Bioquímica Clínica 04/05
Summary
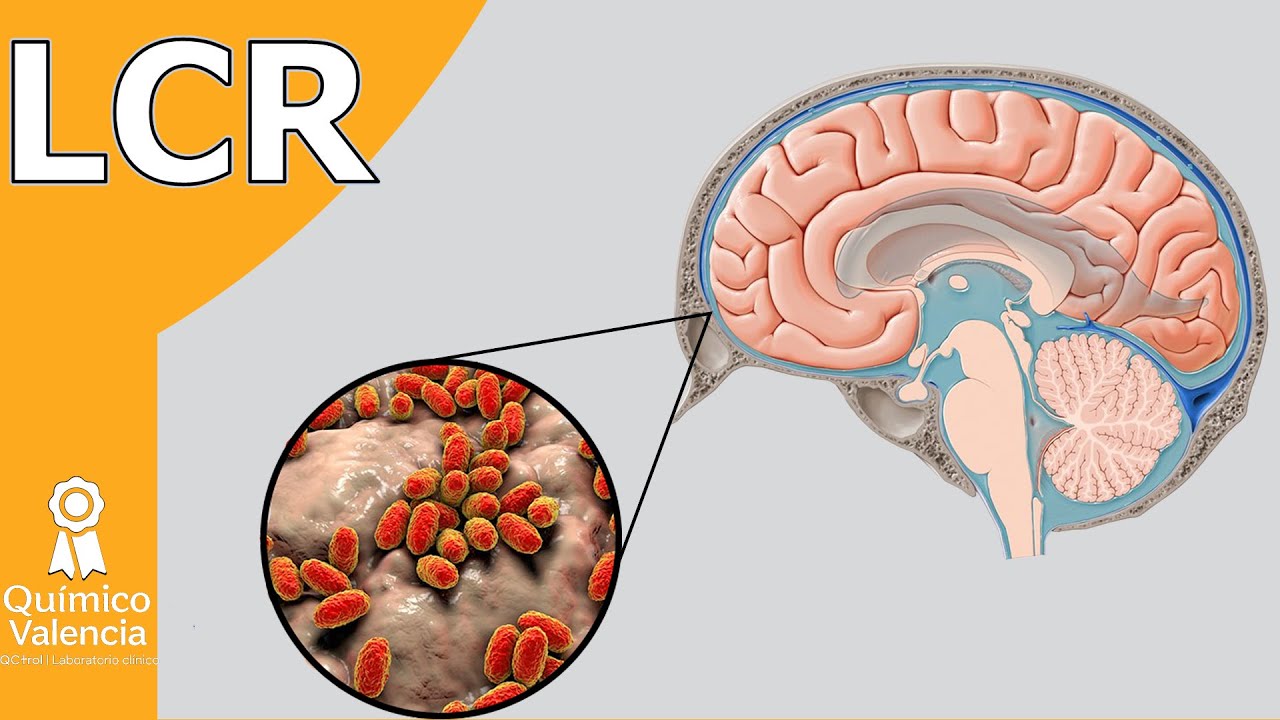
TLDRThis video explains the essential role of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in diagnosing neurological diseases such as meningitis. It covers the physiology of CSF, including its production, circulation, and absorption, as well as how it serves as a protective cushion for the brain and spinal cord. The video also details the procedure for CSF collection via lumbar puncture and the various tests used to analyze the fluid, including macroscopic, biochemical, and microbiological analysis. Understanding CSF's role in disease diagnosis is crucial for medical professionals working in neurology.
Takeaways
- 😀 The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is essential for diagnosing various diseases, including meningitis, by analyzing parameters such as appearance, color, and the presence of cells or microorganisms.
- 😀 CSF is a clear fluid produced in the brain, circulating between the arachnoid and pia mater membranes, providing protection against injuries by acting as a cushion.
- 😀 The majority of CSF (about 70%) is produced by the choroid plexus cells, while the remaining 30% is formed by ependymal cells in the ventricles and subarachnoid space.
- 😀 CSF flows around the neural tissue and is absorbed back into the bloodstream through specialized arachnoid villi.
- 😀 The lumbar puncture procedure (spinal tap) is used to collect CSF for diagnostic purposes, typically performed between the L3-L4 or L4-L5 vertebrae, depending on age.
- 😀 Proper hygiene and local anesthesia are crucial before performing the lumbar puncture to prevent complications during CSF collection.
- 😀 The CSF volume collected from adults usually ranges from 10 to 20 ml, with separate tubes used for biochemical, microbiological, and cell count analysis.
- 😀 If the CSF sample is contaminated by blood due to a traumatic puncture, it may affect the accuracy of protein and microbiological tests, requiring the use of a different tube for further analysis.
- 😀 Analysis of CSF includes macroscopic, microscopic, biochemical, microbiological, and immunological evaluations, which can help diagnose conditions like infections or inflammation of the central nervous system.
- 😀 The color and appearance of the CSF are key indicators; normal CSF is clear and colorless, while changes in color (e.g., yellow or reddish) can indicate bleeding or infection.
- 😀 Specific biochemical markers like glucose and lactate levels in CSF help identify infections or other central nervous system disorders, such as meningitis or hypoxia.
Q & A
What is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and what is its primary role in the body?
-Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless liquid produced in the brain. Its primary role is to protect the brain and spinal cord by providing cushioning, lubrication, and nutrient transport. It also helps in the removal of waste from the central nervous system (CNS).
What types of diseases or infections can be diagnosed using CSF analysis?
