DIFRAÇÃO e POLARIZAÇÃO - ONDULATÓRIA - AULA 6
Summary
TLDRIn this lesson on wave phenomena, Professor Marcelo Mora covers diffraction and polarization. He explains how diffraction allows waves to bend around obstacles, using sound and light examples such as a car horn bending around a wall. The discussion also highlights the principle of Huygens-Fresnel and the distinction between longitudinal and transverse waves, showing that only transverse waves, like light, can be polarized. Practical demonstrations, including a laser and a hair example, illustrate the concepts, with exercises reinforcing the understanding of diffraction and polarization effects.
Takeaways
- 🌊 The video discusses the concept of wave diffraction, explaining how waves bend around obstacles and continue to propagate.
- 🚗 An example of diffraction is given with a car approaching from the left, where the car's sound is heard before it is seen due to the wave diffracting around a corner.
- 🌈 The video also covers the phenomenon of light diffraction using a laser and a strand of hair to illustrate how light waves interfere and diffract.
- 📢 Sound waves can diffract around objects like windows and walls, allowing us to hear sounds even when the source is not in direct line of sight.
- 🚦 The principle of Huygens is introduced, stating that every point on a wavefront can be considered a source of secondary wavelets that spread out in the forward direction at the same speed as the original wave.
- 🌉 Fresnel's contributions to the principle of wave propagation are highlighted, particularly his improvements upon Huygens' principle to better explain reflection and refraction.
- 🚧 The script touches on the historical debate between Newton and others about the nature of light, whether it is a particle or a wave.
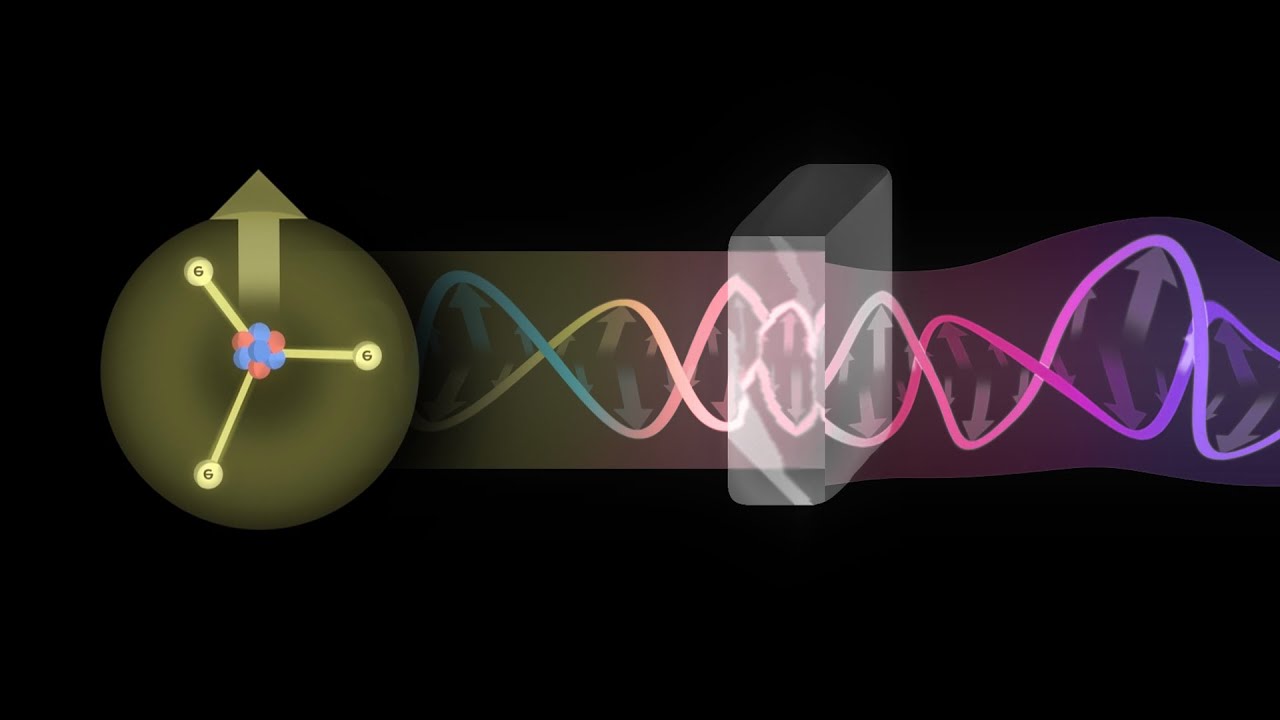
- 📏 The concept of wave polarization is explained, noting that it only occurs in transverse waves, and longitudinal waves like sound cannot be polarized.
- 🕶️ The use of polarizers to filter out certain orientations of light waves is discussed, with examples of how this is used in sunglasses to reduce glare.
- 💡 The video concludes with exercises to test understanding, including questions on diffraction, the behavior of light passing through slits, and the use of polarized lenses to reduce glare from reflected light.
Q & A
What is the diffraction phenomenon mentioned in the script?
-Diffraction is a wave property that allows waves to bend around obstacles or pass through small openings. This is observed when waves, such as sound or light, change their direction and spread out after encountering a barrier or a slit.
How does sound diffraction differ from light diffraction?
-Sound waves, which are longer in wavelength, can easily diffract around obstacles like walls or through openings like windows. This allows sound to be heard even if the source is not directly visible. Light waves, being much shorter in wavelength, do not diffract as easily, which is why we cannot see around obstacles in the same way we can hear around them.
What is the Huygens-Fresnel principle, and how is it related to diffraction?
-The Huygens-Fresnel principle states that every point on a wavefront can be considered a source of secondary wavelets that propagate forward. This principle helps explain how waves, such as light or sound, can diffract when passing through slits or around obstacles.
What is the significance of the fender width in diffraction?
-The width of the opening (fender) must be of the same order as the wavelength of the wave for noticeable diffraction to occur. If the opening is too large compared to the wavelength, the wave passes through with minimal diffraction.
What example does the speaker use to illustrate sound diffraction?
-The speaker uses the example of hearing a car approaching from around a corner before actually seeing it. The sound waves emitted by the car horn can diffract around the corner, allowing the listener to hear the car before it is visible.
What is polarization, and which types of waves can be polarized?
-Polarization is a phenomenon where the oscillations of a wave are restricted to a particular direction. It only occurs in transverse waves, like light. Longitudinal waves, such as sound, cannot be polarized.
What practical application of light polarization is mentioned in the script?
-One practical application of light polarization is in Polaroid lenses, which are used to reduce glare by blocking horizontally polarized light reflected off surfaces like roads or water.
Why do sunglasses with polarized lenses help reduce glare?
-Polarized lenses are designed to block specific polarized light waves, such as those reflected horizontally off surfaces like water or roads. This helps reduce glare and makes vision clearer.
What is the Doppler effect, as briefly mentioned in the script?
-The Doppler effect is the change in frequency or wavelength of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. For example, the pitch of a car horn appears higher as the car approaches and lower as it moves away.
How did Isaac Newton's view of light differ from the wave theory?
-Isaac Newton believed that light was composed of small particles, while the wave theory, supported by figures like Huygens and Fresnel, proposed that light is a wave. This debate was prominent until experiments like diffraction and polarization demonstrated light's wave properties.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)