(New Version Available) Compound Inequalities
Summary
TLDRThis lesson focuses on compound inequalities, explaining how to find the intersection and union of sets, as well as how to express compound inequalities graphically and in interval notation. Key topics include the difference between inequalities connected by 'and' (conjunctions) and 'or' (disjunctions), with examples illustrating both. The video walks through various scenarios, graphing inequalities, and applying interval notation. The importance of understanding the mathematical implications of 'and' versus 'or' is emphasized throughout, providing a clear foundation for solving compound inequalities effectively.
Takeaways
- 🔢 The intersection of two sets 'A' and 'B' includes elements that belong to both sets.
- 📊 Compound inequalities can be expressed graphically and in interval notation.
- ⚙️ When inequalities are connected by 'AND', both conditions must be true for a solution.
- 🌐 The union of two sets 'A' and 'B' includes all elements from either set.
- 🔗 Inequalities connected by 'OR' require only one condition to be true for a solution.
- 📏 Graphing helps visualize where inequalities overlap and identify their intersection or union.
- 📝 Interval notation is a concise way to represent the solution set of inequalities.
- ⚖️ Compound inequalities connected by 'AND' may sometimes have no solution if their ranges don’t overlap.
- 💡 When solving inequalities, flipping the inequality sign is necessary when dividing by a negative number.
- ➕ Complex inequalities often require solving for 'X' before determining the solution graphically and with interval notation.
Q & A
What is the intersection of two sets, and how is it represented?
-The intersection of two sets, 'A' and 'B', is the set of all elements that are present in both 'A' and 'B'. For example, if set A consists of numbers from 1 to 7 and set B consists of numbers from 5 to 10, their intersection is {5, 6, 7}, as those numbers appear in both sets.
How do compound inequalities involving 'AND' work?
-In compound inequalities involving 'AND', both conditions must be true simultaneously. For example, if we have x > -2 and x < 5, we are looking for values of x that satisfy both conditions. Graphically, this is represented as the overlap between the two inequalities, and in interval notation, it would be written as (-2, 5).
What does the union of two sets represent?
-The union of two sets, 'A' and 'B', represents all the elements that are in either set A or set B, or in both. For example, if set A contains numbers from 1 to 7 and set B contains numbers from 5 to 10, the union would be {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}, which includes all numbers from both sets.
How do compound inequalities involving 'OR' work?
-In compound inequalities involving 'OR', either condition can be true. For example, if x ≤ -2 or x ≥ 3, x can satisfy either inequality. Graphically, this is represented by the union of the two inequalities, and in interval notation, it would be written as (-∞, -2] U [3, ∞).
What is the difference between conjunction and disjunction in inequalities?
-Conjunction refers to inequalities connected by 'AND', meaning both inequalities must be true simultaneously. Disjunction refers to inequalities connected by 'OR', meaning either inequality can be true. Mathematically, conjunctions are intersections, and disjunctions are unions.
How do you graph the inequality x > -2 and x < 5?
-To graph x > -2, you place an open circle at -2 and draw an arrow to the right, indicating that all values greater than -2 are included. For x < 5, you place an open circle at 5 and draw an arrow to the left. The intersection, where both inequalities are true, is the interval (-2, 5).
What happens when two inequalities have no overlap?
-When two inequalities have no overlap, their intersection is empty, meaning no values satisfy both conditions. For example, if x > 5 and x ≤ -1, there are no values of x that can satisfy both conditions, so the solution is the empty set.
How do you represent an inequality with all real numbers as the solution?
-When an inequality or system of inequalities covers all possible values of x, the solution is all real numbers. For example, if x ≤ 4 or x > 0, this inequality covers the entire number line. In interval notation, it is written as (-∞, ∞).
What is interval notation, and how is it used to express inequalities?
-Interval notation is a method of writing the set of solutions to an inequality. For example, if x is between -2 and 5, but does not include -2 and 5, it is written as (-2, 5). Brackets [ ] are used to include endpoints, and parentheses ( ) are used when endpoints are not included.
