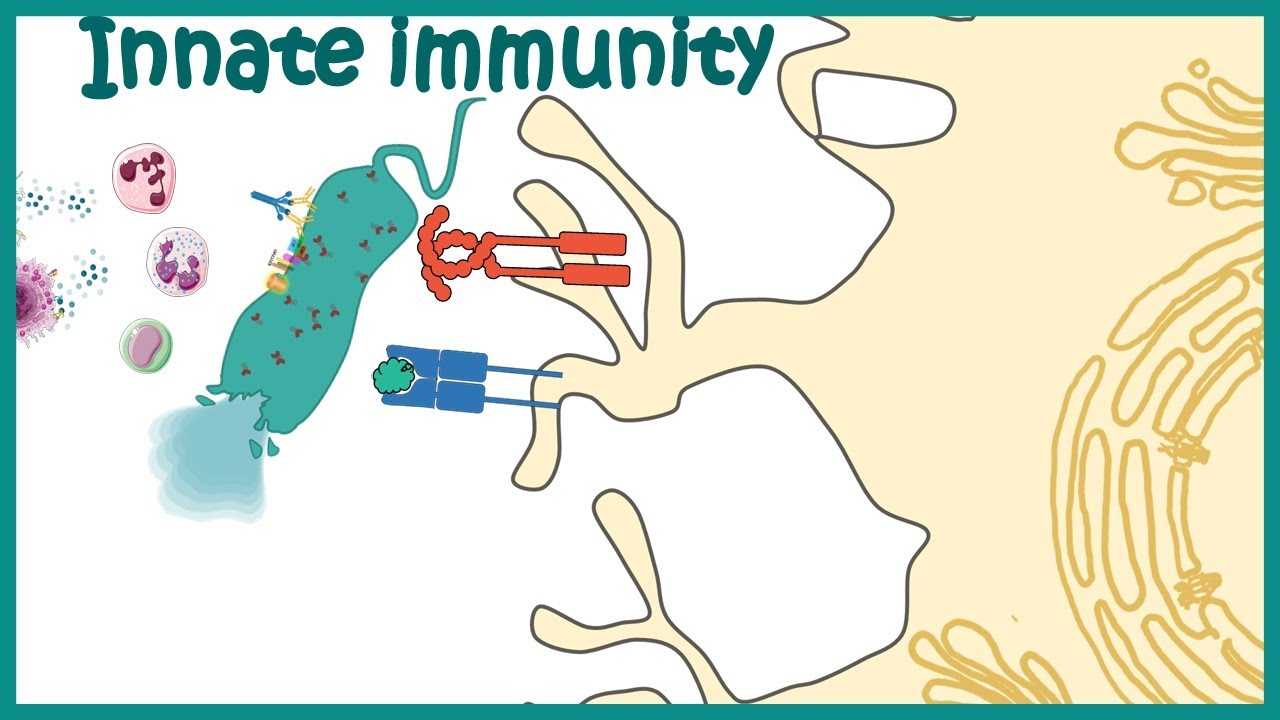
Pattern Recognition Receptors
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the intricate world of innate immunity, focusing on pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that detect pathogens and tissue damage. It explores how these receptors, including Toll-like receptors (TLRs), NOD-like receptors (NLRs), and RIG-I-like helicases, sense pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). The video explains the signaling pathways initiated upon receptor activation, leading to immune responses such as the release of inflammatory cytokines and antiviral interferons. Overall, it provides a detailed look at how the immune system identifies and responds to various threats, both microbial and cellular.
Takeaways
- 😀 Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) are proteins that detect infections or tissue damage, triggering immune responses.
- 😀 PRRs sense specific molecular patterns known as PAMPs (pathogen-associated molecular patterns) and DAMPs (damage-associated molecular patterns).
- 😀 PAMPs are conserved molecular sequences found in pathogens, such as bacterial cell wall components or viral nucleic acids.
