Simple English 4 - Day 3
Summary
TLDRThis English language class transcript focuses on the concept of auxiliary verbs, a grammatical element not present in Indonesian. The instructor explains that auxiliary verbs come in three forms and are essential in English to complete sentences, as every sentence must contain a verb. Examples are given to illustrate the use of auxiliary verbs in simple, continuous, perfect, and modal sentences. The class also practices translating sentences, incorporating auxiliary verbs to ensure grammatical correctness.
Takeaways
- 😀 The lesson is about the third day of English class, focusing on the concept of auxiliary verbs, which are a feature of English but not Indonesian.
- 📚 Auxiliary verbs in English come in three forms: the base form, the past form, and the third form, which are used to construct different types of sentences.
- 🏫 The function of auxiliary verbs is to provide additional meaning to sentences, such as indicating tense or helping to form questions and negative statements.
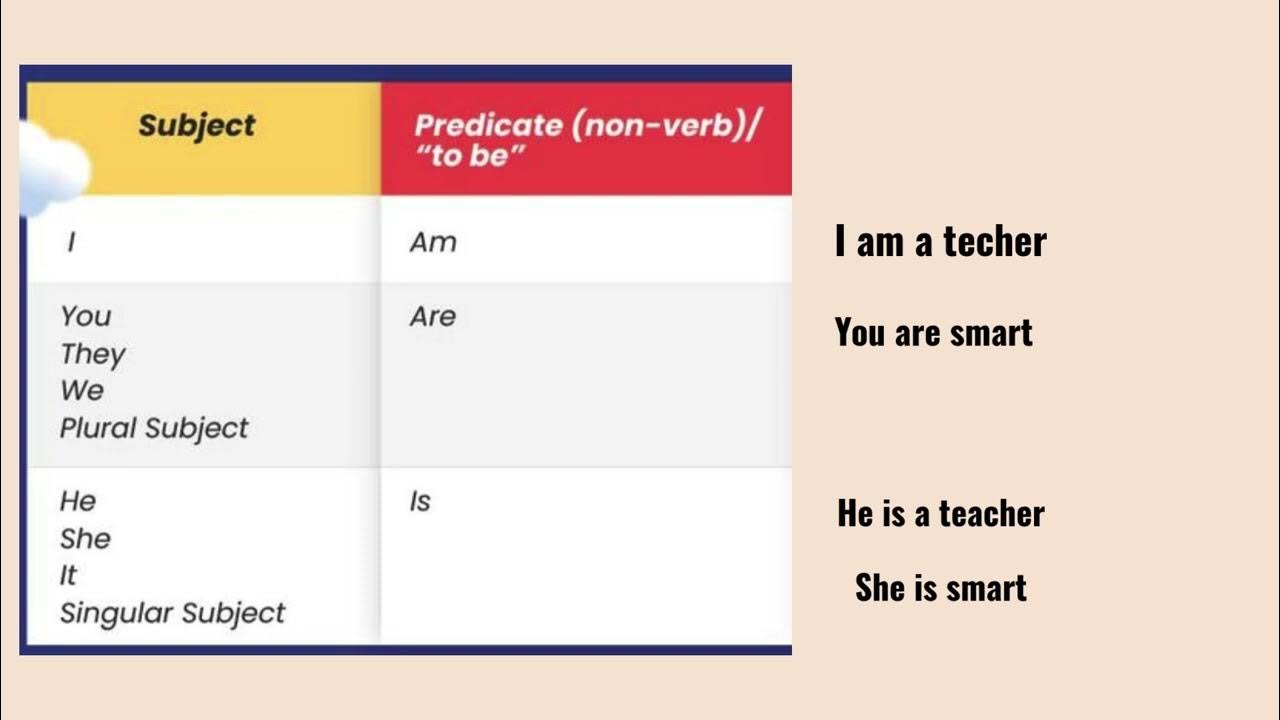
- 🔍 In English, every sentence must contain an auxiliary verb, which is different from Indonesian where sentences can exist without one.
- 📝 Examples are given to illustrate the use of auxiliary verbs in different sentence structures, such as simple present, present continuous, and present perfect.
- 🔑 The base form of auxiliary verbs is used with adjectives to form simple sentences, like 'I am clever', where 'am' is the auxiliary verb.
- 🔄 The continuous form of a verb in English is constructed with the auxiliary verb 'be' followed by the present participle of the main verb.
- 🎯 The present perfect tense is formed with 'have' or 'has' followed by the past participle of the verb, indicating an action that has been completed.
- 🛠 Modal verbs in English, such as 'must', 'can', and 'will', are followed by the base form of the main verb to express obligation, ability, or intention.
- 📚 The lesson includes exercises to practice the correct use of auxiliary verbs in various sentence structures, emphasizing their importance in English grammar.
- 👍 The script concludes with a review of the exercises and a summary of the key points about auxiliary verbs and their usage in English.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the script?
-The main topic discussed in the script is the concept of auxiliary verbs in English, their forms, and their usage in different types of sentences such as simple, continuous, perfect, and modal.
What are the three forms of auxiliary verbs mentioned in the script?
-The three forms of auxiliary verbs mentioned are the first form found in the present simple (e.g., 'am', 'is', 'are'), the second form which is the same as the base form (e.g., 'be', 'do', 'have'), and the third form (e.g., 'been', 'done').
Why is it necessary to include an auxiliary verb in English sentences?
-In English, it is necessary to include an auxiliary verb in every sentence because it helps to form different tenses and aspects of the verb, and it is a fundamental part of the sentence structure.
What is the difference between Indonesian and English sentences in terms of verb usage?
-In Indonesian, sentences can have or not have a verb, whereas in English, every sentence must contain an auxiliary verb to be grammatically correct.
How are auxiliary verbs used in the present simple tense?
-In the present simple tense, auxiliary verbs like 'am', 'is', and 'are' are used to form the sentence structure, especially when the main verb is an adjective or an action that does not have a past tense form.
Can you provide an example of a continuous tense sentence from the script?
-An example of a continuous tense sentence from the script is 'I am working at a hotel.' Here, 'am working' is the present continuous form of the verb 'to work'.
What is the purpose of auxiliary verbs in the perfect tense?
-In the perfect tense, auxiliary verbs are used to connect the past action with the present situation or result. For example, 'I have been to Bali' uses 'have been' to indicate a past action that has relevance to the present.
How do auxiliary verbs function in modal sentences?
-In modal sentences, auxiliary verbs such as 'can', 'will', 'should', and 'must' are used to express ability, permission, obligation, or future intentions.
What is the role of auxiliary verbs in forming negative sentences?
-Auxiliary verbs are used in forming negative sentences by adding 'not' after the auxiliary verb. For example, 'I am not working' uses 'am not' to form the negative present simple tense.
Can you give an example of a question that tests understanding of auxiliary verbs from the script?
-A possible question could be: 'What auxiliary verb should be used in the sentence 'She is like a queen' to make it grammatically correct in English?' The answer would be 'is', as it is the present simple tense auxiliary verb for singular subjects.
How do the exercises in the script help students practice using auxiliary verbs?
-The exercises in the script provide examples of sentences that require the insertion of auxiliary verbs to be grammatically correct. Students are guided to identify the correct form of the auxiliary verb and where to place it in the sentence.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)