How does a Refrigerator work?
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the working principles of modern refrigerators, starting with the basic vapor compression cycle. It highlights key components like the throttling device, evaporator, compressor, and condenser, and describes how cold liquid is circulated to achieve cooling. The video also addresses common issues such as frost buildup and shows how modern solutions like digital inverter compressors improve energy efficiency and temperature control. The digital inverter technology, which allows variable compressor speeds, significantly enhances performance and reduces energy consumption by at least 40%, compared to traditional single-speed compressors.
Takeaways
- 🧊 The basic principle of refrigerators is to pass a colder liquid continuously around the object to be cooled.
- 🌡️ A throttling device, often a capillary tube, is crucial for creating a cold liquid by reducing pressure and causing the refrigerant to evaporate.
- 💧 The refrigerant should be able to change phase with pressure variation at normal temperatures, which is essential for the refrigeration cycle.
- 🔄 The refrigeration cycle involves the refrigerant going through a series of transformations: from liquid to vapor and back to liquid.
- 🌀 An evaporator fan helps maintain different temperature levels inside the refrigerator by circulating the cold refrigerant.
- 🔧 The compressor raises the pressure of the refrigerant back to its initial value after it has been throttled and evaporated.
- 🌡️ The condenser, located outside the refrigerator, converts the high-pressure vapor back into a liquid by releasing heat to the surroundings.
- ❄️ Frost formation in the freezer compartment is a common issue, which can be mitigated by occasional defrosting or using a heating rod.
- 🔧 Modern refrigerators use a compact condenser arrangement and a cooling fan to improve heat rejection and efficiency.
- 🏡 The capillary tube in home refrigerators is often hidden inside the evaporator exit coil, which optimizes the refrigeration effect.
- 🔋 Digital inverter compressors offer variable speed control, leading to smoother temperature management and at least 40% less energy consumption compared to single-speed compressors.
Q & A
What is the basic principle behind the operation of a refrigerator?
-The basic principle of a refrigerator is to pass a colder liquid continuously around the object to be cooled. This creates a cooling effect by absorbing heat from the object.
How is the cold liquid flow achieved inside a refrigerator?
-A cold liquid flow is achieved using a throttling device, like a capillary tube. The refrigerant is in a high-pressure liquid state at the inlet, and as it flows through the tube, the pressure drops, lowering the boiling point and causing part of the refrigerant to evaporate, which cools the remaining liquid.
What role does the compressor play in a refrigerator?
-The compressor raises the pressure of the refrigerant vapor back to its initial high-pressure state after the cooling process. This allows the refrigeration cycle to repeat continuously.
What is the purpose of the condenser in a refrigerator?
-The condenser converts the high-pressure vapor refrigerant into a liquid by releasing heat to the surroundings. This occurs after the refrigerant is compressed and before it returns to the throttling device.
What is the role of the evaporator in the refrigeration cycle?
-The evaporator absorbs heat from the refrigerated space. As the refrigerant passes through the evaporator, it absorbs heat and evaporates, causing the temperature in the space to decrease.
Why does frost form in the freezer compartment, and how is it removed?
-Frost forms when the moisture in the circulating air condenses on the cold evaporator coil. This frost can impede heat transfer, making the refrigerator inefficient. To remove it, modern refrigerators use a heating rod to melt the frost, and the water is collected in a pan at the bottom of the refrigerator.
Why do modern refrigerators have a compact condenser instead of visible condenser fins at the back?
-Modern refrigerators use a compact condenser arrangement with a cooling fan, which achieves the same heat rejection purpose as the older, larger condenser fins. The fan also helps evaporate water from the defrosting process.
Why do some refrigerators only have one visible refrigerant line instead of two?
-Modern refrigerators often have only one visible line because the capillary tube, which carries the cold refrigerant liquid, is routed inside the evaporator exit coil. This design improves the cooling efficiency by bringing the refrigerant temperature down further.
What is the benefit of using a digital inverter compressor in modern refrigerators?
-Digital inverter compressors allow variable speed operation, which leads to smoother temperature control, greater energy efficiency (up to 40% less energy consumption), and increased durability compared to traditional single-speed compressors that switch abruptly between on and off states.
How does the digital inverter compressor control motor speed?
