ELECTRIC DISCHARGE MACHINING PROCESS (Animation): How electric discharge maching works
Summary
TLDRThis video explores Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM), a non-conventional machining process ideal for shaping hard materials. It explains the working principle, where electrical sparks erode metal from the workpiece, and highlights key components like the DC pulse generator and dielectric fluid. The video covers EDM applications, including micro-hole drilling and engraving, while detailing its advantages, such as high precision and complex shape production, alongside disadvantages like high power consumption and slow material removal rates. Viewers are encouraged to subscribe for more insightful content on machining technologies.
Takeaways
- ⚙️ EDM, or Electrical Discharge Machining, is a non-conventional machining process primarily used for very hard materials.
- ⚡ The process is also known as spark eroding, spark machining, wire erosion, and wire burning.
- 🛠️ In EDM, metal is removed from the workpiece using high-frequency electrical sparks discharged from electrodes made of graphite or soft metals.
- 🔌 The working principle involves an electric arc formed between two current-carrying conductors, eroding a small amount of metal at the point of contact.
- 🔥 The intense heat generated by the spark causes the metal to melt and evaporate, creating small cracks in the workpiece.
- 📏 A small gap (0.005mm or 0.05mm) is maintained between the tool and workpiece to facilitate the spark generation.
- 🧪 The process is enhanced by using dielectric fluids, such as hydrocarbon and mineral oils, to increase effectiveness.
- 🏗️ Key components of the EDM setup include a DC pulse generator, tool, servo motor, spark generator, and dielectric fluid supply.
- 🔍 EDM is effective for applications like drilling micro holes, manufacturing gear wheels, thread cutting, and engraving on hard materials.
- ⚖️ Advantages of EDM include the ability to produce complex shapes, achieve tight tolerances, and obtain good surface finishes without tool-workpiece distortion.
Q & A
What is Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)?
-EDM is a non-conventional machining process used to remove material from very hard conductive materials using high-frequency electrical sparks.
How does the EDM process work?
-The EDM process works by creating an electric arc between two conductors, anode and cathode, which erodes the metal at the point of contact due to intense heat generated by the spark.
What are some other names for Electrical Discharge Machining?
-EDM is also referred to as spark eroding, spark machining, wire erosion, and wire burning.
What materials can be machined using EDM?
-EDM is suitable only for metallic or conductive materials.
What role does dielectric fluid play in the EDM process?
-Dielectric fluid, such as de-ionized water or mineral oils, is used to improve the effectiveness of the process by cooling the tool and workpiece, carrying away eroded particles, and aiding in ionization.
What components are essential in the construction of an EDM machine?
-Key components of an EDM machine include a DC pulse generator, tool, servo motor, spark generator, and dielectric fluid system.
What are the advantages of using EDM over conventional machining processes?
-Advantages include the ability to produce complex shapes, achieve tight tolerances of ±0.005 mm, obtain good surface finishes economically, and avoid tool or workpiece distortion due to lack of physical contact.
What are the disadvantages of Electrical Discharge Machining?
-Disadvantages include high power consumption, excessive tool wear, limitation to metallic or conductive materials, and a slow material removal rate (MRR).
In what applications is EDM commonly used?
-EDM is commonly used for drilling micro holes, manufacturing gear wheels, cutting threads, engraving hard materials, and rotary form cutting.
How is the spark generated in the EDM process?
-The spark is generated when high voltage (between 40 volts to 3000 volts) is supplied to the tool, causing ionization of the dielectric fluid and creating a path for current to flow, resulting in an intense arc that vaporizes workpiece material.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Proses Pemesinan Non Tradisional part 1

