PENGERTIAN FOTOSINTESIS
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the crucial process of photosynthesis, where plants use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. It highlights the significance of photosynthesis in sustaining life on Earth, as it not only produces the oxygen necessary for respiration but also serves as the foundation for the food chain. The process involves light absorption by chlorophyll and the transformation of light energy into chemical energy. Factors such as light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature influence the rate of photosynthesis. Overall, the video underscores the importance of this biochemical process for ecological balance.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Photosynthesis is a biochemical process performed by plants and chlorophyll-containing organisms to convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into carbohydrates and oxygen.
- ☀️ The term 'photosynthesis' comes from Greek words, where 'photo' means light and 'synthesis' means combining.
- 💡 Chlorophyll in chloroplasts is essential for capturing sunlight, which drives the photosynthesis process.
- 🍃 The photosynthesis process is crucial for producing oxygen, necessary for respiration in most living organisms.
- 🔄 Photosynthesis contributes to carbon fixation, helping regulate atmospheric carbon dioxide levels and combat climate change.
- 🌡️ The rate of photosynthesis is influenced by environmental factors like light intensity, temperature, and carbon dioxide concentration.
- 🧪 Photosynthesis consists of two main stages: light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle).
- 🍬 The carbohydrates produced during photosynthesis serve as an energy source for plants and other organisms within the food chain.
- 🌍 The oxygen generated through photosynthesis is vital for the survival of living organisms on Earth.
- 🌿 Plants act as a crucial energy source and nutrient provider for other organisms, making them essential in food chains and ecosystems.
Q & A
What is photosynthesis?
-Photosynthesis is a biochemical process carried out by plants and other chlorophyll-containing organisms to convert sunlight into energy, transforming carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates and oxygen.
Why is photosynthesis important for life on Earth?
-Photosynthesis is crucial for life on Earth because it produces oxygen, which is essential for the respiration of most living organisms, and it serves as the primary source of energy for the food chain.
What are the main components required for photosynthesis?
-The primary components needed for photosynthesis are sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water.
How does light intensity affect the rate of photosynthesis?
-Light intensity directly influences the rate of photosynthesis; higher light intensity can increase the rate up to a certain point, beyond which other factors may become limiting.
What role does chlorophyll play in photosynthesis?
-Chlorophyll is a pigment found in the chloroplasts of plants that captures sunlight and plays a vital role in converting light energy into chemical energy during photosynthesis.
What are the two types of photosystems involved in photosynthesis?
-The two types of photosystems involved in photosynthesis are Photosystem I, which absorbs light at a wavelength of 700 nm, and Photosystem II, which absorbs light at 680 nm.
What products are generated through photosynthesis?
-The main products of photosynthesis are glucose and oxygen, with glucose serving as an energy source for plants and oxygen being released into the atmosphere.
How does photosynthesis contribute to the carbon cycle?
-Photosynthesis contributes to the carbon cycle by fixing atmospheric carbon dioxide into organic molecules, thereby helping to regulate carbon levels in the atmosphere.
What factors can limit the rate of photosynthesis?
-Factors that can limit the rate of photosynthesis include light intensity, temperature, carbon dioxide concentration, and the availability of nutrients.
In what ways does photosynthesis benefit other organisms?
-Photosynthesis benefits other organisms by providing oxygen for respiration and serving as the foundation of the food web, as plants produce carbohydrates that serve as food for herbivores and, subsequently, carnivores.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Penjelasan Lengkap Fotosintesis (Reaksi Terang dan Gelap)

Relationship between Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration

how photosynthesis takes place in plants & Process Of Photosynthesis (animated)
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration - Energy Cycle of Life

Photosynthesis Part 1: An Overview
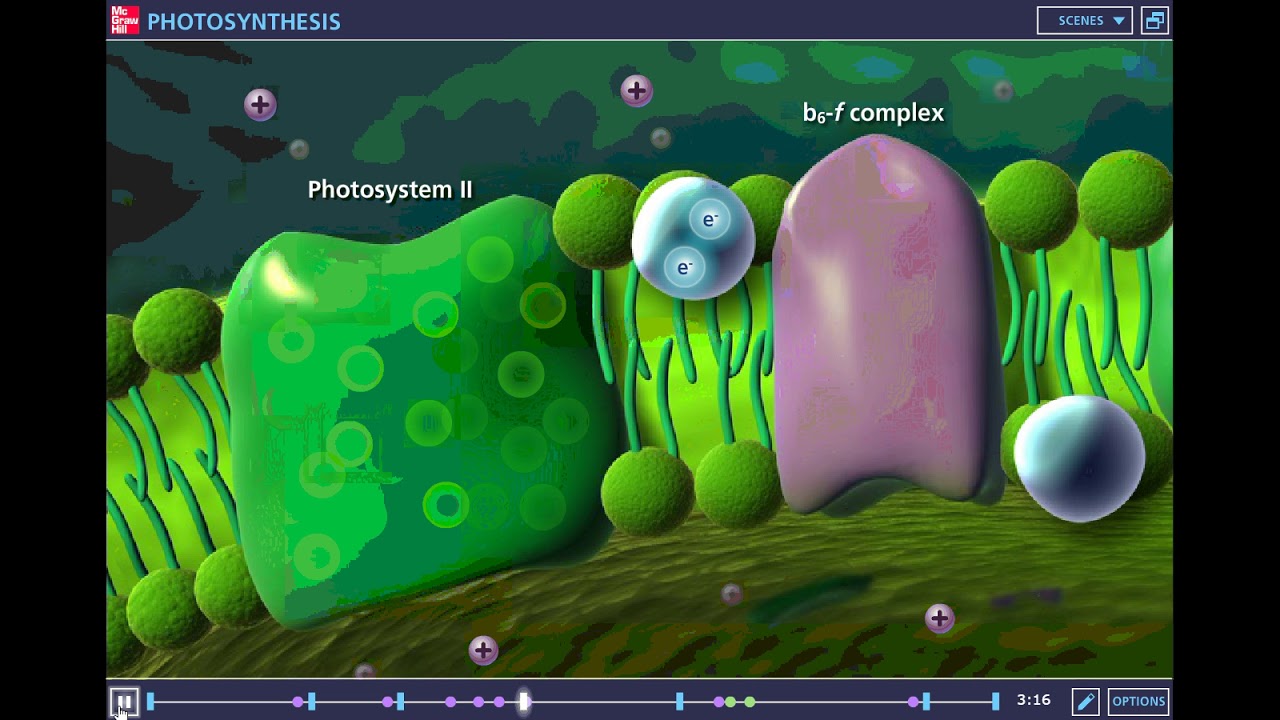
McGraw Hill Photosynthesis Tutorial
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)