Proses Replikasi DNA - Proses Duplikasi atau Penggandaan DNA
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the presenter discusses the fundamental process of DNA replication, which is crucial for passing genetic information from one generation to the next. The video covers the structure of DNA, the semiconservative nature of replication, and the complex roles of various enzymes such as helicase, DNA polymerase, and primase in the replication process. The mechanisms ensuring the accuracy of DNA replication, including proofreading and error correction systems, are also explained. The video provides a comprehensive overview of how DNA is duplicated within cells, emphasizing the intricate and highly coordinated nature of this essential biological process.
Takeaways
- 🧬 DNA is a crucial molecule for all living organisms, as it contains the blueprint and program that determine the type of organism, whether it's a bacterium, chicken, or human.
- 🔄 DNA replication is a fundamental process that allows the inheritance of genetic information from parent cells to daughter cells and from parent organisms to their offspring.
- ⚙️ DNA replication occurs in both prokaryotic (bacteria) and eukaryotic (e.g., human) cells, with eukaryotic replication taking place in the cell nucleus during the S phase of the cell cycle.
- 🧱 DNA is a polymer composed of repeating units called monomers, specifically nucleotides, which are made up of a sugar, phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
- 🧬 The structure of DNA is a double helix, discovered by Watson and Crick, for which they were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology in 1962.
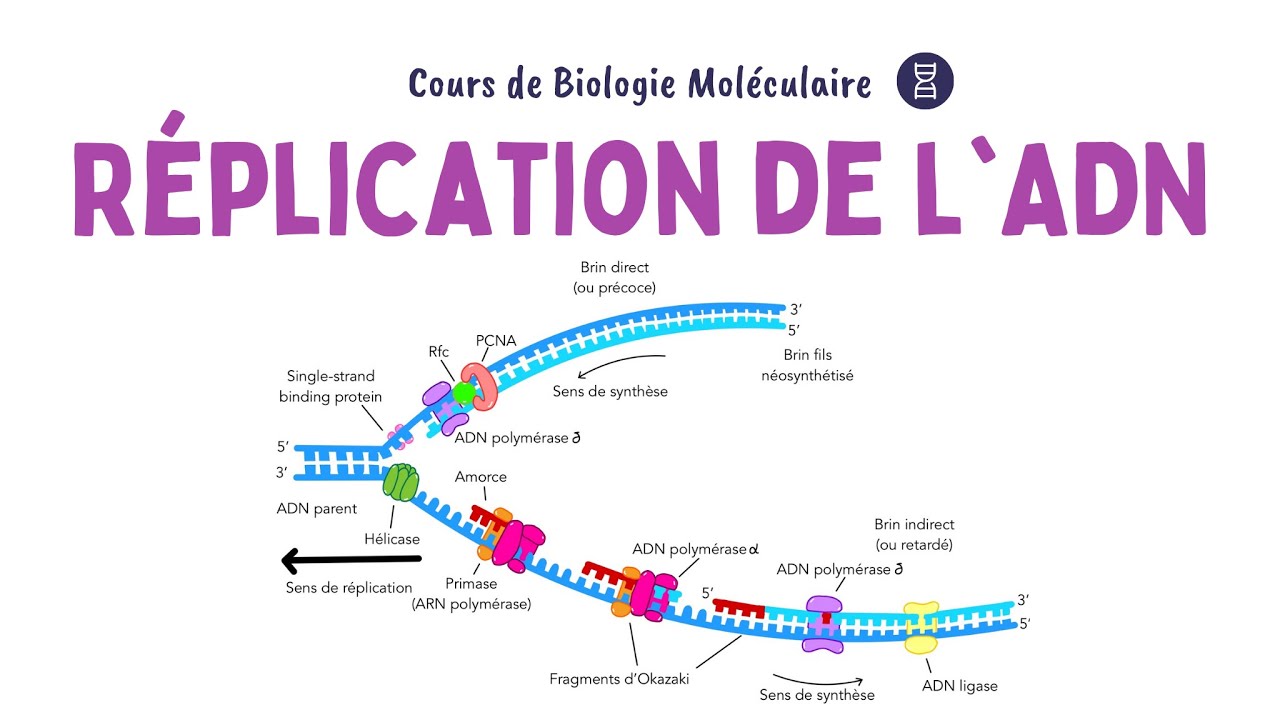
- 🔀 DNA replication is semi-conservative, meaning each new DNA molecule consists of one strand from the original molecule and one newly synthesized strand.
- 🧬 The enzyme helicase unwinds the double helix, allowing DNA polymerase to synthesize a new DNA strand using the single-stranded DNA as a template.
- 🔬 DNA polymerase synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the growing chain, starting from an RNA primer created by primase.
- 🔗 On the lagging strand, DNA synthesis occurs in fragments known as Okazaki fragments, which are later joined together by DNA ligase.
- 🔍 DNA polymerase also has a proofreading function to correct errors during replication, and additional repair mechanisms exist to fix errors that escape initial detection.
Q & A
What is the primary function of DNA in living organisms?
-DNA serves as the blueprint of life, containing the genetic information necessary for the development, functioning, and reproduction of all living organisms. It determines the characteristics of organisms, such as whether they are bacteria, chickens, or humans.
What is DNA replication, and why is it important?
-DNA replication is the process by which a cell duplicates its DNA, ensuring that each daughter cell receives an exact copy of the genetic material. This process is crucial for cell division and the inheritance of genetic information.
Where does DNA replication occur in eukaryotic cells, and during which phase?
-In eukaryotic cells, DNA replication occurs in the cell nucleus during the S phase of the cell cycle's interphase.
Why is understanding the structure of DNA important for studying its replication?
-Understanding the structure of DNA is essential for studying replication because the replication process depends on the arrangement of the DNA's components, such as the sugar-phosphate backbone and the nucleotide bases that form complementary pairs.
What is the significance of the double helix structure of DNA?
-The double helix structure of DNA, discovered by Watson and Crick, provides stability to the molecule and allows the two strands to serve as templates during replication, ensuring accurate copying of genetic information.
Explain the term 'semiconservative replication' in the context of DNA replication.
-Semiconservative replication refers to the process in which each new DNA molecule consists of one original (parental) strand and one newly synthesized strand, preserving half of the original DNA molecule in each daughter DNA.
What role does the enzyme helicase play in DNA replication?
-Helicase unwinds and separates the double-stranded DNA, creating single strands that serve as templates for new DNA synthesis. It uses energy from ATP to move along the DNA and open the helix.
How does DNA polymerase contribute to DNA replication?
-DNA polymerase is the main enzyme responsible for synthesizing new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to a pre-existing strand, using the original DNA as a template. It also has proofreading abilities to correct errors during replication.
What are Okazaki fragments, and how are they formed?
-Okazaki fragments are short DNA sequences synthesized on the lagging strand during DNA replication. They are formed because DNA polymerase can only synthesize DNA in one direction (5' to 3'), so the lagging strand is replicated in short segments.
What mechanisms ensure the accuracy of DNA replication?
-DNA replication accuracy is ensured by the proofreading activity of DNA polymerase, which corrects mismatches, and other repair mechanisms such as the mismatch repair system that fixes errors missed during initial replication.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

4: Replication in Prokaryotes | Molecular Biology| Biochemistry | N'JOY Biochemistry

DNA and RNA - DNA Replication

Genética e Biologia Molecular – Aula 03 – Replicação do DNA

Introduction to DNA Replication | A-level Biology | OCR, AQA, Edexcel
RÉPLICATION DE L'ADN | ACIDES NUCLÉIQUES | Biochimie Facile

Introduction to Next Generation Sequencing
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