-In a digital inverter compressor, AC power is converted to DC using a controller, which supplies electric power at variable frequencies to control the motor speed accurately. This allows for more precise temperature regulation inside the refrigerator.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
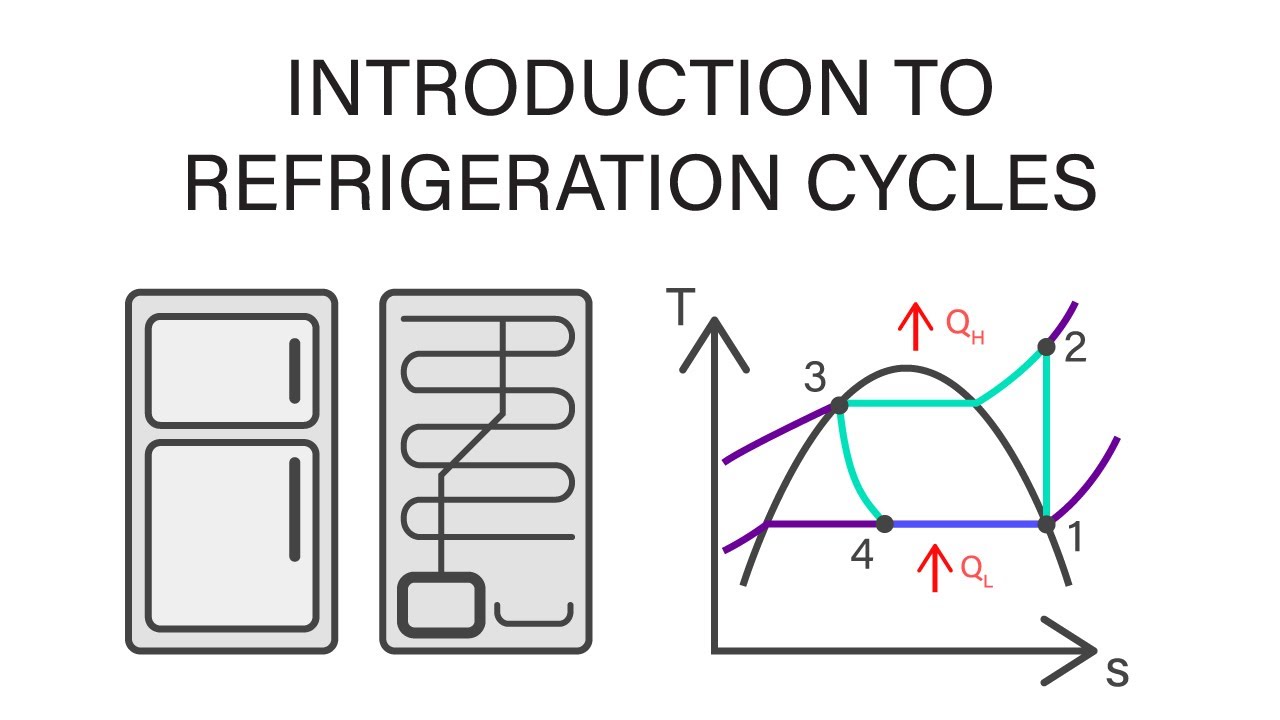
Mechanical Engineering Thermodynamics - Lec 23, pt 1 of 4: Introduction to Refrigeration Cycles