- 😀 DAMPs are host molecules that appear in incorrect locations, like ATP found outside cells signaling tissue damage.
- 😀 The location of PRRs is crucial; some are found on the cell surface, while others are in the cytosol or endosomes.
- 😀 Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a well-studied family of PRRs that detect pathogens and initiate immune responses.
- 😀 TLRs bind ligands and undergo dimerization, allowing for signal transduction via adaptor proteins like MyD88 and TRIF.
- 😀 MyD88 and TRIF are the two main adaptor proteins that drive immune responses through NF-κB activation or type I interferon production.
- 😀 Specific TLRs recognize different PAMPs, such as TLR-2 for bacterial lipoproteins and TLR-3 for double-stranded RNA from viruses.
- 😀 NOD-like receptors (NLRs) sense intracellular bacteria and use CARD domains for signal transduction, activating NF-κB.
- 😀 RIG-I-like helicases detect viral RNA and trigger antiviral responses by producing type I interferons.
- 😀 Dedicated DAMP receptors like P2X7 and RAGE sense molecules like extracellular ATP and HMGB1, contributing to inflammation.
- 😀 Many PRRs can recognize both PAMPs and DAMPs, enabling a rapid response to diverse immune threats.
Q & A
What are pattern recognition receptors (PRRs)?
-Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) are protein sensors found in and on cells that detect signs of infection or tissue damage. They trigger a signaling cascade that helps the immune system respond to threats.
What are PAMPs and DAMPs?
-PAMPs (Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns) are molecular patterns found in pathogens, like bacterial cell walls or viral RNA. DAMPs (Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns) are molecules released from host cells when they are damaged, such as extracellular ATP.
Why are PAMPs considered to be highly conserved?
-PAMPs are considered highly conserved because they are essential for the survival of pathogens, making it difficult for them to evolve away from being recognized by the innate immune system.
How do the locations of PRRs affect immune responses?
-The locations of PRRs are crucial for proper immune responses. Some PRRs are located on the cell surface to detect extracellular threats, while others are in the cytosol or endosomes to sense intracellular or endocytosed pathogens.
What is the role of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) in the immune system?
-Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are important pattern recognition receptors that detect various microbial components. They are involved in initiating immune responses by activating signaling pathways that lead to the production of inflammatory cytokines.
What happens when TLRs bind their ligands?
-When TLRs bind their ligands, they either homo-dimerize or form heterodimers. This dimerization triggers the activation of adaptor proteins like MyD88 and TRIF, which lead to signaling cascades resulting in immune responses.
How do the MyD88 and TRIF pathways differ in TLR signaling?
-The MyD88 pathway involves the activation of kinases like IRAK4, leading to NF-κB activation, which promotes inflammatory cytokine production. The TRIF pathway also activates NF-κB but additionally activates IRF3, which drives the production of type I interferons critical for antiviral responses.
How do different TLRs recognize different PAMPs?
-Each TLR is specialized to recognize specific PAMPs. For example, TLR-2 recognizes bacterial lipoproteins, TLR-3 detects viral double-stranded RNA in endosomes, and TLR-4 recognizes lipopolysaccharides from Gram-negative bacteria.
What are NOD-like receptors (NLRs) and their function?
-NOD-like receptors (NLRs) are intracellular PRRs that detect microbial components like peptidoglycan. They play a key role in sensing bacterial infections and triggering inflammatory pathways similar to TLRs.
How do RIG-I-like helicases sense viral infections?
-RIG-I-like helicases sense viral RNA in the cytosol. They have helicase-like domains that bind to viral RNA, and their CARD domains initiate signaling that leads to the production of type I interferons to combat viral infections.
What is the role of receptors like P2X7 and RAGE in sensing DAMPs?
-P2X7 and RAGE are receptors that sense specific DAMPs. P2X7 detects extracellular ATP, while RAGE recognizes HMGB1 and other S100 proteins. These receptors help initiate pro-inflammatory responses when cellular damage occurs.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)