Uji T (T-Test) Konsep Dasar, Contoh Kasus dan Penerapan Menggunakan SPSS
Summary
TLDRThis lecture covers the essential concepts of the T-test, including its history, types, and applications in hypothesis testing. Introduced by WS Gosset in 1908, the T-test is used to analyze small sample sizes and is crucial for testing means. The types discussed include the one-sample, paired-sample, and independent-sample T-tests, each suited for specific research scenarios. The lecture also provides practical guidance on how to use SPSS for performing T-tests, with examples such as comparing productivities or sales before and after an intervention. The session ensures clarity on how to interpret results for valid conclusions.
Takeaways
- 😀 The T-test, first introduced by WS Gosset in 1908, is used to analyze differences between sample means. It is called the Student's T-distribution because Gosset used the pseudonym 'Student.'
- 😀 The T-test is used to test two main hypotheses: (1) testing the mean of a single sample, and (2) comparing the means of two samples to check for significant differences.
- 😀 The T-test requires interval or ratio scale data and assumes that the data follows a normal distribution. If the sample size is larger than 30, a Z-test is used instead.
- 😀 The T-test is suitable for small sample sizes, typically less than 30. The standard deviation of the population is assumed to be unknown in T-tests.
- 😀 There are three types of T-tests: One-sample T-test, paired sample T-test, and independent sample T-test.
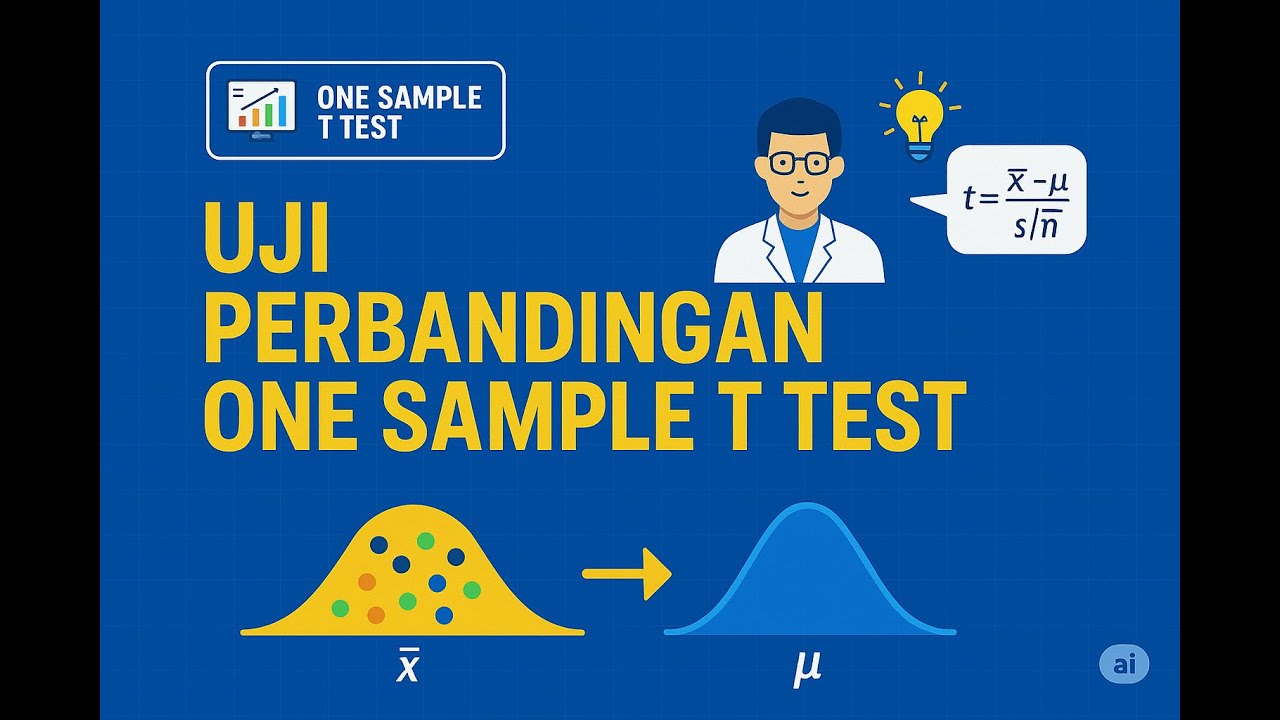
- 😀 The One-sample T-test compares the mean of a sample with a specific constant value. For example, testing if the average weight of students in a class is 52 kg.
- 😀 The Paired T-test compares the means of two related groups, such as testing the impact of a pandemic on students' weight before and after the event.
- 😀 The Independent Sample T-test compares the means of two independent groups, like comparing the average weight of students in two different classes.
- 😀 The formula for the One-sample T-test involves calculating the sample mean, the constant value, and the sample standard deviation. The test compares the calculated T-value to a critical value from the T-distribution.
- 😀 SPSS can be used to perform T-tests, with steps such as entering data, checking for normality, and running the analysis to calculate T-values and p-values. The hypothesis is rejected if the T-value is greater than the critical value or if the p-value is smaller than the significance level.
