Model Inventori EOQ Deterministik (Pendahuluan)
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces inventory theory, focusing on Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) models. It explains key inventory concepts, such as the importance of balancing stock levels to meet customer demand while minimizing costs. The video outlines four primary inventory costs: ordering, purchase, holding, and stockout. It also discusses assumptions in EOQ models, such as repetitive ordering, constant demand, and fixed lead time. The goal is to determine the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs, using the EOQ formula. This foundational knowledge is essential for managing inventory effectively in business operations.
Takeaways
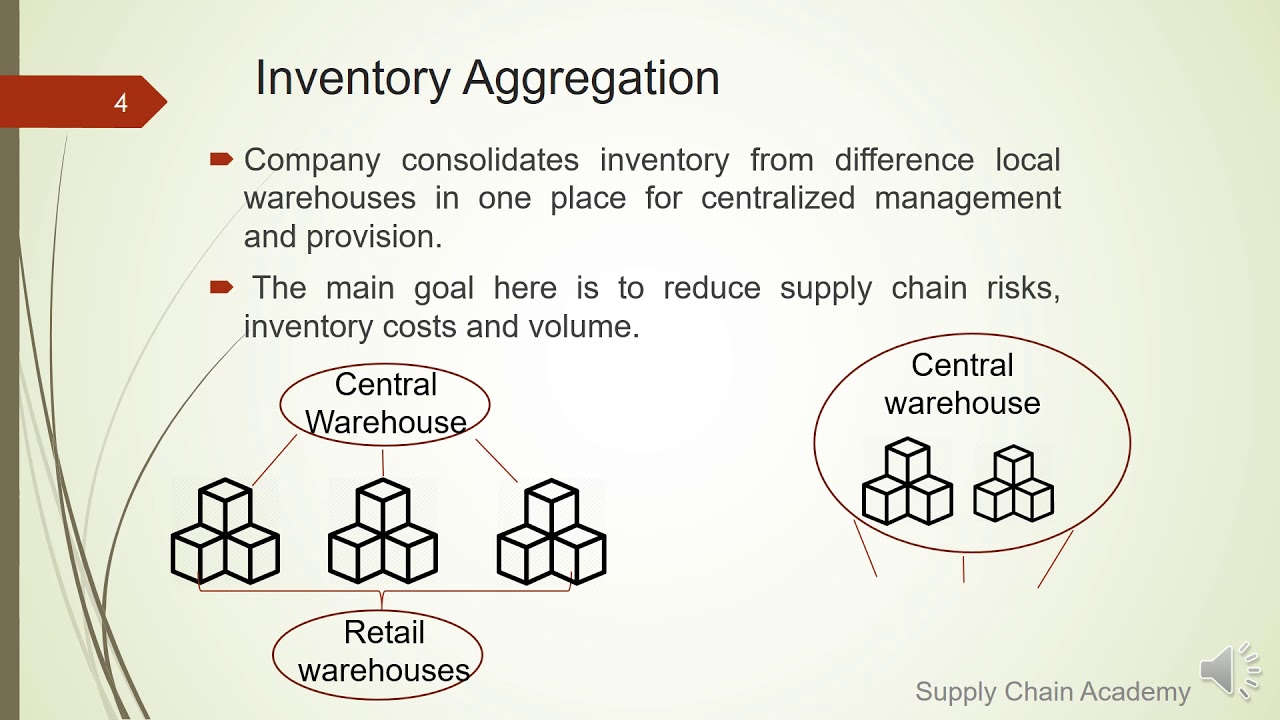
- 😀 Inventory is crucial for business operations as it represents the stock of goods waiting for processing or sale.
- 😀 The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model helps determine the optimal amount of inventory to order, balancing ordering costs and holding costs.
- 😀 The two main types of inventory models are deterministic (known demand) and probabilistic (uncertain demand).
- 😀 An efficient inventory strategy helps balance supply and demand while minimizing costs such as storage, insurance, and potential loss of customer trust due to stockouts.
- 😀 Key costs involved in inventory management include ordering costs, unit purchase costs, holding costs, and stockout costs.
- 😀 Ordering costs are fixed and do not change based on the order quantity, such as phone calls to suppliers or inspection fees.
- 😀 Holding costs involve expenses like warehouse rental, insurance, and the opportunity cost of capital tied up in inventory.
- 😀 Stockout costs arise from not having enough inventory to meet customer demand, which can lead to lost sales and damage to customer loyalty.
- 😀 Assumptions for EOQ models include constant demand, repetitive ordering, constant lead time, and the ability to order continuously without specific timing restrictions.
- 😀 The goal of inventory management is to minimize total costs while ensuring enough stock to meet customer demand at all times.
- 😀 The famous EOQ formula (Q*) aims to minimize total inventory costs by considering ordering and holding costs, and is expressed as √(2 * Order Cost * Demand / Holding Cost).
Q & A
What is the primary goal of inventory theory?
-The primary goal of inventory theory is to balance customer demand fulfillment with minimizing inventory-related costs, such as ordering, holding, and stockout costs.
What is the difference between deterministic and probabilistic inventory models?
-In deterministic models, demand is known and constant, while in probabilistic models, demand is uncertain and follows a probability distribution.
Why is inventory important for a business?
-Inventory is essential for a business because it ensures that there is enough stock to meet customer demand without over-investing in goods, which could lead to excessive holding costs.
What are the four key costs involved in inventory management?
-The four key costs are ordering costs, setup costs, holding costs, and stockout costs.
How do ordering costs impact inventory management?
-Ordering costs are fixed per order and do not vary with the amount ordered. They include expenses such as phone calls, administrative fees, and inspections.
What are setup costs, and how do they relate to inventory management?
-Setup costs are the costs associated with preparing for production or operation, such as machinery setup or transportation expenses, and they do not change based on the quantity ordered.
What are holding costs and why are they significant?
-Holding costs are expenses related to storing inventory, including warehouse rent, insurance, and potential investment returns. These costs increase as the amount of inventory grows.
What is stockout cost and how is it calculated?
-Stockout cost refers to the cost incurred when inventory is insufficient to meet demand, leading to customer dissatisfaction or lost sales. It is difficult to calculate but can be approximated by estimating the lost profit from unavailable items.
What assumptions are made in the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model?
-The EOQ model assumes repetitive ordering, constant demand, constant lead time, and continuous ordering, meaning orders can be placed at any time.
How does the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) formula help businesses?
-The EOQ formula helps businesses determine the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs by balancing ordering and holding costs. The formula is EOQ = sqrt((2 * D * S) / H), where D is demand, S is ordering cost, and H is holding cost.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Pertemuan 6 : Penentuan Tingkat Persedian (lanjutan)

[PRESENTASI] TEKNIK PERSEDIAAN METODE JIT (JUST IN TIME) DAN EOQ (ECONOMIC ORDER QUANTITY)

Pengajian Perniagaan Semester 1: Pengeluaran (alat kawalan inventori: EOQ dan ROP)

OM (Practicum/Project) - Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
Inventory Management Lesson 2/3 Placement and quantity calculations ENG

E learning : Manajemen Operasional - Sesi 8, Manajemen Persediaan | by Siti Mariam
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
