Budget line//Price line// Analysis of consumer behaviour, bbs 1st Year Economics//(part-3)
Summary
TLDRThis script discusses key economic concepts like the budget line, income, and the price of goods such as apples and oranges. It highlights how the budget line changes due to variations in prices and income, explaining how price and quantity impact a consumer's choices. The script also touches on shifts in the budget line, which occur when either prices or income change. Additionally, there are references to indifference curves, a concept used to visualize consumer preferences, and the importance of understanding these economic tools for making informed decisions about consumption.
Takeaways
- 😀 The budget line equation is a key concept in consumer economics, illustrating how the prices of goods and a consumer's income determine the quantities of goods they can afford.
- 😀 The budget line equation is represented as: Income = Price of X * Quantity of X + Price of Y * Quantity of Y, where X and Y are the two goods being considered.
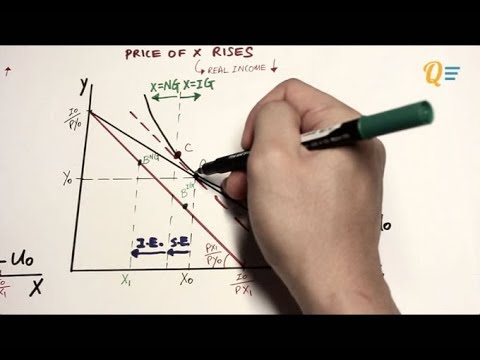
- 😀 Price changes affect the budget line by causing it to pivot or swing, depending on which good's price has changed.
- 😀 A change in income causes the budget line to shift, indicating that a consumer can now afford different combinations of goods.
- 😀 The budget line illustrates the trade-offs consumers face when allocating their limited income across different goods.
- 😀 A higher income shifts the budget line outward, enabling the consumer to afford more of both goods.
- 😀 A price increase for one good causes the budget line to rotate inward for that good, making it less affordable relative to the other good.
- 😀 The concept of indifference curves is related to the budget line and helps illustrate the consumer's preferences for different combinations of goods.
- 😀 The budget line framework can be used to demonstrate how consumers respond to changes in prices and income, adjusting their consumption choices accordingly.
- 😀 Understanding budget lines and indifference curves is essential for analyzing consumer behavior in economics, particularly in the context of constrained optimization.
Q & A
What is a budget line in economics?
-A budget line represents all possible combinations of two goods that a consumer can afford, given their income and the prices of the goods.
How is the budget line equation structured?
-The budget line equation is: Income = (Price of Good X * Quantity of X) + (Price of Good Y * Quantity of Y), where the prices and quantities of two goods determine the consumer's purchasing options.
What happens to the budget line when the price of one good changes?
-When the price of one good changes, the budget line 'swings' or pivots. If the price of a good increases, the consumer can afford less of that good, and if the price decreases, they can afford more of it.
How does a change in income affect the budget line?
-A change in income causes the entire budget line to shift. If income increases, the budget line shifts outward, allowing the consumer to afford more of both goods. If income decreases, the budget line shifts inward.
What is an indifference curve in economics?
-An indifference curve represents combinations of two goods that give a consumer the same level of satisfaction or utility. The consumer is indifferent between these combinations.
How do price changes and income changes differ in their effects on the budget line?
-Price changes cause the budget line to swing (pivot), altering the combination of goods a consumer can afford. Income changes cause the budget line to shift entirely, allowing for more or fewer goods to be purchased.
What does it mean when the budget line swings?
-When the budget line swings, it means the relative affordability of one good changes due to a price change, while the consumer's income remains the same.
Can a consumer buy more of a good if their income stays the same but the price of the good decreases?
-Yes, if the price of a good decreases and income stays the same, the consumer can afford more of that good, which will cause the budget line to swing outward along the axis of that good.
What does a shift in the budget line due to an increase in income indicate?
-An increase in income shifts the budget line outward, indicating that the consumer can now afford more of both goods, as their purchasing power has increased.
Is the concept of indifference curves related to consumer preferences?
-Yes, indifference curves are related to consumer preferences as they show different combinations of goods that provide the same level of satisfaction, helping to analyze how consumers make choices based on their preferences.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Kurva Indiferen (Teori Konsumsi) - PART 2

Budget Line | Ekonomi | Alternatifa

Microeconomics for Beginners - Week 2_Video 5_Budget Line
EC1002 Chapter 2 Lesson 3 - Normal, Inferior, Giffen Goods; Complements & Substitutes [Full]

Demand Aralin Panlipunan (Ekonomiks) Grade 10

PERMINTAAN DAN PENAWARAN MATERI IPS KELAS 7
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