Introduction: Advanced Machining Processes
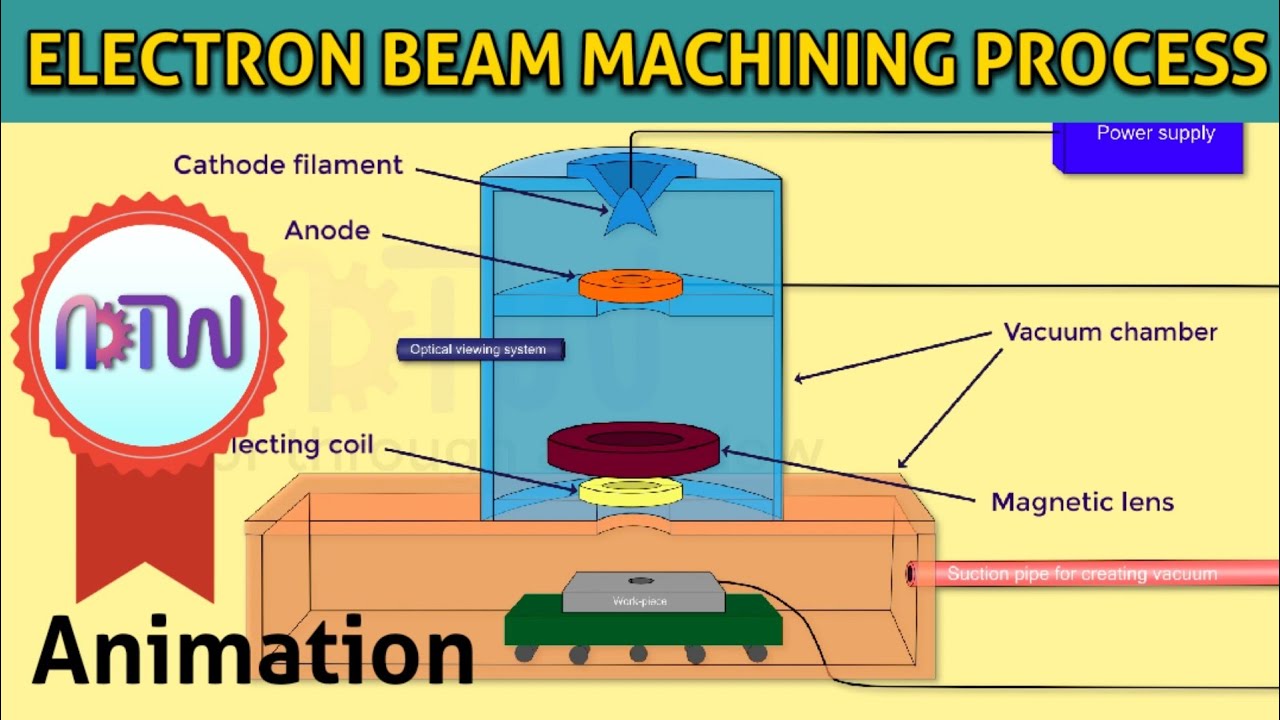
ELECTRON BEAM MACHINING PROCESS (EBM): Construction and Working of electron beam machining process.

WATER JET MACHINE PROCESS : Working of abrasive water Jet machining process (animation).
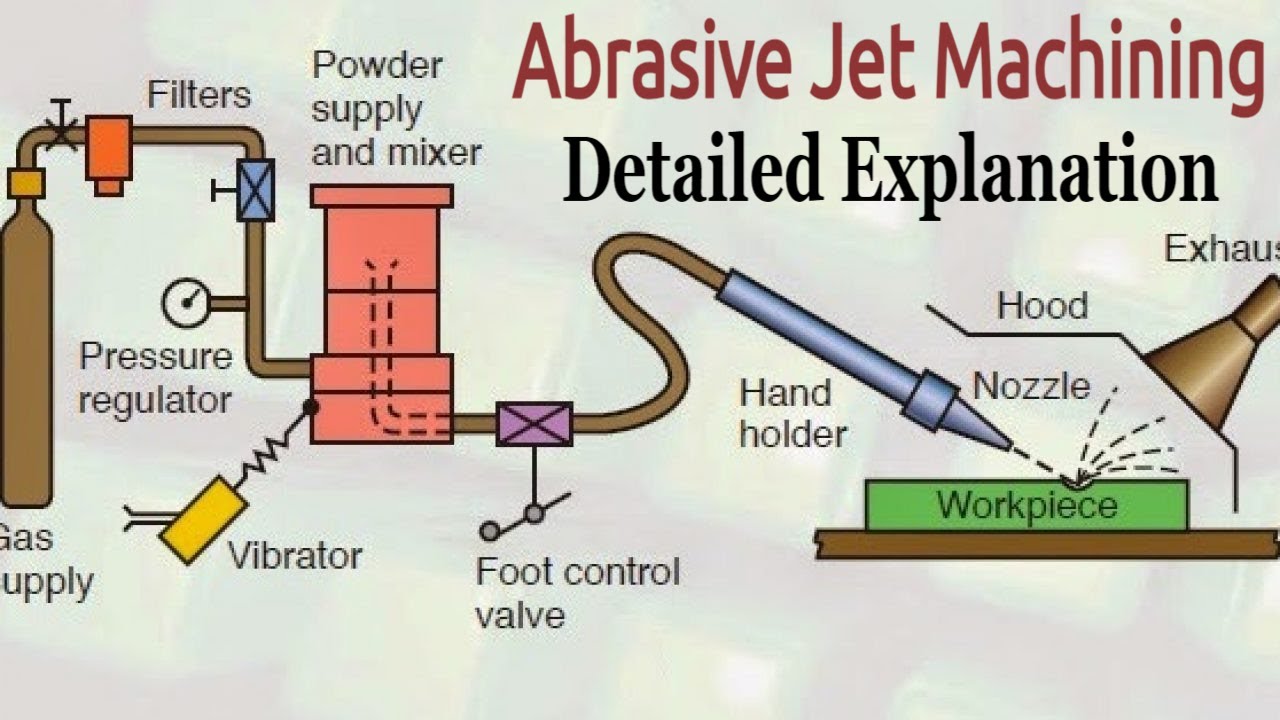
How an Abrasive Jet Machining Works?

Materiais e Processos de Fabricação para Engenharia de Produção - Usinagem não convencional...
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
