CRYSTAL LATTICE AND UNIT CELL
Summary
TLDRThe video script delves into the fascinating world of crystal lattices, explaining their three-dimensional cubic arrangement as points in space. It introduces the concept of unit cells, which are the building blocks of crystals, and distinguishes between primitive and centered unit cells. The script further explores the seven crystal systems and 14 Bravais lattices, highlighting the importance of unit cell parameters and angles in understanding crystal structures.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Crystal lattices are three-dimensional arrangements of particles in space.
- 🌐 There are 14 different three-dimensional lattices known as Bravais lattices, named after French mathematician Auguste Bravais.
- 📏 Unit cells are the basic building blocks of crystals, with parameters a, b, c for edges and alpha, beta, gamma for angles between them.
- 🏠 Unit cells can be of two types: Primitive (particles only at corners) and Centered (particles also at other positions).
- 🔶 Primitive unit cells have particles only at the corners.
- 🔵 Centered unit cells have particles at additional positions besides the corners and are further divided into three types: body-centered, face-centered, and end-centered.
- 🔵 Body-centered unit cells have a particle at the center of the body in addition to the corners.
- 🔵 Face-centered unit cells have particles at the centers of all six faces plus the corners.
- 🔵 End-centered unit cells have particles at the centers of any two opposite faces along with the corners.
- 🌐 There are seven crystal systems that classify crystal forms based on symmetry and crystallographic parameters a, b, c, and angles alpha, beta, gamma.
- 📊 Crystal systems are further divided into 32 classes based on symmetry.
Q & A
What is a crystal lattice?
-A crystal lattice is a three-dimensional arrangement of particles as points in space, which forms the basis of a crystal's structure.
Who was Bravais?
-Bravais was a French mathematician who identified 14 different three-dimensional lattices that are possible in crystals.
What are the unit cell parameters?
-The unit cell parameters are 'a', 'b', and 'c', which are the lengths of the edges of the unit cell, and 'alpha', 'beta', and 'gamma', which are the angles between them.
What is a unit cell?
-A unit cell is the smallest part of a crystal lattice that, when repeated, generates the entire crystal structure.
What are the two types of unit cells?
-There are two types of unit cells: Primitive, where particles are only at the corners, and Centered, where particles are at additional positions along with corners.
What is a Primitive unit cell?
-A Primitive unit cell is one where the constituent particles are present only at the corners.
What are the three types of Centered unit cells?
-The three types of Centered unit cells are Body-centered, Face-centered, and End-centered.
Define a Body-centered unit cell.
-A Body-centered unit cell is one where a particle is present at the body center along with the particles at the corners.
What is a Face-centered unit cell?
-A Face-centered unit cell is one where particles are present at the centers of all six faces along with the particles at the corners.
Explain an End-centered unit cell.
-An End-centered unit cell is one where particles are present at the centers of any two opposite faces along with the particles at the corners.
What are crystal systems?
-Crystal systems are the classification of crystal forms based on symmetry, which are divided into seven categories depending on the crystallographic parameters a, b, c, and alpha, beta, gamma.
How many crystal systems are there?
-There are seven crystal systems.
How many classes are there in the classification of crystal systems?
-There are 32 classes in the classification of crystal systems based on symmetry.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
1.4 Classification of latices

Aula 10 – Estruturas Cristalinas Cúbicas de Face Centrada, Corpo Centrado e Hexagonal Compacta.

2A Conceitos básicos de simetria e cristalografia

What is a Unit Cell?

noc19-cy16 Lecture 06-Solid state Chemistry-Week 2 Lecture-1 Unit Cell
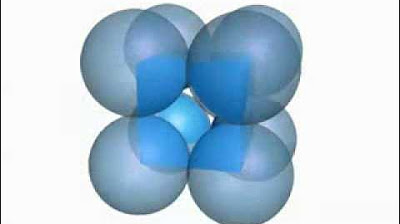
The primitive, body-centred and face-centred cubic unit cells
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