Refrigerasi02

Termodinamika • Part 4: Hukum Kedua Termodinamika, Mesin Carnot & Mesin Pendingin
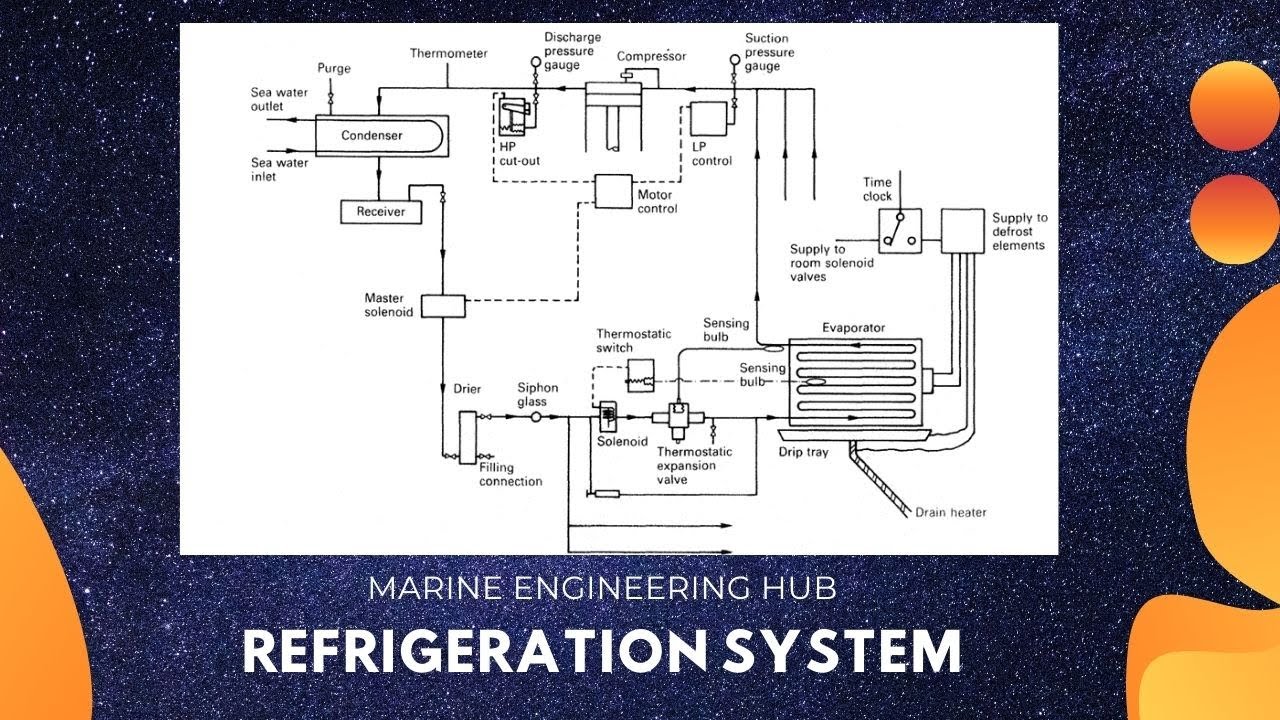
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM| (PART-1)|

Bagaimana Kulkas Menghasilkan Dingin | Termodinamika
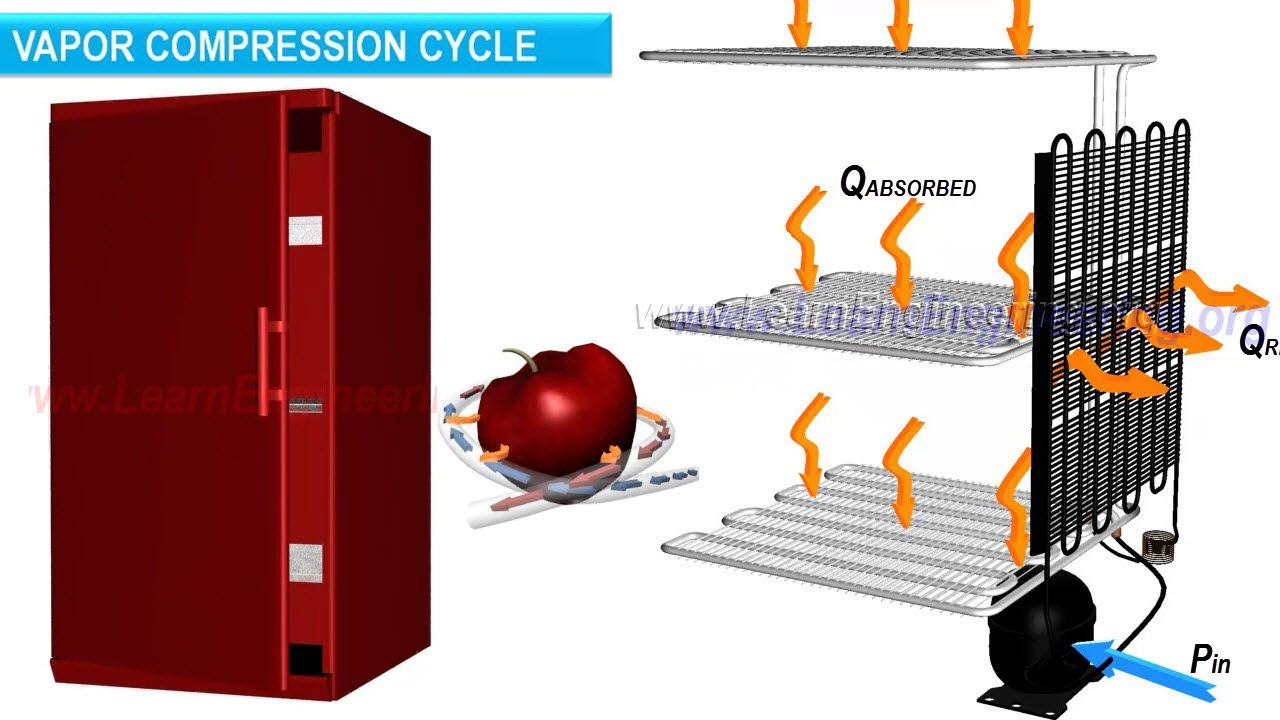
Refrigerator working - The Basics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
