Kekebalan di Dapatkan / acquired immunity (Sistem Imunitas)
Summary
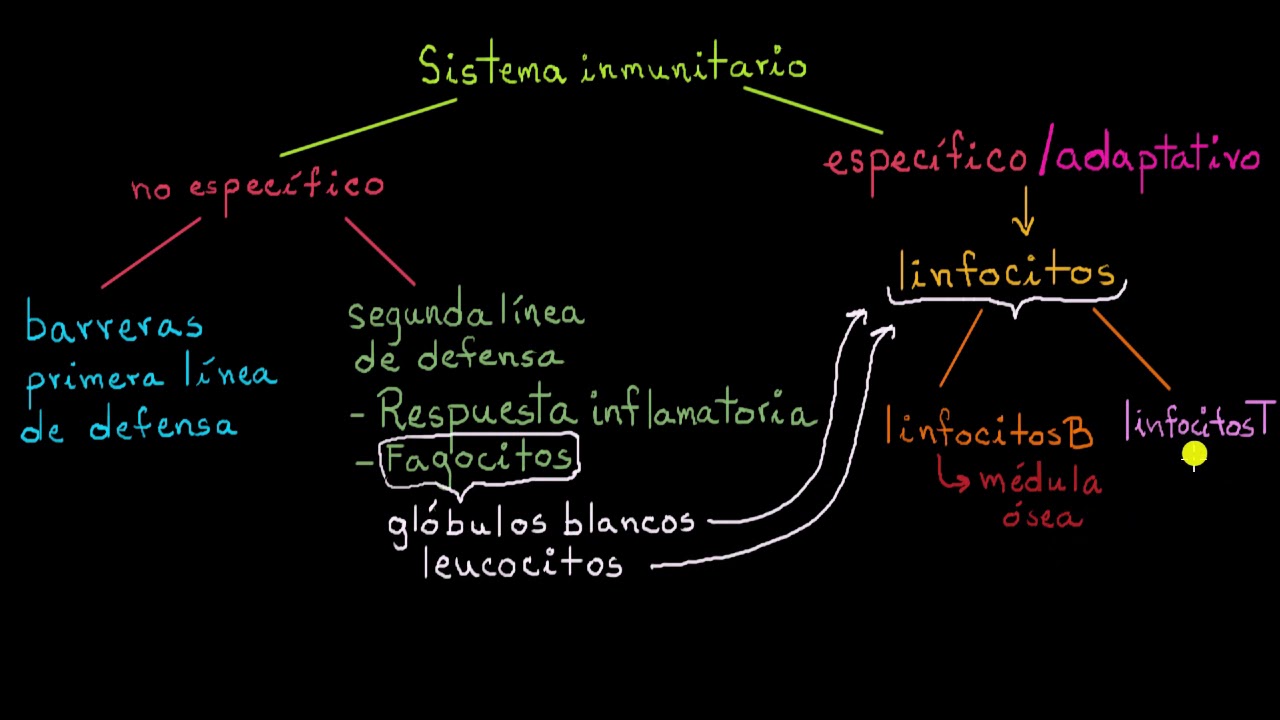
TLDRThis educational video delves into adaptive immunity, explaining the roles of B and T lymphocytes in immune responses. B cells produce antibodies that neutralize pathogens in the humoral response, while T cells destroy infected cells through cell-mediated immunity. The video covers both primary and secondary immune responses, illustrating how memory cells enhance defense upon re-infection. It also details the types of T cells—memory, helper, cytotoxic, and suppressor—and their respective functions in regulating immune reactions. A comprehensive guide to understanding how the body defends itself from specific pathogens with long-lasting immunity.
Takeaways
- 😀 Adaptive immunity involves the body's response to specific antigens, which occurs slowly but is more effective and long-lasting compared to the innate immune response.
- 😀 B lymphocytes (B cells) play a critical role in humoral immunity by producing antibodies to fight infections.
- 😀 T lymphocytes (T cells) are key players in cell-mediated immunity, targeting and destroying infected cells directly.
- 😀 B cells are divided into three types: plasma cells (produce antibodies), memory B cells (store information about past infections), and dividing B cells (increase the number of B cells).
- 😀 The humoral immune response begins with the activation of B cells, which then produce antibodies to neutralize pathogens.
- 😀 T helper cells activate B cells and other T cells to enhance the immune response against infections.
- 😀 Cytotoxic T cells destroy infected cells by inducing apoptosis, which is programmed cell death.
- 😀 Memory B and T cells 'remember' specific pathogens, allowing for a faster and stronger immune response upon subsequent infections.
- 😀 The primary immune response involves the initial activation of B and T cells to fight off a pathogen, while the secondary response is faster due to the memory cells.
- 😀 Cell-mediated immunity involves T cells, which destroy infected cells directly, without producing antibodies.
- 😀 The process of antigen presentation involves phagocytosis of pathogens, followed by the display of their fragments on the surface of phagocytes for recognition by T cells.
Q & A
What is adaptive immunity, and how is it different from other types of immunity?
-Adaptive immunity is a type of immunity that develops after the body recognizes a specific antigen. It is a slower response compared to innate immunity and involves a specific immune response mediated by B and T lymphocytes. Unlike innate immunity, which provides immediate but nonspecific defense, adaptive immunity is more targeted and involves the creation of antibodies and memory cells.
What are the key components of adaptive immunity?
-The key components of adaptive immunity are B lymphocytes, which mediate humoral immunity through antibody production, and T lymphocytes, which mediate cell-mediated immunity by destroying infected cells and regulating immune responses.
How do B cells contribute to humoral immunity?
-B cells contribute to humoral immunity by recognizing antigens and producing antibodies. Once a B cell encounters an antigen, it divides and differentiates into plasma cells that secrete antibodies, which help neutralize the pathogen.
What is the difference between B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes?
-B lymphocytes are responsible for humoral immunity, producing antibodies to fight infections, while T lymphocytes are involved in cell-mediated immunity. T cells can destroy infected cells directly (cytotoxic T cells) or help regulate the immune response (helper T cells).
What are the different types of B cells and their functions?
-There are three types of B cells: plasma B cells, which produce antibodies; memory B cells, which retain information about past infections and respond quickly to future exposures; and B cell precursors, which help increase the number of B cells through division.
What is the primary difference between primary and secondary immune responses?
-The primary immune response occurs when the body first encounters an antigen, and B cells and T cells are activated to fight the infection. The secondary immune response happens when the body encounters the same antigen again, and memory cells quickly activate to produce a more rapid and efficient immune response.
How do T cells participate in cell-mediated immunity?
-T cells play a central role in cell-mediated immunity by identifying and destroying infected cells. Cytotoxic T cells recognize infected cells and induce apoptosis, while helper T cells aid in activating B cells and cytotoxic T cells.
What is the role of helper T cells in the immune response?
-Helper T cells play a crucial role in coordinating the immune response. They activate B cells to produce antibodies and also stimulate cytotoxic T cells to destroy infected cells. Helper T cells are essential for both humoral and cell-mediated immunity.
What is the function of memory T cells?
-Memory T cells are programmed to remember specific antigens. They persist in the body after an infection and provide faster and more effective responses if the same antigen is encountered again.
What is the difference between humoral immunity and cell-mediated immunity?
-Humoral immunity involves the production of antibodies by B cells to neutralize pathogens, while cell-mediated immunity involves T cells that directly attack infected cells. Humoral immunity is primarily focused on pathogens circulating in the body, while cell-mediated immunity targets infected cells.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)