Types of Human Body Tissue
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the four types of tissues in the human body: connective, epithelial, nervous, and muscle tissue. It describes connective tissue's role in structure, support, and material transport, along with various types like loose connective tissue, cartilage, and bone. Epithelial tissue is explained for its protective, absorptive, and sensory functions. The video also covers nervous tissue, focusing on neurons and their role in transmitting electrical signals. Lastly, it discusses muscle tissue types—skeletal, smooth, and cardiac—and their roles in movement, posture, and circulation.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Connective tissue provides structure, support, and defense, and helps transport materials and bind things together.
- 🧵 Connective tissue is made up of cells, fibers (collagen and elastic), and ground substance (water, fluid, and proteins).
- 🩹 Types of connective tissues include loose connective tissue, fibrous connective tissue, cartilage, adipose (fat), blood, and bone.
- 🦠 Epithelial tissue lines cavities and covers surfaces, providing protection, secretion, absorption, and sensation.
- 🛡️ Epithelial tissues are classified by shape (squamous, cuboidal, columnar) and the number of layers (simple, stratified).
- ⚡ Nervous tissue, made up of neurons, transmits electrical signals between the brain, spinal cord, and body.
- 🌿 Neurons consist of a cell body, dendrites (for receiving signals), and an axon (for sending signals).
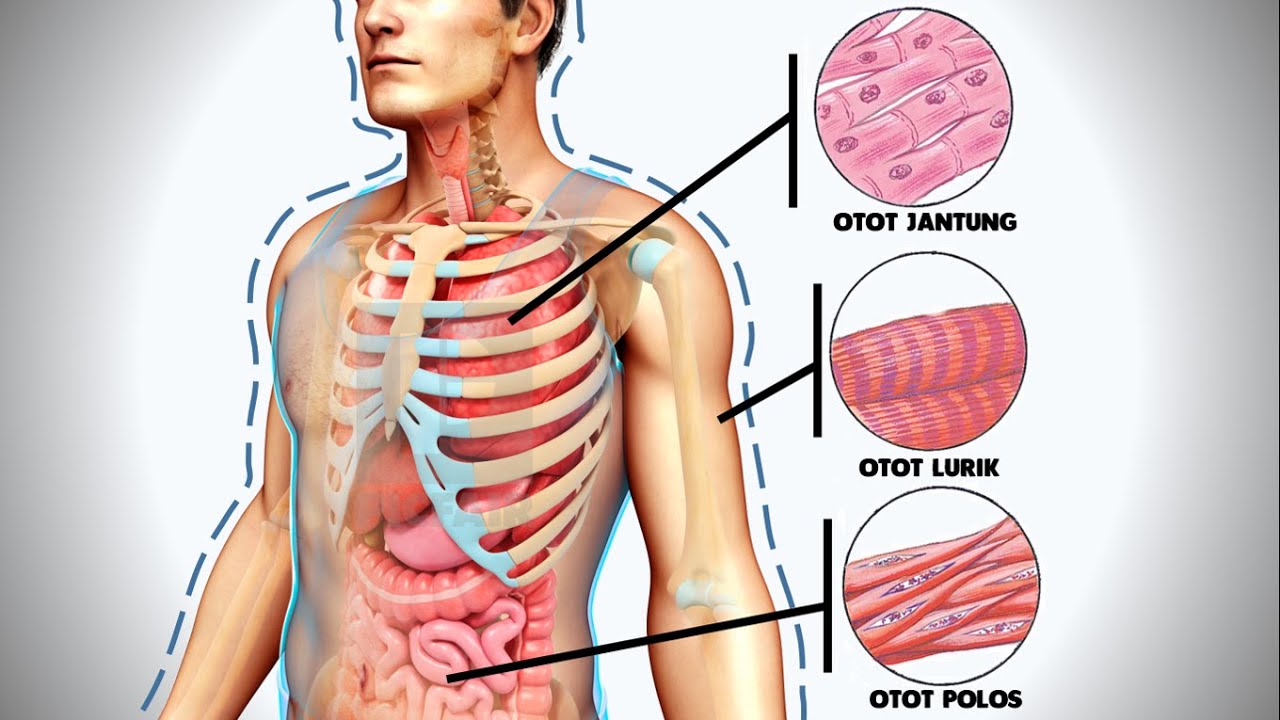
- 💪 Muscle tissue is responsible for movement, posture, and heat production in the body.
- 🏋️ There are three types of muscle tissues: smooth (involuntary, found in organs), skeletal (voluntary, attached to bones), and cardiac (found in the heart).
- ❤️ Cardiac muscle is striated like skeletal muscle but works involuntarily like smooth muscle, helping the heart pump blood.
Q & A
What is the function of connective tissue in the body?
-Connective tissue provides structure, support, defense, transport of materials, and binds other tissues together in the body.
What are the main components of connective tissue?
-Connective tissue is made up of cells, fibers (collagen and elastic fibers), and a ground substance, which consists of water, fluid, and proteins called the matrix.
What are some examples of different types of connective tissues?
-Examples include loose connective tissue, fibrous connective tissue, cartilage, adipose tissue (body fat), blood, and bones.
What are epithelial tissues, and what is their function?
-Epithelial tissues line cavities and cover the surfaces of organs and vessels. They provide protection, secretion, absorption, exchange, and sensation functions.
How are epithelial tissues classified?
-Epithelial tissues are classified by their shape (squamous, cuboidal, or columnar) and the number of layers (simple for one layer, stratified for multiple layers).
What are neurons, and what role do they play in nerve tissue?
-Neurons are nerve cells that transmit electrical signals throughout the body, allowing communication between the brain and various body parts.
What are the main parts of a neuron?
-A neuron consists of a cell body (containing the nucleus), dendrites (which receive signals), and an axon (which transmits signals, often covered by a myelin sheath).
What are the three types of muscle tissue in the body?
-The three types of muscle tissue are smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and skeletal muscle.
What is the difference between smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscles?
-Smooth muscles are involuntary and found in internal organs, cardiac muscles are striated and found in the heart, and skeletal muscles are voluntary and attached to bones to help with movement.
How do muscle tissues contribute to movement and posture?
-Muscle tissues contract to enable movement and help maintain body posture. Skeletal muscles, in particular, work with bones to allow voluntary movements.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

MATERI MARTIKULASI | JARINGAN TUBUH MANUSIA
Media Pembelajaran Jaringan Hewan - Kelas Daring Biologi SMA Kelas XI

what are tissues in human body, what are tissues made of, what are tissues class 9, Human tissues,

Cells and tissues: types and characteristics - Human histology | Kenhub

Resumão: HISTOLOGIA

Jaringan Hewan
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
