PV System Mechanical Components | Solar Energy Basics | edX Series
Summary
TLDRThis video script provides a comprehensive overview of the mechanical components involved in photovoltaic system installations. It covers the connection of photovoltaic panels to building structures using metal racks, mounting points, and waterproofing systems. Different roof types, such as standing seam and flat roofs, are addressed, with details on attachment methods and considerations for weight load and wind shear. Ground-mounted and pole-mounted systems are also discussed, highlighting their advantages, including tilt and tracking system compatibility. The script concludes by referencing key components like modules, inverters, batteries, charge controllers, and relevant codes, setting the stage for future lessons.
Takeaways
- 😀 Photovoltaic systems involve several mechanical components that connect the panels to the building, including racks, clips, and mounting points.
- 😀 Racks are attached to the rooftop using lag bolts or clamps, with weight considerations managed by engineers or architects before installation.
- 😀 Waterproofing systems, such as rubber gaskets and sealed boots, prevent water penetration and protect the roof and building.
- 😀 Mount points are connected to rafters using lag bolts, securing the system from the rafter to the module.
- 😀 For standing seam roofs, metal seam clamps prevent roof penetration while attaching the rack to the roof.
- 😀 Ballasting systems on flat roofs provide weighted support, preventing wind shear and ensuring panels stay secure without roof penetration.
- 😀 Ground-mounted systems are simpler to install as they do not involve roof weight considerations, with racks connected to posts or concrete pads.
- 😀 Pole-mounted systems can be tilted and turned, including compatibility with tracking systems for optimal panel positioning.
- 😀 Tracking systems enhance solar panel efficiency by adjusting their position based on the sun's movement, to be discussed in future lessons.
- 😀 The major components of a solar photovoltaic system include the module, inverter, battery, charge controller, and the balance of system components like the mounting system, wiring, and electrical protections.
- 😀 Article 690 in the National Electrical Code (NEC) addresses the regulations for solar photovoltaic systems in the United States, ensuring safety and compliance.
Q & A
What are the mechanical components of a photovoltaic system?
-The mechanical components of a photovoltaic system include the photovoltaic panels, racking systems, and mounting components that attach the system to the building or ground.
How are photovoltaic panels connected to the building?
-Photovoltaic panels are connected to the building through metal racks that use specialized clips to secure the panels. These racks are then mounted to the roof using lag bolts or clamps.
What is the role of an engineer or architect in the installation process?
-An engineer or architect must address weight considerations before installation to ensure the building or roof can safely support the solar system and that it complies with load-bearing specifications.
What is the function of waterproofing systems in photovoltaic installation?
-Waterproofing systems, using rubber gaskets and sealed boots, are used to prevent water penetration through the mounting points and into the roof or building structure.
How is a system installed on a standing seam roof?
-In a standing seam roof, a metal seam clamp is used to attach the racking system to the roof without penetrating it, preventing potential leaks.
What is ballasting, and how is it used in flat roof installations?
-Ballasting involves using weight to secure the photovoltaic panels on flat roofs without penetrating the surface. It ensures the panels stay in place and resist wind shear.
What is the advantage of using ballasting on a flat roof?
-The primary advantage of ballasting is that it eliminates the need for roof penetration, making it easier to install while still securing the panels against strong winds.
What should be considered when using a ballasting system on a flat roof?
-When using a ballasting system, it is crucial to consult an engineer to ensure the roof can handle the added weight and prevent structural damage or issues with wind shear.
How are ground-mounted systems different from roof-mounted systems?
-Ground-mounted systems are generally simpler to design and install because they are located on the ground. The weight loading is typically less of a concern, and they can be supported by concrete pads or posts.
What is the advantage of using pole-mounted systems for photovoltaic installations?
-Pole-mounted systems offer the advantage of being adjustable, allowing the panels to be tilted and turned. This feature can also support tracking systems, which can enhance the system’s efficiency by following the sun's movement.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Controls & Indicators - Hydraulics - Airframes & Aircraft Systems #12

Resumão: SISTEMA DIGESTÓRIO
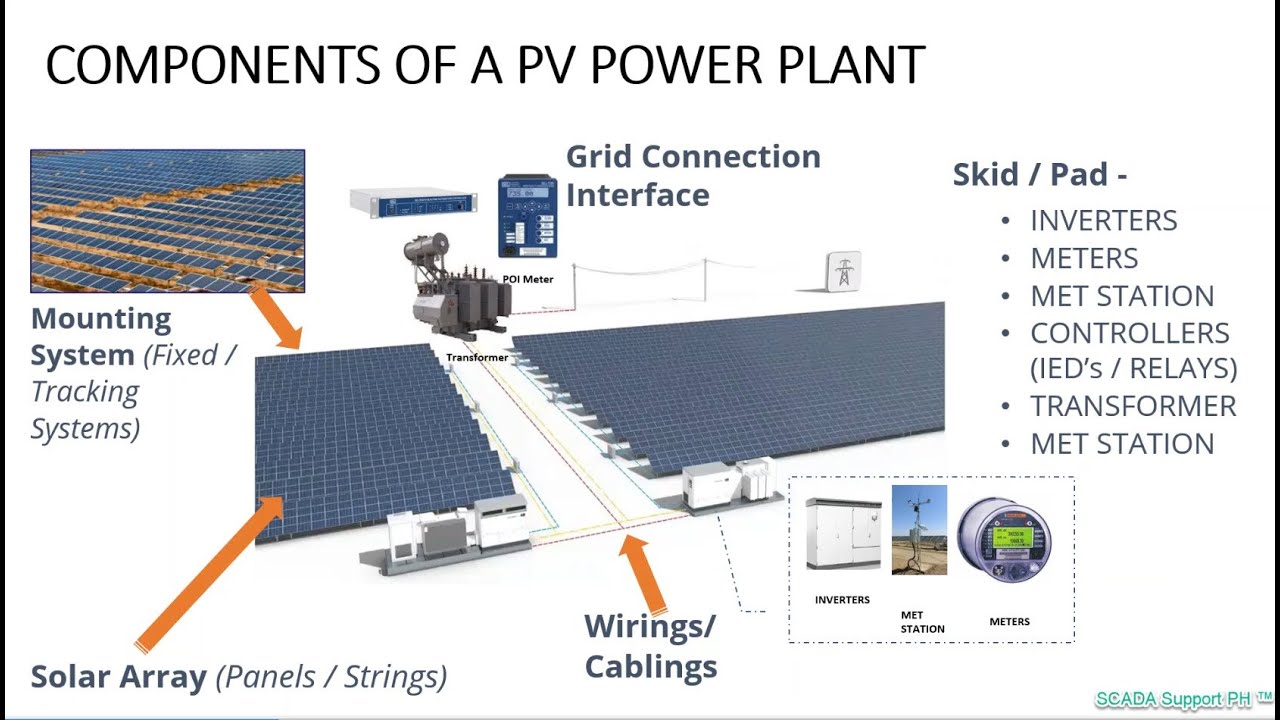
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Power Plant

Shock depan motor 3D ( cara kerja )

Penggunaan Media Pembelajaran Trainer Pengaman Arus Bocor Pada Instalasi Listrik Rumah Tinggal

Thermal Power Plant | Boiler | Economizer | Turbine | Khan GS Research Centre
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
