An introduction to Late Antiquity
Summary
TLDRThe video delves into the period of late antiquity, exploring the transition from the Roman and Persian empires to the rise of Christianity and Islam. It challenges the traditional narrative of decline by highlighting the cultural growth and intellectual advancements during this era, as noted by historian Peter Brown in his influential work. The script emphasizes the importance of new religious movements, the evolution of social hierarchies, and architectural changes, while also examining the complexities of identity, education, and masculinity within the shifting societal landscape. Ultimately, it portrays late antiquity as a dynamic period rich in transformation and renewal.
Takeaways
- 😀 The concept of late antiquity covers the Roman Empire from approximately 300 to 800 AD, focusing on cultural growth rather than decline.
- 😀 Peter Brown's 1971 work, 'The World of Late Antiquity,' transformed historical perceptions of this era, emphasizing new beginnings in contrast to decline.
- 😀 Edward Gibbon's thesis in 'The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire' attributed the fall to Christianity's moral weakening and barbarian invasions.
- 😀 Late antiquity is characterized by significant developments in Christianity and Islam, influencing the sociopolitical landscape of Europe and the Near East.
- 😀 The linguistic diversity of sources from this period includes Latin, Greek, and various dialects, providing a rich tapestry of cultural expression.
- 😀 A key focus of late antiquity studies is the rise of holy figures and asceticism, reflecting a preoccupation with the afterlife and spiritual intercession.
- 😀 Education in late antiquity became increasingly important for social distinction among the Roman elite, marking a shift in societal roles.
- 😀 Masculinity in the late Roman Empire was linked to military prowess, contrasting with earlier ideals of cultured leisure among the aristocracy.
- 😀 The period saw transformations in architecture and city structures, with many urban centers shrinking while others in the East remained stable or grew.
- 😀 The Eastern Roman Empire, or Byzantine Empire, played a crucial role in the continuation of classical traditions and cultural developments during this time.
Q & A
What major historical narrative about the Roman Empire does Peter Brown challenge in his work?
-Peter Brown challenges the narrative of decline and fall, proposing that the late antique period was characterized by cultural growth and new beginnings rather than mere decay.
What are the approximate dates defining the late antiquity period?
-The late antiquity period is generally defined as spanning from around 300 to 800 AD.
How did Peter Brown's view differ from Edward Gibbon's perspective on the fall of the Roman Empire?
-While Gibbon attributed the fall of the Roman Empire to moral decay caused by Christianity and barbarian invasions, Brown emphasized the complex cultural developments and argued that the empire faced challenges it had encountered before, leading to significant growth.
What key religious developments occurred during late antiquity?
-During late antiquity, Christianity and Islam emerged and spread, transforming the religious landscape of Europe and the Near East.
How did the understanding of masculinity change in late antiquity?
-Masculinity in late antiquity evolved to emphasize military prowess and dominance, contrasting with previous ideals that focused more on education and cultured leisure.
What role did education play in late antiquity for the upper classes?
-Education became increasingly important for social distinction among the upper classes, with a focus on classical knowledge and fluency in Greek and Latin to demonstrate their status.
What evidence suggests a transformation in urban life during late antiquity?
-Archaeological evidence indicates that cities in Western Europe began to shrink in size, while cities in the Eastern Roman Empire often maintained or expanded, reflecting a contrast in urban development.
What is the significance of monasticism in late antiquity?
-Monasticism became significant as ascetic individuals sought spiritual purity, engaging in extreme practices and establishing monasteries that served as centers of religious life and learning.
What new cultural practices emerged in relation to the afterlife during this period?
-A preoccupation with the afterlife and the soul grew, as evidenced by art depicting figures gazing upwards and the rise of holy individuals who served as intercessors between God and the people.
How did the rise of popular Christianity affect societal structures?
-The rise of popular Christianity led to the restructuring of civic life, with older religious structures being repurposed into churches, reflecting the new religious dynamics of the late antique world.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Overview of the Middle Ages | World History | Khan Academy

O IMPÉRIO PERSA

Eps 144 | SEJARAH UANG KERTAS

COMO A IDADE MÉDIA COMEÇOU? A Queda do Império Romano e o Início da Idade Média
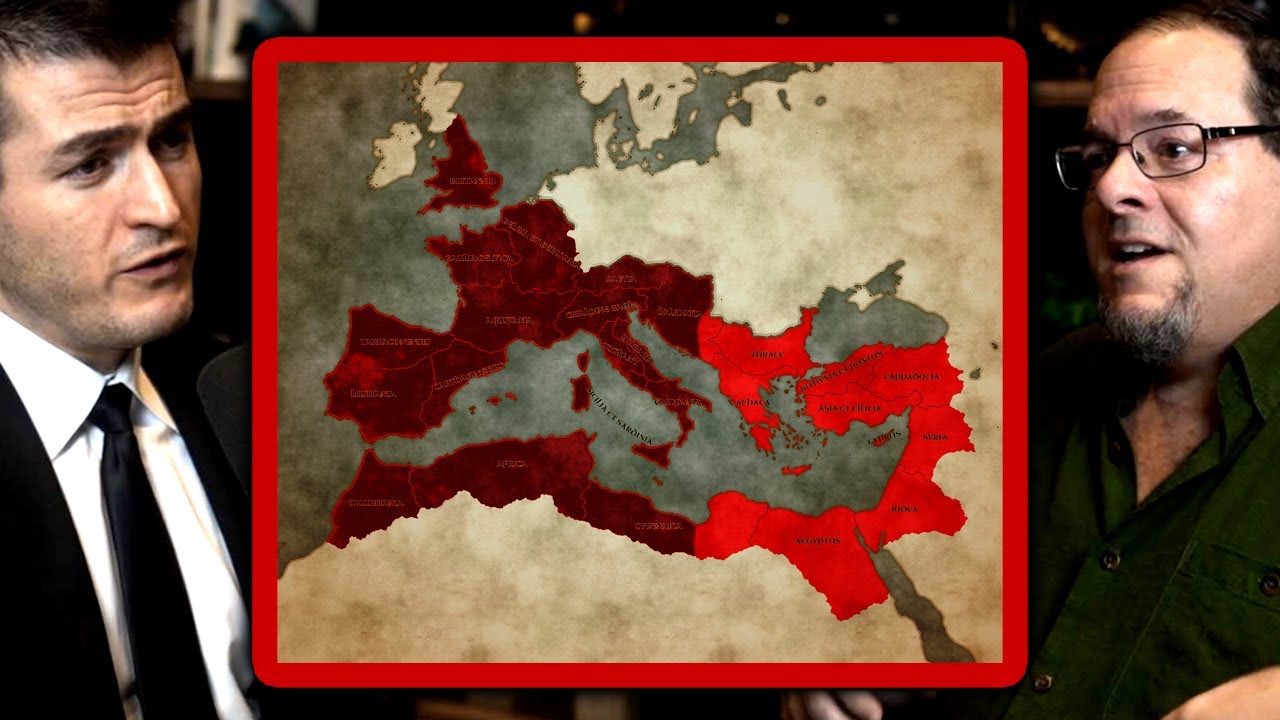
How the Roman Empire split into Western and Eastern empires | Gregory Aldrete and Lex Fridman

The First 150 Years of Christianity in the Roman World | The Early Church [AD 50 - 200]
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