- 😀 In practical examples, the T-test can be applied to test hypotheses like comparing productivity with a national average or evaluating the impact of policy changes, such as the effect of tax increases on motorcycle sales.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of the t-test?
-The t-test is used to compare the means of one or two groups to determine if there is a significant difference between them.
Who introduced the t-test, and why is it named 'Student's t-distribution'?
-The t-test was introduced by William Sealy Gosset in 1908. It is called 'Student's t-distribution' because Gosset used the pseudonym 'Student' when publishing his work.
When is a t-test appropriate to use?
-A t-test is appropriate when testing the mean of a small sample (less than 30), where the population standard deviation is unknown, and the data is assumed to be normally distributed.
What are the types of t-tests mentioned in the script?
-The script mentions three types of t-tests: one-sample t-test, paired t-test (dependent samples), and independent samples t-test.
What is the difference between a paired t-test and an independent t-test?
-A paired t-test is used when the two samples are related or matched (e.g., measurements taken before and after a treatment on the same subjects). An independent t-test is used when the samples are from different, unrelated groups.
What is the formula for the one-sample t-test?
-The formula for the one-sample t-test is t = (x̄ - μ) / (s / √n), where x̄ is the sample mean, μ is the population mean, s is the sample standard deviation, and n is the sample size.
What assumptions must be met for the t-test to be valid?
-The t-test assumes that the data is normally distributed, the sample size is small (less than 30), and the population standard deviation is unknown.
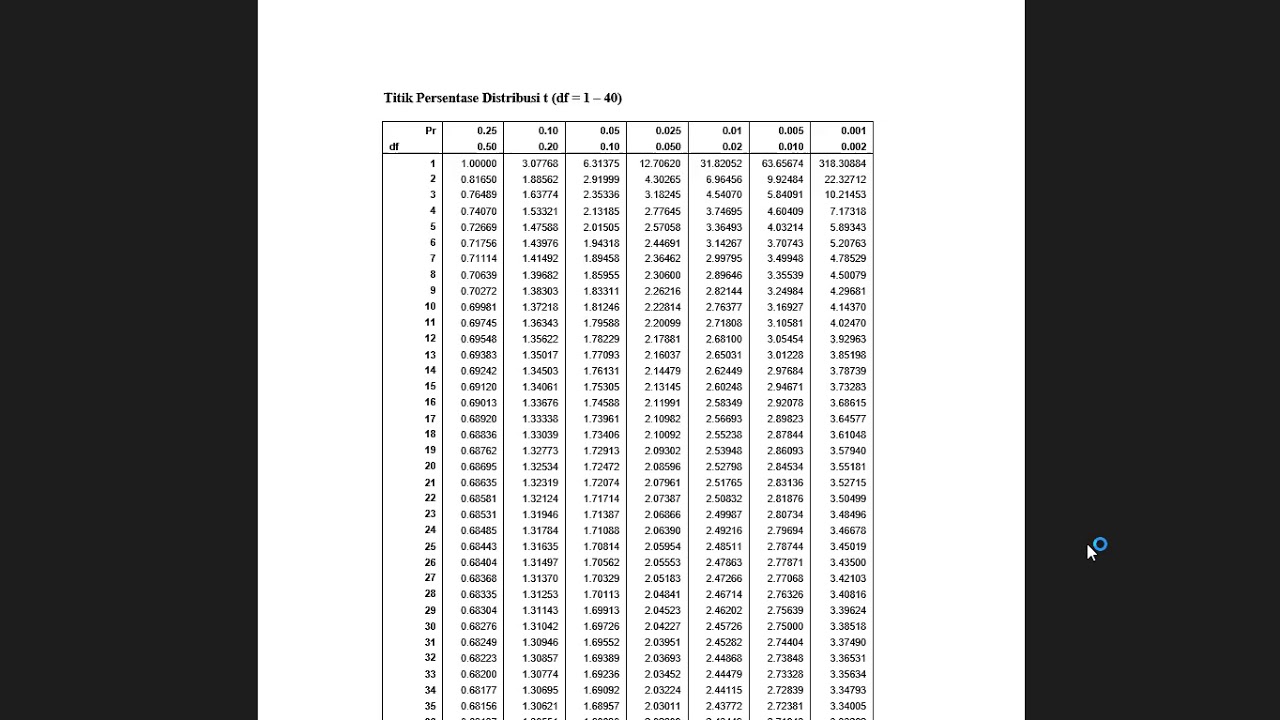
What is the critical value (t-table) used for in a t-test?
-The critical value from the t-table is used to determine whether the test statistic (t-value) is significant. If the absolute value of the t-statistic exceeds the critical t-value, the null hypothesis is rejected.
How do you interpret the p-value in a t-test?
-If the p-value is less than the significance level (α, typically 0.05), you reject the null hypothesis. A p-value greater than α means you fail to reject the null hypothesis.
How did the SPSS analysis help in determining the results of the t-tests?
-SPSS was used to perform the t-tests by inputting the data and conducting normality tests. It provided the t-statistic and p-value, which were compared to the critical values to draw conclusions about whether to accept or reject the null hypothesis.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)