' is introduced, where events can occur simultaneously.
- 🔢 A formula is provided to calculate the probability of non-mutually exclusive events, involving subtracting the probability of the intersection of events A and B from the sum of their individual probabilities.
- 🃏 An example with dice of different colors is used to demonstrate how to calculate the probability of non-mutually exclusive events.
- 🆓 The term 'independent events' is explained, where the occurrence of event A does not affect the probability of event B, and vice versa.
- 🎰 The formula for the probability of independent events is P(A and B) = P(A) * P(B).
- 🏆 An example involving the roll of a die and the flip of a coin is used to explain the calculation of independent events.
- 💡 The final topic is 'conditional probability', which is the probability of event B occurring given that event A has already occurred.
- 👨👩👧👦 An example is given involving the selection of a class president from a pool of candidates, some of whom are ranked in the top 10.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the video?
-The main topic discussed in the video is the concept of probability in events, specifically focusing on independent, mutually exclusive, and conditional events.
What are the four types of events discussed in the video?
-The video discusses four types of events: mutually exclusive events, independent events, events that are neither mutually exclusive nor independent, and conditional events.
How are mutually exclusive events defined in the video?
-Mutually exclusive events are defined as events that cannot occur at the same time or do not overlap. They are represented in a Venn diagram without any intersection.
What is the formula for calculating the probability of mutually exclusive events?
-The formula for calculating the probability of mutually exclusive events is P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B), where P(A) is the probability of event A and P(B) is the probability of event B.
Can you provide an example of mutually exclusive events given in the video?
-An example of mutually exclusive events given in the video is rolling a die and getting a number 6 or rolling a sum of 11 with two dice.
What is the definition of independent events as explained in the video?
-Independent events are those where the occurrence of one event does not affect the occurrence of another event.
How is the probability of independent events calculated according to the video?
-The probability of independent events is calculated by multiplying the probability of each event, which is P(A and B) = P(A) * P(B).
What is the example given in the video to explain independent events?
-The example given in the video is rolling a die and flipping a coin simultaneously, where the outcome of the die does not affect the outcome of the coin.
What is the concept of conditional probability mentioned in the video?
-Conditional probability is the probability of an event occurring given that another event has already occurred. It is denoted as P(B|A), which means the probability of event B happening given that event A has occurred.
Can you provide an example of conditional probability from the video?
-An example of conditional probability from the video is selecting a male candidate who ranks in the top 10 from a pool of candidates, where there are 14 candidates in total, including 8 males and 6 females.
How does the video explain the difference between mutually exclusive and non-mutually exclusive events?
-The video explains that non-mutually exclusive events are those that can occur at the same time, and there is an overlap between them, unlike mutually exclusive events which cannot occur simultaneously.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Kaidah Pencacahan 1 - Aturan Penjumlahan dan Aturan Perkalian Matematika Wajib Kelas 12

Peluang Kejadian Saling Bebas dan Bersyarat (Tidak Saling Bebas)
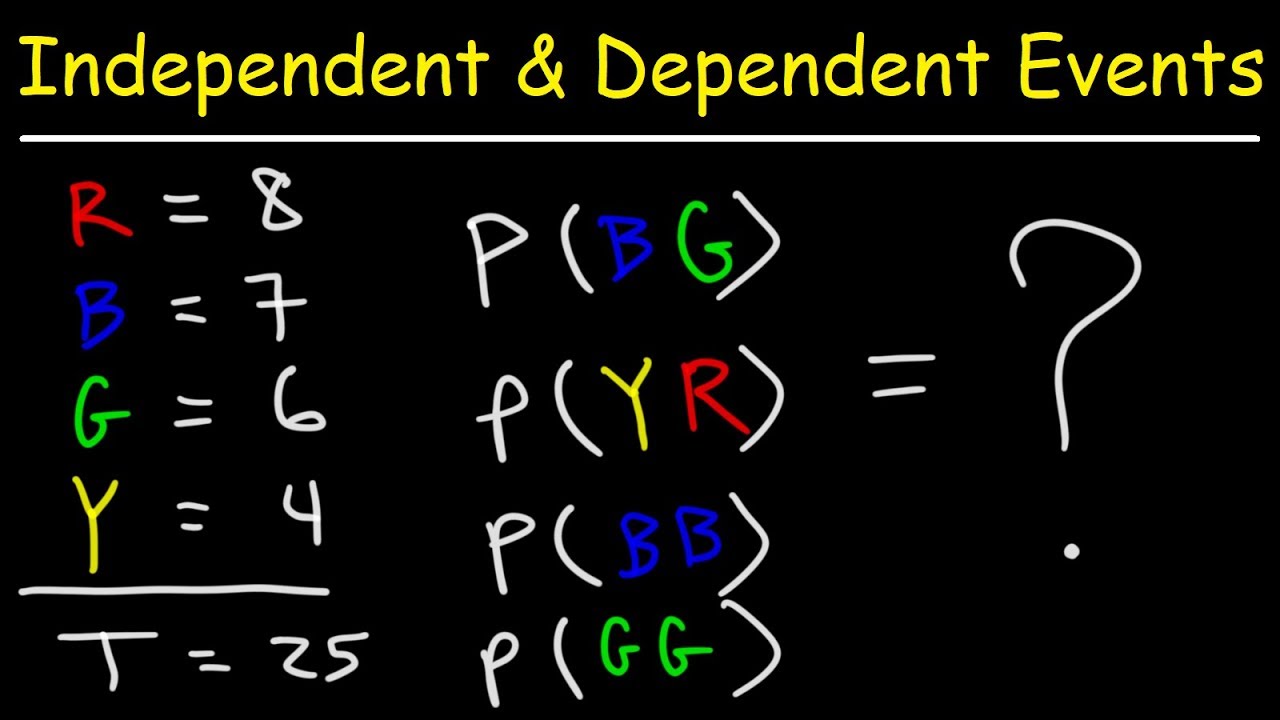
Probability - Independent and Dependent Events

Probability of Independent and Dependent Events (6.2)

(Part 1) PELUANG MATEMATIKA SMA KELAS 10 #kurikulummerdeka #matematikasma #bukupaket

LEC_3 | PROBABILITY| CONDITIONAL Prob.|BAYE'S THEOREM| UNIT-4 (ST-2) #aktu #math4 @monikamittalmm
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
