Matematika Kelas 9 : Fungsi Kuadrat (Part 1 : Bentuk umum dan grafik fungsi kuadrat)
Summary
TLDRThis video is an introduction to quadratic functions for 9th-grade students. It covers the general form of quadratic functions (y = ax² + bx + c), explaining the roles of the coefficients a, b, and c, and how to identify them in various examples. The video also demonstrates how to find the value of a quadratic function by substituting known x values. Additionally, it explains key concepts such as the graph of a quadratic function (parabola), vertex, and x- and y-intercepts, with examples and a step-by-step guide for solving problems and graphing quadratic functions.
Takeaways
- 😀 The general form of a quadratic function is given by f(x) = ax² + bx + c, where 'a' cannot be zero.
- 😀 The coefficient 'a' is the number in front of x², 'b' is the number in front of x, and 'c' is the constant term.
- 😀 If 'a' equals zero, the equation is no longer a quadratic function.
- 😀 Quadratic functions can be represented with different variables, such as 't' instead of 'x', but they remain quadratic as long as there is an x² or t² term.
- 😀 The value of a, b, and c can sometimes be letters or variables, such as 'p' or 'q', in more general forms of quadratic functions.
- 😀 The graph of a quadratic function is called a parabola, which can open upwards or downwards depending on the sign of 'a'.
- 😀 When 'a' is positive, the parabola opens upwards; when 'a' is negative, it opens downwards.
- 😀 Key points on the parabola include the vertex (or turning point) and the x- and y-intercepts.
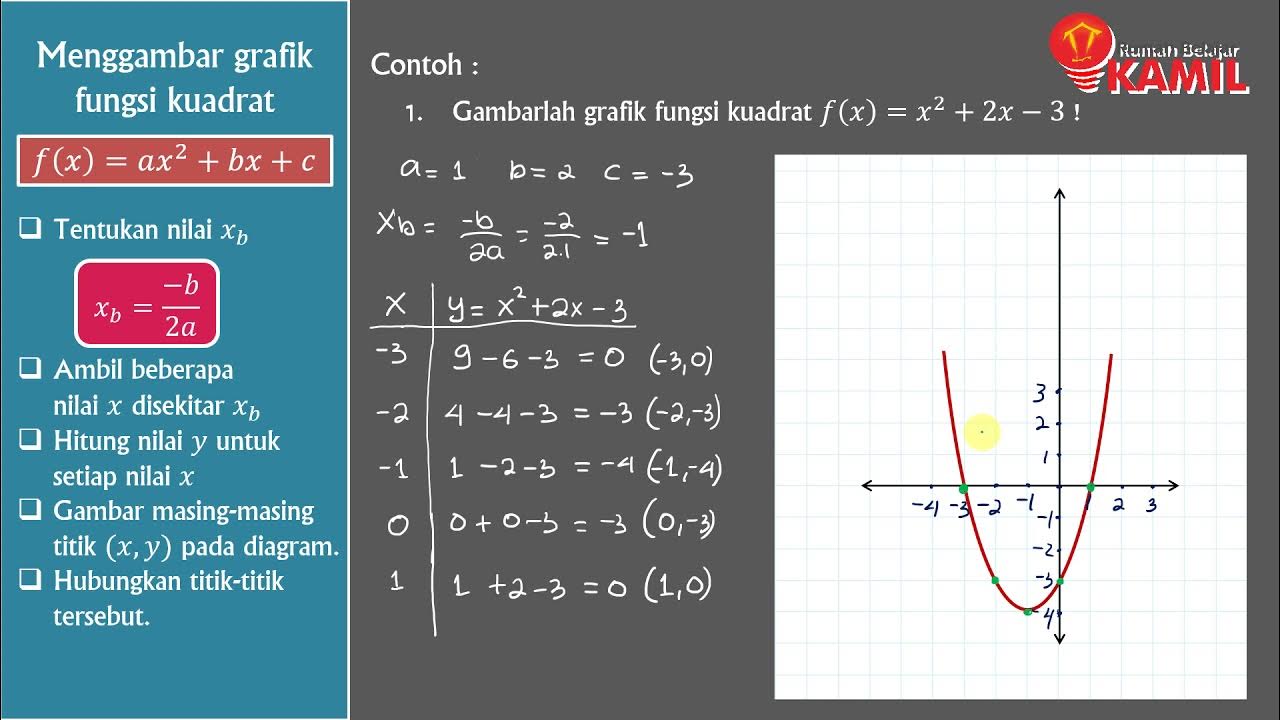
- 😀 The vertex (turning point) can be found using the formula xₓ = -b/2a and yₓ = f(xₓ), where xₓ is the x-coordinate of the vertex.
- 😀 The y-intercept occurs when x = 0, and its value is simply 'c', the constant term of the quadratic function.
Q & A
What is the general form of a quadratic function?
-The general form of a quadratic function is fx = ax² + bx + c, where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants, and 'a' cannot be zero.
What happens if the coefficient 'a' in a quadratic function is zero?
-If 'a' is zero, the equation no longer represents a quadratic function, as the term 'ax²' disappears and the equation becomes linear.
How can you identify the values of 'a', 'b', and 'c' from a quadratic equation?
-You can identify 'a', 'b', and 'c' from the quadratic equation in the form fx = ax² + bx + c. 'a' is the coefficient of x², 'b' is the coefficient of x, and 'c' is the constant term.
What is the role of the discriminant in quadratic functions?
-The discriminant, given by the formula b² - 4ac, helps determine the nature of the roots of a quadratic equation. If the discriminant is positive, the equation has two real roots; if it's zero, there is one real root; and if it's negative, there are no real roots.
What is the significance of the vertex (turning point) in a quadratic function's graph?
-The vertex, or turning point, is the point where the graph of the quadratic function changes direction. It can be found using the formula xb = -b/2a for the x-coordinate and substituting this value back into the quadratic function for the y-coordinate.
How do you find the y-intercept of a quadratic function?
-To find the y-intercept, set x = 0 in the quadratic equation. The result will be the value of 'y', which corresponds to the y-coordinate of the point where the graph intersects the y-axis.
What is the method for finding the x-intercepts (or roots) of a quadratic function?
-The x-intercepts, or roots, are found by setting y = 0 and solving the resulting quadratic equation. This can be done using factoring, completing the square, or the quadratic formula.
What is the difference between a quadratic function opening upward or downward?
-A quadratic function opens upward if the coefficient 'a' is positive, and it opens downward if the coefficient 'a' is negative. This affects the direction in which the graph curves.
What is the formula for calculating the x-coordinate of the vertex of a quadratic function?
-The x-coordinate of the vertex is calculated using the formula xb = -b/2a, where 'b' is the coefficient of x, and 'a' is the coefficient of x².
How do you calculate the value of the quadratic function at a specific point, like f(2)?
-To calculate the value of the quadratic function at a specific point, substitute the given x-value into the quadratic equation and simplify the expression to find the corresponding y-value.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
Matematika Kelas 9 : Fungsi Kuadrat (Part 3 : Menggambar grafik fungsi kuadrat)

Bab 2 sistem koordinasi manusia (sistem hormon) ipa kelas 9 kurikulum merdeka #ipakelas9

9. SINIF - 2. DÖNEM 2. YAZILI - BİYOLOJİ - YAZILIYA HAZIRLIK + PDF

ALL OF GRADE 11 MATH IN 1 HOUR! (exam review part 1) | jensenmath.ca

Introduction to Exponential Functions - Nerdstudy

Fungsi Kuadrat [Part 6] - Bentuk Umum Fungsi Kuadrat
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
