Photosynthesis - Light Dependent Reactions and the Calvin Cycle
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into photosynthesis, explaining it as the process where plants convert light energy into chemical energy. It outlines the light-dependent reactions occurring in the chloroplast's thylakoids, where water is split to produce oxygen and electrons, leading to ATP and NADPH formation. The light-independent reactions, or Calvin cycle, take place in the stroma, fixing carbon dioxide into glucose. The video highlights the role of chlorophyll in light absorption and the significance of the electron transport chain, emphasizing the interplay between photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
Takeaways
- 🌞 Photosynthesis uses light energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates, specifically glucose, with oxygen as a byproduct.
- 🪴 Water is absorbed through the roots, while carbon dioxide enters the leaves through stomata, and oxygen is released through the same openings.
- 🍃 The chloroplast is the organelle responsible for photosynthesis, while the mitochondria handle cellular respiration.
- 🌱 Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are opposite processes: photosynthesis builds glucose and oxygen, while respiration breaks down glucose and oxygen into carbon dioxide and water.
- 🌈 Chlorophyll, the pigment in the chloroplast, absorbs blue and red light but reflects green light, giving plants their green color.
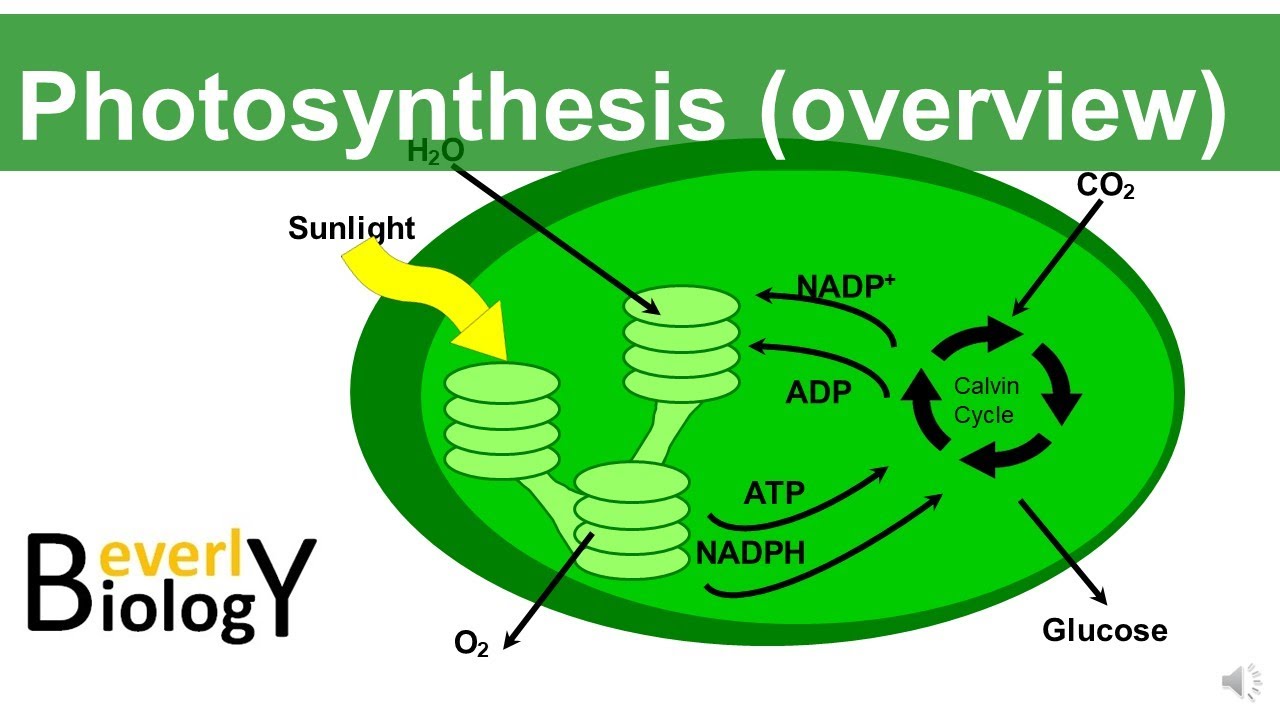
- 🔆 Photosynthesis consists of two stages: light-dependent reactions (in the thylakoids) and light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle in the stroma).
- ⚡ Light-dependent reactions produce oxygen, ATP, and NADPH by oxidizing water and using sunlight energy.
- 🌀 The Calvin cycle converts carbon dioxide into glucose using ATP and NADPH, with NADPH being oxidized back to NADP+.
- 🔋 The products of light-dependent reactions fuel the Calvin cycle, enabling the reduction of CO2 into sugars.
- 🔗 The electron transport chain in the thylakoid membrane generates a proton gradient, driving ATP synthesis through chemiosmosis.
Q & A
What is the meaning of the word 'photosynthesis'?
-Photosynthesis is derived from the Greek words 'photo' meaning light, and 'synthesis' meaning to build. It refers to the process by which plants use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
What are the net reactants and products of photosynthesis?
-The net reactants in photosynthesis are six water molecules (H2O) and six carbon dioxide molecules (CO2), and the products are glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen gas (O2).
How do plants intake water and carbon dioxide, and release oxygen during photosynthesis?
-Water is taken up by the roots from the soil, while carbon dioxide enters through the stomata in the leaves. Oxygen is released back into the atmosphere through the same stomata.
What is the role of chloroplasts in photosynthesis?
-Chloroplasts are the organelles within plant cells that carry out photosynthesis. They contain chlorophyll, which is essential for capturing light energy.
How are photosynthesis and cellular respiration different?
-Photosynthesis converts carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using light energy, whereas cellular respiration converts glucose and oxygen back into carbon dioxide and water, releasing energy in the process.
What is the function of chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
-Chlorophyll is the pigment that absorbs light energy, particularly in the blue and red parts of the spectrum, and is essential for the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
Why do most plants appear green?
-Most plants appear green because chlorophyll reflects green light while absorbing blue and red light, which is why the green light is seen by our eyes.
What are the two stages of photosynthesis?
-The two stages of photosynthesis are the light-dependent reactions, which occur in the thylakoids and involve the conversion of light energy into chemical energy, and the light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle, which occur in the stroma and involve the fixation of carbon dioxide into glucose.
What happens during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis?
-During the light-dependent reactions, water is oxidized to produce oxygen, and light energy is used to generate ATP and NADPH, which are energy carriers for the subsequent reactions.
What is the role of ATP and NADPH in the Calvin cycle?
-ATP provides the energy required for the reduction of carbon dioxide into sugars like glucose, and NADPH provides the electrons needed for this reduction process during the Calvin cycle.
How many ATP and NADPH molecules are required to produce one molecule of glucose in the Calvin cycle?
-To produce one molecule of glucose, the Calvin cycle requires 18 ATP molecules and 12 NADPH molecules.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)