Nodal Analysis EP.16 (Tagalog/English Electronics)
Summary
TLDRThis video script is a tutorial on nodal analysis, a method for analyzing electrical circuits. It guides viewers through selecting a reference node, assigning voltages to other nodes, and applying Kirchhoff's Current Law to derive equations. The tutorial uses Ohm's Law to express branch currents in terms of node voltages and demonstrates solving simultaneous equations to find unknown voltages. An example circuit is used to illustrate the process, showing calculations for node voltages and currents through resistors.
Takeaways
- 🔌 Nodal analysis is a method for analyzing electrical circuits by considering the voltages at various nodes.
- 🔧 The first step in nodal analysis is to select a reference node and assign voltages to the remaining nodes.
- 📐 Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) is applied to each node to set up equations relating the node voltages.
- ⚖️ Ohm's Law is used to express branch currents in terms of node voltages and resistance.
- 🧮 Solving the simultaneous equations obtained from the KCL and Ohm's Law applications yields the unknown node voltages.
- 📚 Nodal analysis is particularly useful for circuits with multiple nodes and complex interactions.
- 💡 The reference node is often grounded to simplify calculations, making it a common point of reference.
- 🔄 Current directions are assigned for each node, and the currents entering and leaving a node are balanced according to KCL.
- 📉 The script provides a step-by-step example of applying nodal analysis to a circuit with a voltage source and resistors.
- 🛠️ The solution involves calculating currents through resistors and voltages across nodes using the derived nodal equations.
Q & A
What is nodal analysis in electrical circuits?
-Nodal analysis is a method used to analyze electrical circuits by considering the voltages at different nodes and applying Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) to derive equations that can be solved to find the unknown node voltages.
Why is selecting a reference node important in nodal analysis?
-Selecting a reference node, typically grounded, is crucial because it provides a common point of reference for measuring the voltages at other nodes in the circuit, simplifying the formulation of nodal equations.
How do you assign voltages to nodes in nodal analysis?
-In nodal analysis, you assign voltages (v1, v2, ..., v(n-1)) to the remaining nodes after selecting a reference node. The reference node is often assigned a voltage of zero.
