eLog7 Photosynthesis
Summary
TLDRThis educational script delves into the intricacies of photosynthesis, explaining how plants convert light energy into ATP and carbohydrates. It covers the role of chlorophyll, the structure of chloroplasts, and the light-dependent reactions within. The script also explores the Calvin cycle, the process of C3, C4, and CAM photosynthesis, and their adaptations to different environmental conditions, emphasizing the importance of plants in carbon sequestration and oxygen production.
Takeaways
- 🥪 The script starts with a discussion about a sandwich, symbolizing how food is derived from photosynthesis.
- 🌿 Photosynthesis is crucial for understanding where food components like ham, cheese, and wheat come from.
- 🔋 ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the cellular energy currency, produced through photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
- 🌞 Light energy plays a critical role in photosynthesis, where it's used to convert ADP and inorganic phosphate into ATP.
- 🍃 Chlorophyll and other pigments absorb different wavelengths of light, essential for the photosynthetic process.
- 📍 The chloroplast is the organelle in plant cells where photosynthesis occurs, containing its own DNA.
- 🔄 ATP synthase is a key enzyme that operates in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration, catalyzing the conversion of ADP to ATP.
- 💧 The process of photosynthesis involves the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, facilitated by light energy.
- 🌱 Plants act as carbon sinks, helping to mitigate the greenhouse effect by storing carbon and producing oxygen.
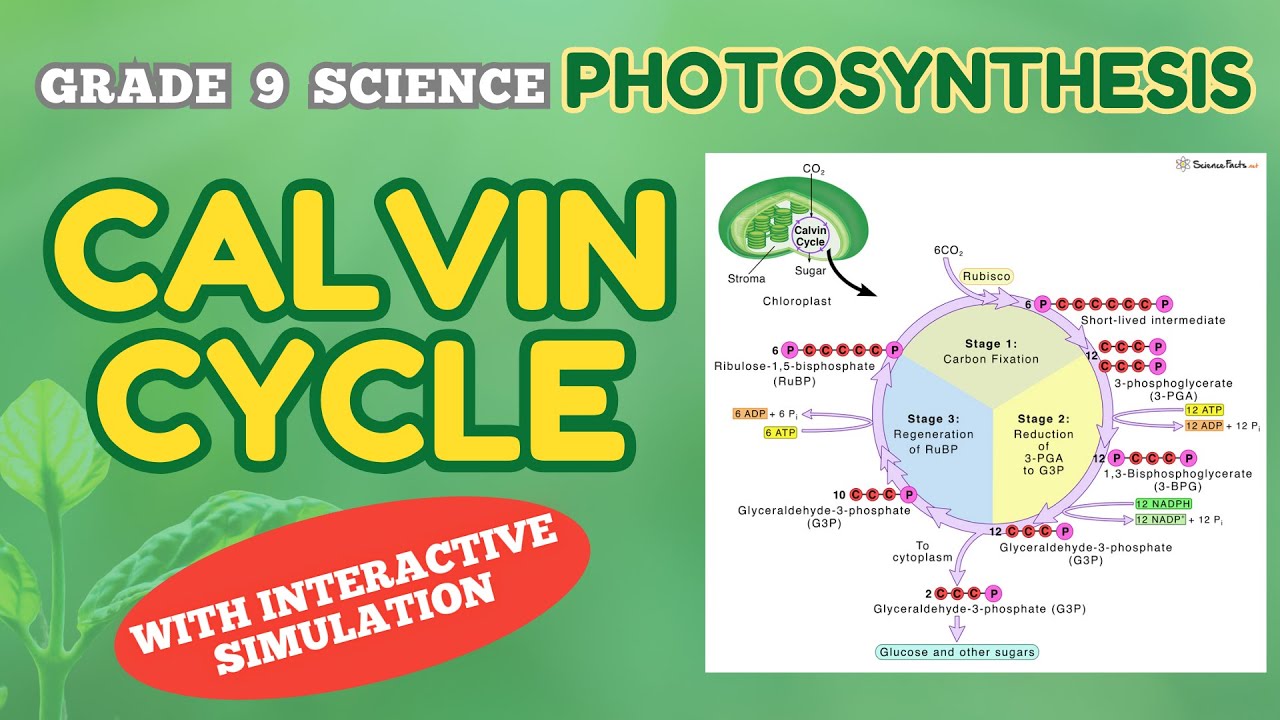
- 🔄 The Calvin cycle is the light-independent reaction of photosynthesis, where carbon dioxide is fixed into glucose using ATP and NADPH.
- 🌱 C3, C4, and CAM photosynthesis are different evolutionary adaptations plants have developed to optimize photosynthesis under various environmental conditions.
Q & A
What is ATP and why is it important in photosynthesis?
-ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is a molecule that provides energy for many cellular processes. In photosynthesis, ATP is produced during the light-dependent reactions and is essential for powering the synthesis of carbohydrates during the Calvin cycle.
How is ATP produced in photosynthesis?
-ATP is produced through a process called ATP synthase. Light energy energizes electrons, which move through the electron transport chain, pumping hydrogen ions into the thylakoid. These ions flow back through ATP synthase, causing it to spin and catalyze the production of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
What is the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
-Chlorophyll is the primary pigment responsible for absorbing light energy, which is used to energize electrons during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Chlorophyll absorbs mostly blue and red light, while reflecting green, which is why plants appear green.
What are the two stages of photosynthesis?
-Photosynthesis consists of two stages: light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle (light-independent reactions). The light-dependent reactions convert light energy into chemical energy (ATP and NADPH), while the Calvin cycle uses that energy to fix carbon dioxide into glucose.
Why do plants change color in the fall?
-Plants change color in the fall because chlorophyll breaks down, revealing other pigments such as beta carotene and xanthophyll. These auxiliary pigments absorb different wavelengths of light and become more visible as chlorophyll is depleted.
What is the function of the electron transport chain in photosynthesis?
-The electron transport chain in photosynthesis moves high-energy electrons between protein complexes. As electrons travel through the chain, their energy is used to pump hydrogen ions into the thylakoid, creating a concentration gradient that drives ATP production.
What is the Calvin cycle and what does it produce?
-The Calvin cycle is a series of reactions that occur in the stroma of the chloroplast. It uses ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions to fix carbon dioxide into a three-carbon molecule, G3P, which is later used to form glucose.
What is the significance of NADPH in photosynthesis?
-NADPH is a high-energy electron carrier produced during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. It provides the reducing power needed to convert carbon dioxide into glucose during the Calvin cycle.
What is C4 photosynthesis and when do plants use it?
-C4 photosynthesis is an adaptation for plants in environments with low carbon dioxide concentrations, such as dense plant populations (e.g., cornfields). It spatially separates the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle to optimize carbon dioxide usage and reduce photorespiration.
What is CAM photosynthesis and how does it help plants in dry environments?
-CAM photosynthesis is an adaptation that allows plants to survive in dry environments. These plants open their stomata at night to take in carbon dioxide and close them during the day to reduce water loss. The carbon dioxide is stored at night and used during the day for photosynthesis when light is available.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)