-CSF analysis is used to diagnose various infections and diseases of the central nervous system (CNS), including meningitis (bacterial, viral, fungal), encephalitis, and certain cancers like brain tumors. It helps by analyzing parameters such as appearance, protein levels, glucose concentration, and the presence of microorganisms.
How is CSF collected from a patient?
-CSF is collected via a procedure called lumbar puncture, where a needle is inserted into the subarachnoid space between the vertebrae, typically between L3 and L4 in adults, or between L4 and L5 in children. The fluid is then extracted for analysis.
What anatomical structures are involved in the circulation of CSF?
-CSF circulates in the space between two membranes: the pia mater and the arachnoid mater. It is produced by the choroid plexus, flows around the brain and spinal cord, and is absorbed back into the bloodstream through specialized villi in the arachnoid membrane.
What are some key parameters analyzed in CSF to diagnose CNS diseases?
-Key parameters analyzed in CSF include its macroscopic appearance (color and clarity), microscopic analysis of cell count and types (e.g., white blood cells), biochemical analysis (such as protein and glucose levels), and microbiological analysis for pathogens like bacteria, fungi, or viruses.
How does CSF help protect the brain from injury?
-CSF acts as a cushion around the brain and spinal cord, helping to absorb and reduce the impact of physical forces, such as trauma or sudden movements, that could otherwise damage these sensitive structures.
What is the significance of protein levels in CSF analysis?
-Elevated protein levels in CSF can indicate an inflammatory process or infection, such as bacterial meningitis. Specific proteins, like beta-amyloid, can also be linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's.
Why is glucose important in CSF analysis, and what do changes in its levels indicate?
-Glucose levels in CSF reflect the metabolic activity in the central nervous system. Normal levels are about 60-70% of plasma glucose. A decrease in glucose levels often indicates an infection, as microorganisms consume glucose. Elevated glucose could indicate conditions like hyperglycemia or trauma.
What is the role of lactate levels in CSF, and how do they correlate with CNS health?
-Lactate levels in CSF reflect the oxygen supply to CNS tissues. Increased lactate levels can indicate hypoxia (low oxygen levels), which may be caused by conditions like bacterial meningitis or other neurological issues that impair oxygen delivery to the brain.
What is a traumatic lumbar puncture, and how can it affect the CSF sample?
-A traumatic lumbar puncture occurs when the needle damages blood vessels during the procedure, causing blood to mix with the CSF. This can lead to a bloody or discolored sample, which may complicate analysis, particularly for microbiological tests.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): Chemical, cytological and culture analysis

One more reason to get a good night’s sleep | Jeff Iliff

Detailed Animation on Circulation of CSF

CONFIRMED STUDY: This Harvard Expert Shows How to Activate Your Third Eye

Meningitis - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, pathology

The ventricular system
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
