The Physics of Refraction and Mirages via Huygens principle
Summary
TLDRThis video explains how Huygens' principle can help us understand wave behavior in various scenarios. By visualizing wave propagation through secondary wavelets, the principle provides insight into phenomena like light refraction, Doppler effect, and the behavior of waves as they interact with different mediums. It demonstrates how Huygens' principle clarifies concepts such as Snell's Law, the bending of light in water, and mirages caused by temperature-induced changes in the index of refraction. The video showcases the power of Huygens' principle in predicting and explaining wave behavior in real-world situations.
Takeaways
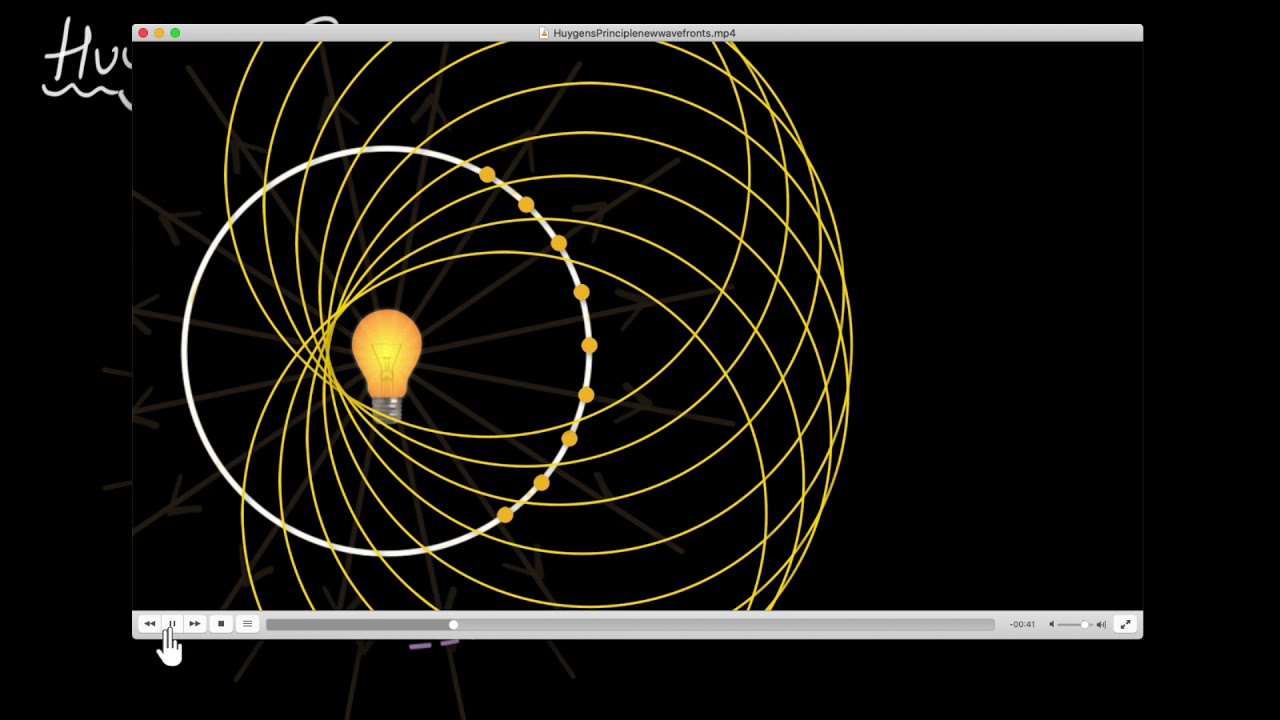
- 😀 Huygens' Principle explains how waves propagate from various points and helps visualize wavefronts at later times.
- 😀 Huygens' Principle can be applied to both light and sound waves, predicting their behavior when the source is moving, like in the Doppler effect.
- 😀 The principle helps visualize how waves split apart, making it easier to understand experiments like Young's double-slit experiment.
- 😀 Huygens' Principle is useful for understanding how waves behave when they travel between media with different propagation speeds.
- 😀 The principle is essential in explaining how light bends when it refracts as it passes from one medium to another (e.g., from air to water).
- 😀 A laser beam refracts when entering water because the speed of light in water is slower, causing the light to bend and follow a new path.
- 😀 Snell's Law of refraction can be derived from Huygens' Principle, providing a clear explanation of how light bends at the boundary between media.
- 😀 Refraction can explain optical illusions like the bending of light seen with objects (e.g., a spoon) in water.
- 😀 Huygens' Principle also helps explain phenomena like mirages, where heat causes light to bend due to varying temperatures and refractive indices.
- 😀 The principle's utility extends to explaining real-world phenomena by modeling wave behavior in different conditions, helping predict outcomes in wave-related scenarios.
Q & A
What is Huygens' principle and how does it help explain wave propagation?
-Huygens' principle states that every point on a wavefront can be considered a source of secondary wavelets, which propagate outward with the same speed as the initial wave. This principle helps predict the future position of a wavefront and explains phenomena like refraction, diffraction, and the Doppler effect.
How does Huygens' principle explain the formation of wavefronts?
-Huygens' principle explains that the new wavefront can be determined by considering all the secondary wavelets formed at each point on the current wavefront. The position of the new wavefront is then found by combining these wavelets at a later time.
What is the role of secondary wavelets in understanding wavefronts?
-Secondary wavelets are crucial as they represent the individual waves originating from each point on the current wavefront. These wavelets combine over time to form the new wavefront, enabling the prediction of wave behavior in various situations.