What does it mean to reverse an inequality when dividing by a negative number?
-When you divide both sides of an inequality by a negative number, the inequality sign must be reversed. For example, if you have -2x < 6 and you divide both sides by -2, the inequality becomes x > -3, reversing the direction of the inequality.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
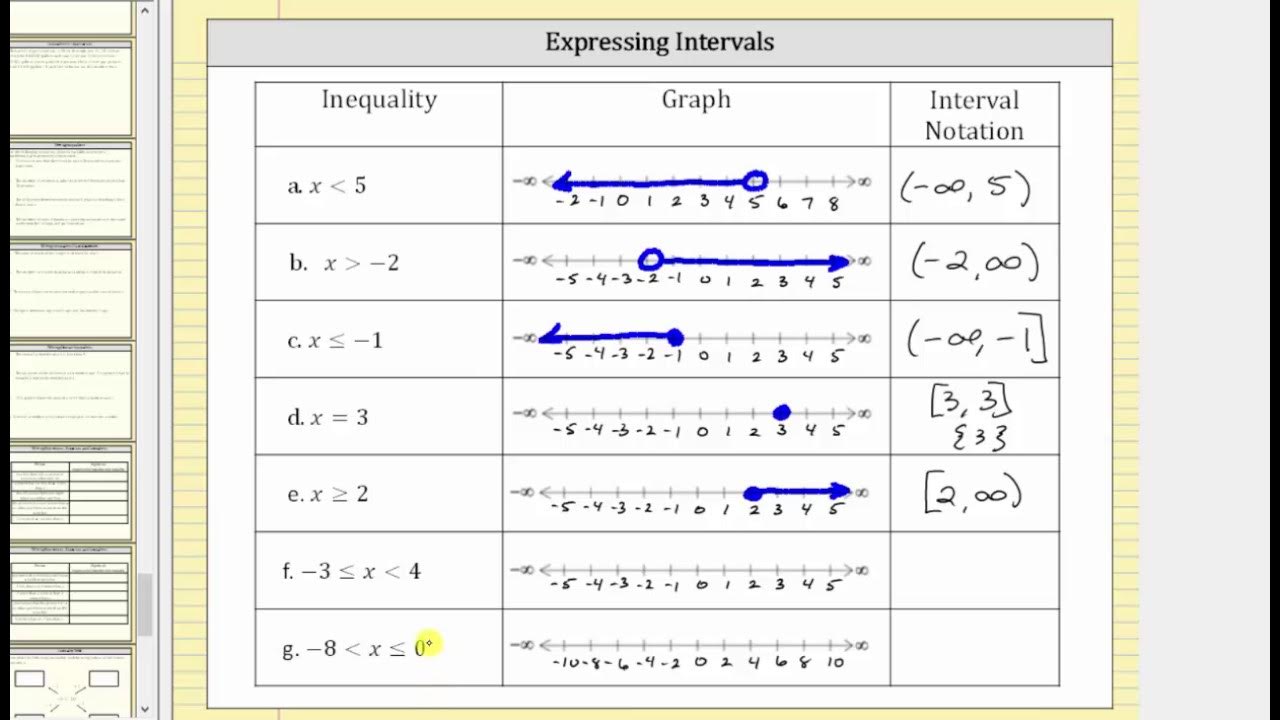
Express Inequalities as a Graph and Interval Notation

Absolute value inequalities | Linear equations | Algebra I | Khan Academy

FÁCIL e RÁPIDO | INTERVALOS REAIS | UNIÃO | INTERSEÇÃO e DIFERENÇA
SOLVING LOGARITHMIC INEQUALITIES | GRADE 11 GENERAL MATHEMATICS Q1
GCSE Maths - What are Inequalities? (Inequalities Part 1) #56
Rational Inequalities
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