What is the role of Ohm's Law in nodal analysis?
-Ohm's Law is used in nodal analysis to express the branch currents in terms of node voltages by relating the voltage across a resistor to the current through it (V = IR), which helps in formulating the nodal equations.
How many nodal equations are typically formed in a nodal analysis?
-The number of nodal equations formed is typically one less than the number of nodes (N-1), where N is the total number of nodes in the circuit.
What is the significance of Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) in nodal analysis?
-KCL is essential in nodal analysis as it states that the sum of currents entering a node is equal to the sum of currents leaving that node, which is used to set up the equations for each node.
Can you explain how to solve the simultaneous equations obtained from nodal analysis?
-The simultaneous equations from nodal analysis can be solved using algebraic methods like Cramer's rule, or numerical methods using software like MATLAB. The goal is to find the unknown node voltages.
What is the purpose of assigning currents in the direction of voltage drops in nodal analysis?
-Assigning currents in the direction of voltage drops helps in determining the sign of the current terms when formulating the nodal equations, which is necessary for accurately representing the flow of current in the circuit.
How does the choice of the reference node affect the nodal analysis?
-The choice of the reference node does not affect the solution of the nodal analysis but simplifies the process by reducing the number of unknowns and making the equations easier to set up and solve.
What are the common techniques used to solve the equations resulting from nodal analysis?
-Common techniques to solve the equations from nodal analysis include Cramer's rule for small systems, matrix methods for larger systems, and numerical methods or software tools like MATLAB for complex circuits.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
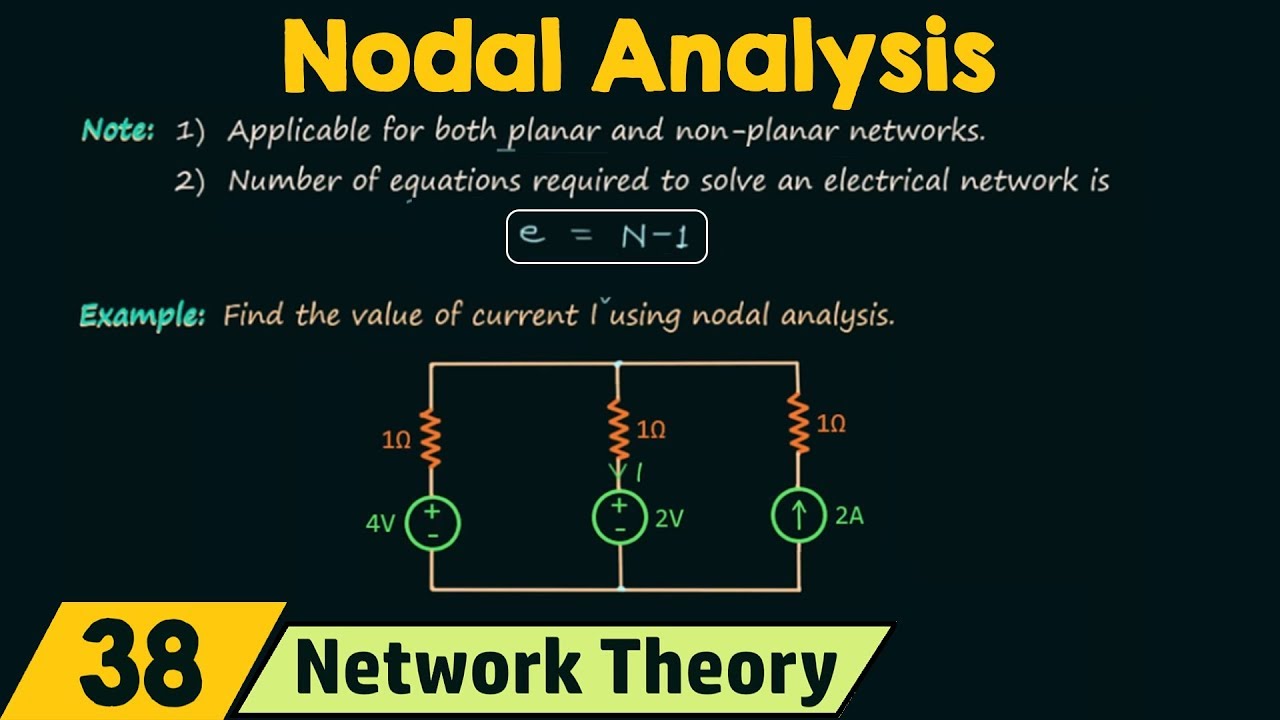
Nodal Analysis
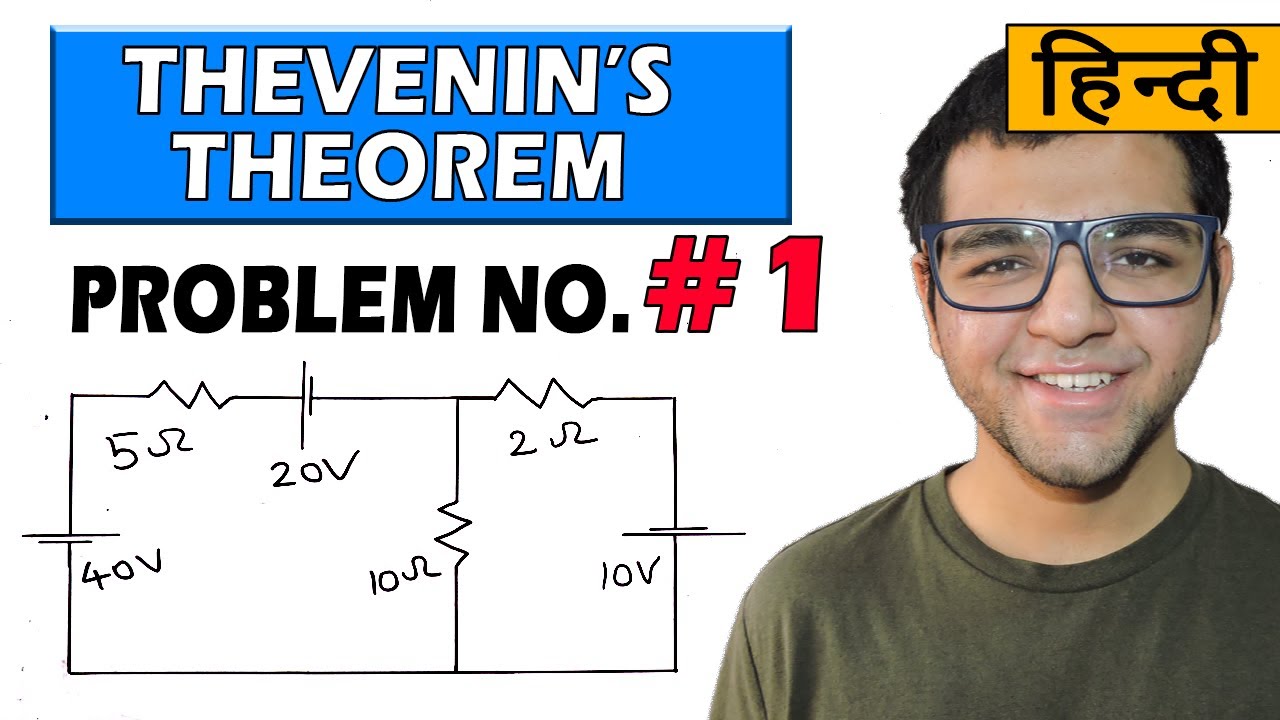
Thevenin Theorem problems in Hindi [ Problem 1 ]

Rangkaian Listrik - Analisis Mesh (Genap 2019/2020)

Electrical Engineering: Basic Laws (18 of 31) Finding the Equivalent Resistor Ex. 3

Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) Explained
Open circuit | closed circuit | Short circuit | Easiest way to understand
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
