Introduction to Next Generation Sequencing
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the significance of DNA, likening it to an encyclopedia of genetic information made up of four nucleotides. It outlines the evolution of DNA sequencing, particularly through Next Generation Sequencing (NGS), which has drastically reduced costs and improved efficiency. The process consists of four key phases: Library Preparation, Cluster Generation, Sequencing, and Data Analysis. Each step is crucial for accurately analyzing DNA sequences and identifying variations using advanced bioinformatics tools. NGS has opened new avenues in scientific research, enabling rapid processing of millions of DNA sequences.
Takeaways
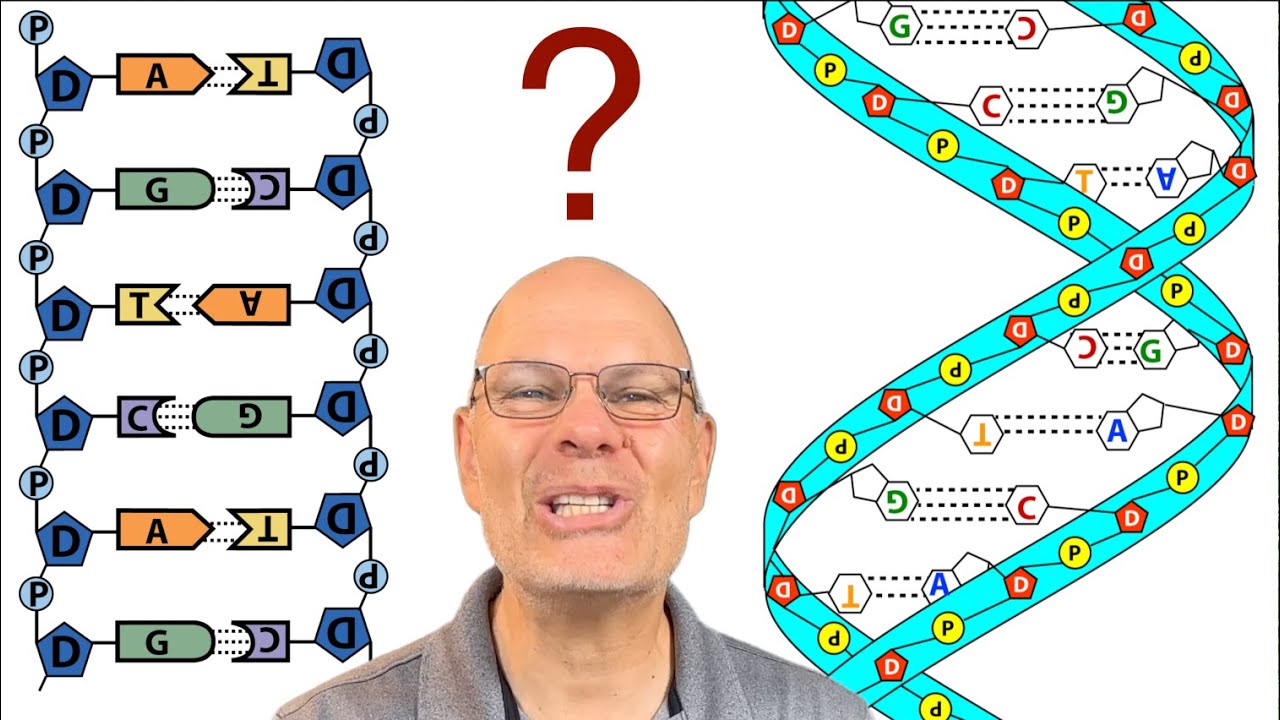
- 🧬 DNA is composed of four nucleotides: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T), which together form an encyclopedia of genetic information.
- 🔍 Scientists analyze DNA sequences to unlock biological insights and advancements across various scientific fields.
- 💻 Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) has revolutionized DNA analysis by significantly reducing the costs associated with sequencing.
- 🏭 Illumina is a leading biotechnology company in NGS, providing essential technology for efficient DNA sequencing.
- 📚 The DNA sequencing process begins with library preparation, where DNA samples are fragmented and prepared with special adapters.
- 🔗 Cluster generation follows, where DNA fragments are attached to a flow cell for amplification through bridge amplification cycles.
- 🔬 Sequencing involves adding fluorescently labeled nucleotides, allowing scientists to visualize and analyze DNA clusters effectively.
- 📊 Data analysis is the final phase, where DNA sequences are aligned to a reference genome to identify variances and create visual models.
- 🌐 A reference genome is a synthetic DNA sequence representing a species' genes, used as a standard for comparison.
- 🚀 NGS can rapidly process millions of DNA sequences, paving the way for advancements in genomics and related scientific fields.
Q & A
What does DNA stand for?
-DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid.
Why are scientists interested in DNA?
-Scientists are interested in DNA because it serves as a comprehensive encyclopedia of genetic information, essential for understanding biological processes and advancements in various scientific fields.
What are the four bases that make up DNA?
-The four bases that compose DNA are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T).
How has DNA sequencing technology evolved since the 1900s?
-DNA sequencing technology has evolved significantly, with advancements such as Sanger sequencing and Next Generation Sequencing (NGS), allowing for more accurate and cost-effective analysis of large DNA portions.
What is Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)?
-Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) is a modern DNA sequencing technology that enables the rapid sequencing of large amounts of DNA at significantly lower costs compared to previous methods.
What role does Illumina play in DNA sequencing?
-Illumina is a leading biotechnology company that specializes in Next Generation Sequencing, providing technology and processes that facilitate accurate and efficient DNA sequencing.
What are the four main steps in the NGS process?
-The four main steps in the NGS process are Library Preparation, Cluster Generation, Sequencing, and Data Analysis.
What happens during the Library Preparation phase?
-In the Library Preparation phase, a DNA sample is fragmented, specialized adapters are attached to both ends, and the fragments undergo PCR amplification and gel purification.
How does Cluster Generation work?
-In Cluster Generation, the DNA library is placed into a flow cell where the DNA fragments attach and go through a bridge amplification cycle, crucial for preparing them for sequencing.
What is the purpose of the Data Analysis phase?
-The Data Analysis phase involves aligning the sequenced DNA reads with a reference genome to identify variances, aided by advanced bioinformatics programs that help in visualizing the data.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)