Why does Huygens' principle work even when waves are traveling in three dimensions?
-Huygens' principle works in three dimensions because each point on a wavefront can emit secondary wavelets that propagate in all directions. The principle accounts for the spread of waves in three-dimensional space, helping predict the new wavefront's shape and position.
What is the significance of Huygens' principle in understanding the Doppler effect?
-Huygens' principle helps visualize the Doppler effect by showing how the speed of a moving source affects the propagation of waves. For instance, when a plane moves through sound waves, the principle can help visualize the shockwave formed due to the change in wave speed relative to the observer.
How can Huygens' principle be applied to understand Young's double-slit experiment?
-Huygens' principle can explain the interference pattern seen in Young's double-slit experiment. By considering each slit as a source of secondary wavelets, we can predict the constructive and destructive interference that results in the observed pattern of bright and dark fringes.
How does Huygens' principle explain the bending of light when it passes through different mediums?
-Huygens' principle explains that when light passes from one medium to another, the change in the speed of light causes the secondary wavelets to spread at different rates. This results in the bending of the wavefront, which is observed as refraction.
What role does Huygens' principle play in the phenomenon of light bending at the water-air interface?
-Huygens' principle shows that when light transitions from air into water, it slows down, causing the wavefront to bend towards the normal. The individual secondary wavelets spread at a slower rate in water, resulting in the observed bending of the light.
How does Huygens' principle help explain the reflection of light from surfaces?
-Huygens' principle explains that when light reflects off a surface, the wavefronts reverse direction and maintain the angle of reflection equal to the angle of incidence. This occurs because each point on the wavefront acts as a source of secondary wavelets, which follow the law of reflection.
How does Huygens' principle contribute to the explanation of mirages?
-Mirages occur due to the varying refractive index of air at different temperatures. Huygens' principle helps explain how light rays bend towards the ground in hotter areas, causing a distorted image of distant objects to appear, like a car or water on a hot road.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Huygen's principle of secondary waves | Wave optics | Physics | Khan Academy

AP Physics 2: Light 1: Light Wave and Huygens' Principle

Propagation of Light (Reflection and Refraction) as Explained by the Wave and Particle Models

Experimentos Difracción, Refracción y Reflexión de Ondas

Reflection laws proof using Huygen's principle | Wave optics | Physics | Khan Academy

Huygen's theory of light & wavefronts | Wave optics | Physics | Khan Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)