Huygens principle and Wavefront || Animated Hindi explanation ||Wave optics || 12th class || physics
Summary
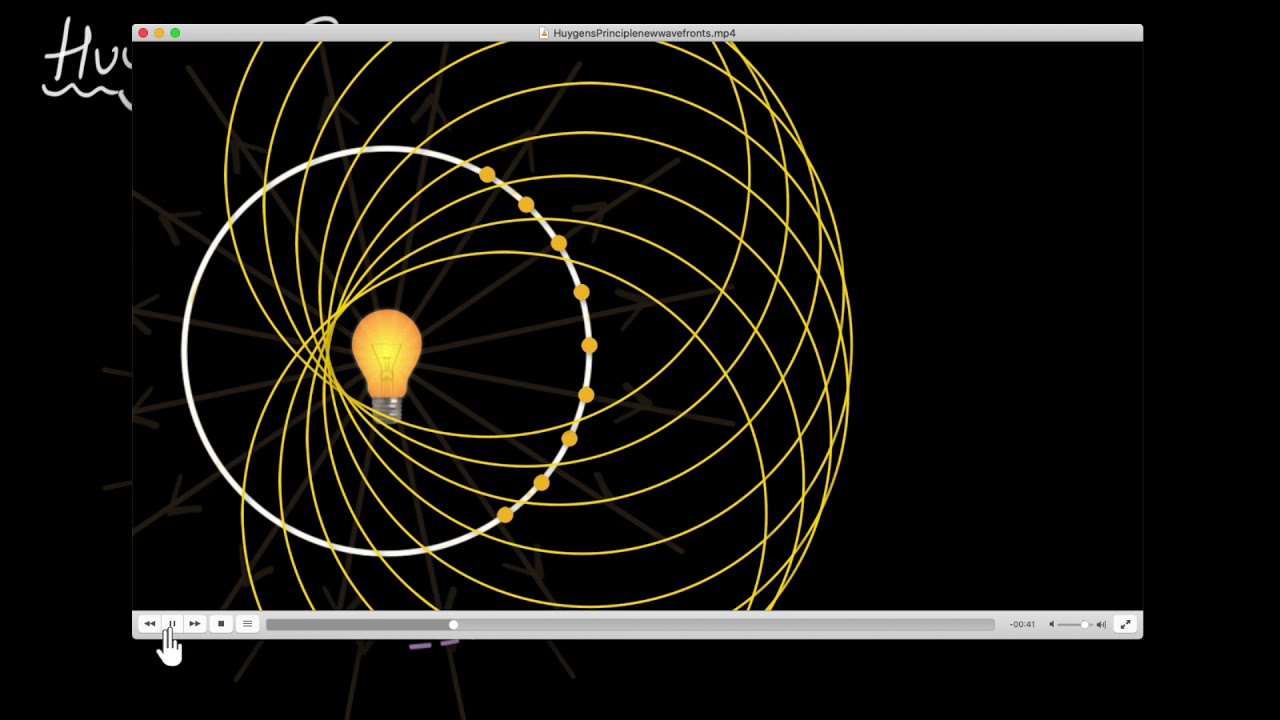
TLDRThe video explains the concept of a wavefront and Huygens' principle. It describes how light waves, originating from a point light source, travel at the same speed in a homogeneous medium. The video elaborates on different types of wavefronts—spherical, cylindrical, and plane—based on the light source's distance and nature. It then details Huygens' principle, which states that every point on a wavefront acts as a secondary source of disturbance, forming secondary wavelets. The video further illustrates how these wavelets help determine the position and shape of a new wavefront over time.
Takeaways
- 💡 Wavefront represents the locus of points in a medium where light waves travel with the same speed.
- 🌟 A point light source emits waves in all directions, and these waves touch different points in the medium over time.
- 📏 The distance traveled by each light wave depends on the speed of light and the time elapsed.
- 🌍 Wavefronts are of three types: spherical, cylindrical, and plane, based on the source of the light.
- 🔵 Spherical wavefronts are produced by point light sources, while cylindrical wavefronts come from linear light sources.
- 🛫 Plane wavefronts appear when the light source is far away from the observer, behaving like a plane surface.
- 🔄 Huygens' Principle explains how to construct and predict the future shape and position of a wavefront.
- ⚡ According to Huygens' Principle, each point on a wavefront acts as a source of secondary wavelets that spread in all directions.
- 🌀 The secondary wavelets combine to form a new wavefront, which gives the wave's next position after a certain time interval.
- 🔬 Using Huygens' Principle, the shape and location of any wavefront can be geometrically determined based on its current state.
Q & A
What is a wavefront?
-A wavefront is the locus of points in a medium that light waves touch simultaneously as they propagate. It is essentially a surface where all points on it are vibrating in phase.
What are the three types of wavefronts mentioned in the script?
-The three types of wavefronts are spherical wavefront, cylindrical wavefront, and plane wavefront.
When is a spherical wavefront formed?
-A spherical wavefront is formed when light emanates from a point source, causing waves to spread out uniformly in all directions.
When does a cylindrical wavefront occur?
-A cylindrical wavefront occurs when light originates from a linear source, causing waves to expand in cylindrical shapes.
What conditions lead to the formation of a plane wavefront?
-A plane wavefront forms when the light source, whether point or linear, is at a large distance. At this distance, the curvature of the wavefront becomes so small that it appears as a plane.
What does Huygens’ Principle explain?
-Huygens’ Principle explains the geometric construction and position of a wavefront at any point in time. It allows the prediction of a wavefront's future position based on its current shape.
What are the two statements of Huygens’ Principle?
-The first statement says that every point on a wavefront acts as a source of secondary disturbances called wavelets. The second statement says that the envelope of these secondary wavelets forms a new wavefront.
How does Huygens' Principle help in determining the position of a wavefront?
-By considering each point on the current wavefront as a secondary source of wavelets and tracing their envelopes over time, Huygens' Principle helps predict the new position and shape of the wavefront.
What is a secondary wavelet?
-A secondary wavelet is a small wave that originates from each point on the wavefront, acting as a new disturbance source, and propagates in all directions.
How do wavelets help in constructing the new wavefront?
-The envelope formed by all secondary wavelets at a specific time forms a new wavefront, showing the future position of the wave.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
Huygen's principle of secondary waves | Wave optics | Physics | Khan Academy

Reflection laws proof using Huygen's principle | Wave optics | Physics | Khan Academy

AP Physics 2: Light 1: Light Wave and Huygens' Principle

The Physics of Refraction and Mirages via Huygens principle

Huygen's theory of light & wavefronts | Wave optics | Physics | Khan Academy

DIFRAÇÃO e POLARIZAÇÃO - ONDULATÓRIA - AULA 6
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
