Respiratory System Anatomy (v2.0)
Summary
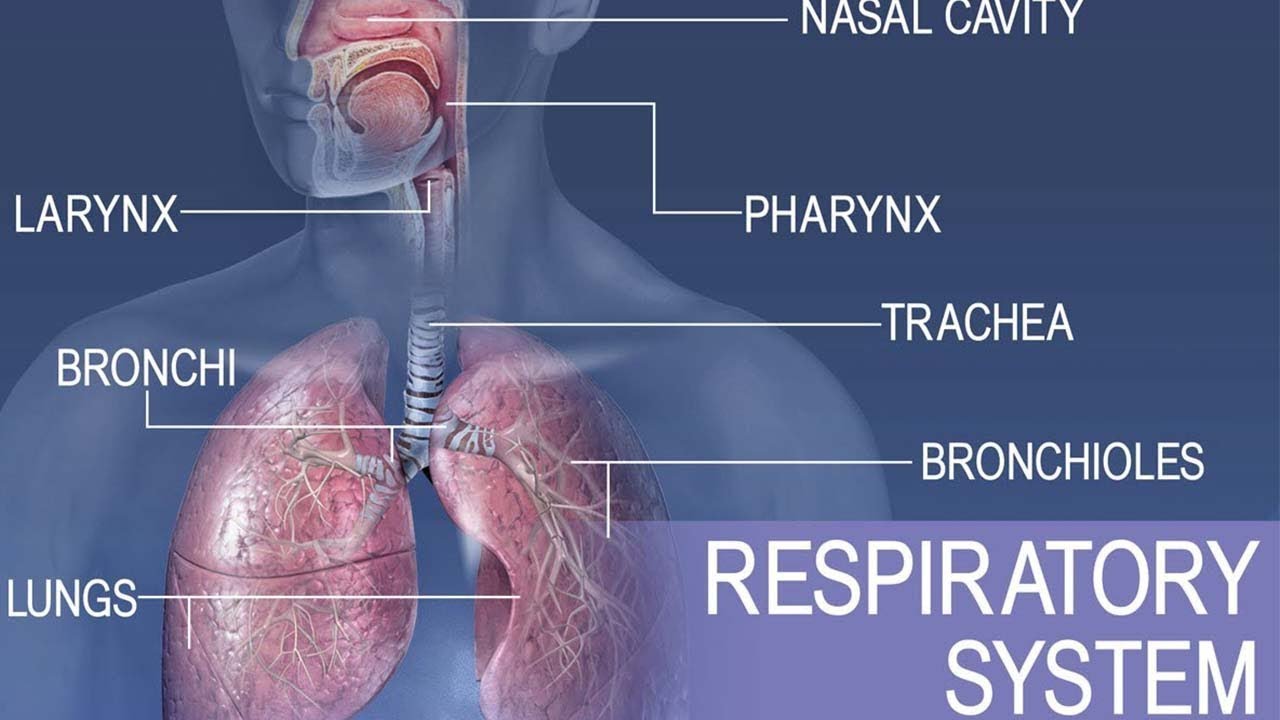
TLDRThe respiratory system is essential for oxygen intake and carbon dioxide release, divided into upper and lower tracts. The upper tract includes the nasal cavity with conchae for air processing, the pharynx with three parts, and the larynx with the epiglottis and vocal cords. The lower tract comprises the trachea, bronchi, and lungs, where the trachea splits into bronchi and further into bronchioles leading to alveoli for gas exchange. The alveoli contain type I and II pneumocytes, with the latter secreting surfactant to prevent lung collapse. The lungs are protected by pleural membranes and have fissures for structural division.
Takeaways
- 👃 The respiratory system is divided into upper and lower tracts, responsible for taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide.
- 🌀 The upper respiratory tract includes the nasal cavity, pharynx, and larynx, which are essential for filtering, warming, and humidifying the air.
- 🔍 The nasal cavity features conchae or turbinates that create turbulent airflow for efficient heating, cleaning, and humidifying of air.
- 📚 The pharynx is divided into three parts: nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx, each serving a distinct role in the respiratory process.
- 🗣️ The larynx, located below the hyoid bone, contains the thyroid and cricoid cartilages, and is critical for sound production and airway protection.
- 🚫 The epiglottis in the larynx acts as a flap to prevent food and liquid from entering the airway during swallowing.
- 🎤 The vocal cords, both true and false, are crucial for sound production, with the true cords producing sound and the false cords providing additional support.
- 🌿 The trachea, supported by rings of hyaline cartilage, splits into primary bronchi at the carina and is lined with cells that help clean the respiratory tract.
- 💨 The bronchi further divide into smaller passages, eventually leading to bronchioles and alveoli, where gas exchange occurs.
- 🌫️ Alveoli, the functional units of the lungs, contain type I and II pneumocytes; the latter secretes surfactant to prevent lung collapse.
- 🔄 The lungs are structured into lobes, with the right lung having three lobes and the left lung having two, adapted to the space occupied by the heart.
Q & A
What are the two main sections of the respiratory system?
-The respiratory system is divided into the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract.
What are the components of the upper respiratory tract?
-The upper respiratory tract consists of the nasal cavity, pharynx, and larynx.
What is the function of the nasal conchae?
-The nasal conchae create turbulent airflow for heating, cleaning, and humidifying the air.
How many parts are there in the pharynx and what are they?
-There are three parts of the pharynx: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx.
What is the role of the epiglottis in the respiratory system?
-The epiglottis closes during swallowing to protect the airway from food and liquids.
What are the true and false vocal cords, and what is their function?
-The true vocal cords produce sound, while the false vocal cords, or vestibular folds, are membranes that extend from the arytenoid cartilages.
How does the trachea contribute to the respiratory system?
-The trachea splits at the carina into two primary bronchi and contains rings of hyaline cartilage that allow for flexibility.
What is the function of the ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium in the trachea?
-The cilia in the trachea work to clean the respiratory tract by moving debris toward the pharynx.
Describe the structure and function of the alveolus in the lungs.
-The alveolus is the functional unit of the lung where gas exchange occurs, containing type I pneumocytes for gas exchange and type II pneumocytes that secrete surfactant.
How many lobes does the right lung have and what are they?
-The right lung has three lobes: superior, middle, and inferior lobes.
What is the purpose of the pleural cavity and the fluid within it?
-The pleural cavity contains fluid that reduces friction and helps keep the lungs inflated by sticking to them.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)