F23 - Kesetimbangan Benda Tegar ,cara mudah memahami.
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive guide to the equilibrium of rigid bodies, explaining translational, rotational, and combined equilibrium. It demonstrates step-by-step methods to solve equilibrium problems, including analyzing forces with components, using torque calculations, and applying the sine rule for three-force systems. The tutorial covers practical examples such as tension in ropes, rods leaning against walls, and beams with loads, emphasizing free-body diagrams and strategic axis selection for torque calculations. Viewers learn efficient problem-solving techniques for both simple and complex scenarios, with clear numerical examples and tips for minimizing calculations while ensuring accurate results.
Takeaways
- 😀 Equilibrium of rigid objects is divided into three types: translational, rotational, and combined equilibrium.
- 😀 Translational equilibrium occurs when the sum of all forces on an object is zero (ΣF = 0).
- 😀 Rotational equilibrium occurs when the sum of all torques on an object is zero (Στ = 0).
- 😀 Combined equilibrium requires both ΣF = 0 and Στ = 0 simultaneously.
- 😀 Forces can be broken into x and y components to solve translational equilibrium problems.
- 😀 Torque is calculated as the product of force and the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation.
- 😀 The sine rule can be used to find unknown forces when three forces act on a point and their angles are known.
- 😀 For rods leaning on walls or surfaces, friction and normal forces must be considered to prevent slipping.
- -
- 😀 Choosing an appropriate rotation axis can simplify torque calculations and eliminate unknowns.
- 😀 Free-body diagrams are essential for visualizing forces, angles, and distances in equilibrium problems.
- 😀 Problem-solving strategies include using analytical methods, sine rule, and torque equations to find tensions, support forces, or friction coefficients.
Q & A
What are the three types of equilibrium for rigid bodies?
-The three types are: 1) Translational equilibrium (particle equilibrium) where net force is zero, 2) Rotational equilibrium where net torque is zero, and 3) Combined equilibrium where both net force and net torque are zero.
What is the condition for translational equilibrium?
-The condition is that the sum of all forces acting on the object must be zero: ΣF_x = 0 and ΣF_y = 0.
How do you determine the net torque for rotational equilibrium?
-Net torque is calculated as the sum of all moments of force about a chosen axis. Torque = Force × perpendicular distance from the axis, and for equilibrium, Στ = 0.
When is the sine rule method applicable in equilibrium problems?
-The sine rule method can be used when a point is in equilibrium under exactly three forces. The angles between the forces are used to calculate unknown forces.
How would you find the tension in ropes supporting a hanging load using the analytical method?
-Resolve the forces along x and y axes and apply ΣF_x = 0 and ΣF_y = 0. Then solve the resulting equations for the unknown tensions.
In the example with a 60 N hanging load and ropes at 45°, what are the rope tensions?
-Using the analytical method: T2 = 60√2 N and T1 = 60 N.
How can torque be used to find the tension in a rope supporting a rod?
-Choose an axis of rotation to eliminate unknown forces passing through it. Then apply Στ = 0, multiplying each force by its perpendicular distance to the axis, to solve for the rope tension.
What is the significance of choosing the axis at the point where a force acts?
-Choosing the axis at the point of action of a force eliminates its contribution to torque, simplifying calculations.
In the rod and child example, how do you calculate the support force at one end?
-Apply the torque condition Στ = 0 about the other end. Multiply each force by its perpendicular distance from the chosen axis and solve for the unknown support force.
How do you find the angle of a rope relative to the wall in an equilibrium problem?
-Use vector components or the Pythagorean theorem on the right triangle formed by the forces. Then use trigonometric ratios such as sin or tan to calculate the angle.
What is the minimum friction coefficient required to prevent a rod from slipping on a rough floor?
-Draw the free-body diagram, apply ΣF = 0 and Στ = 0. Then use the ratio of friction force to normal force (f = μN) to find the minimum coefficient μ that prevents slipping.
Why is it sometimes unnecessary to use all equilibrium conditions for a problem?
-In many cases, using only torque (Στ = 0) is sufficient to solve for unknowns, especially when selecting the rotation axis strategically to eliminate other unknowns.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
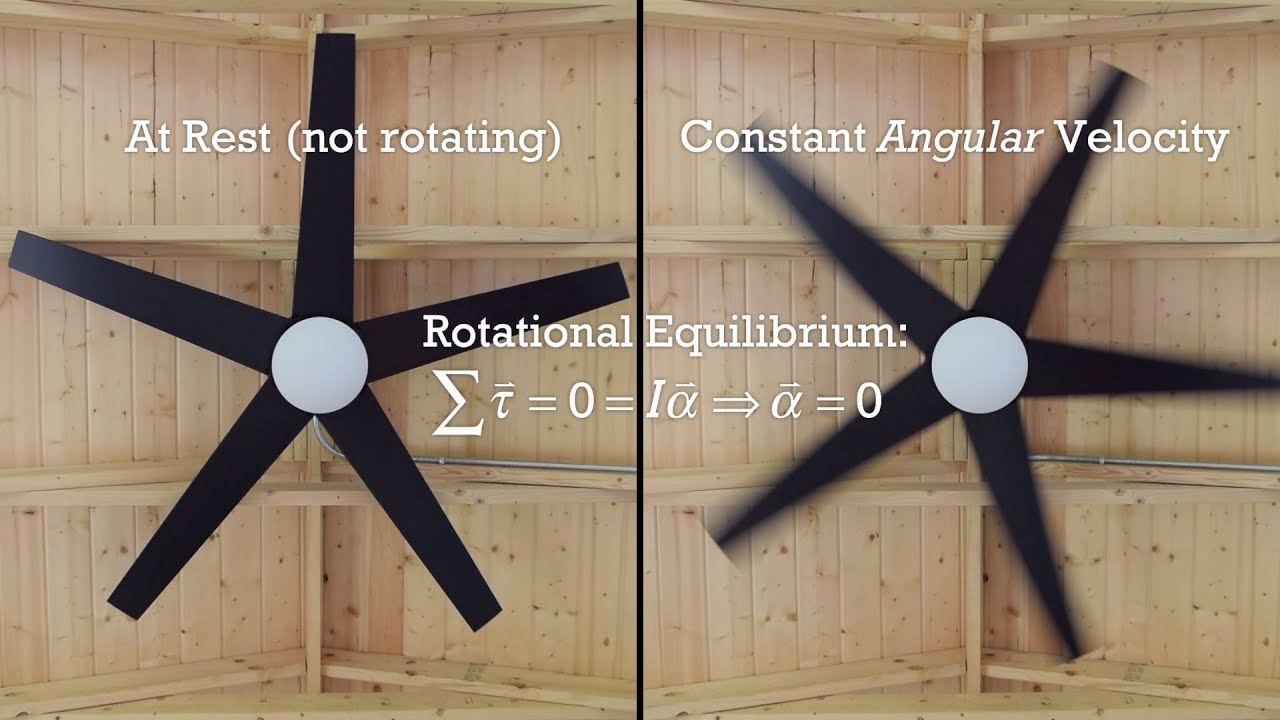
Rotational Equilibrium Introduction (and Static Equilibrium too!!)

Equilíbrio de corpo extenso rígido | estática

FISIKA KELAS XI || Kesetimbangan || DINAMIKA ROTASI & KESETIMBANGAN BENDA TEGAR

Kesetimbangan Kimia • Part 1: Konsep, Hukum, Tetapan Kesetimbangan Kc dan Kp
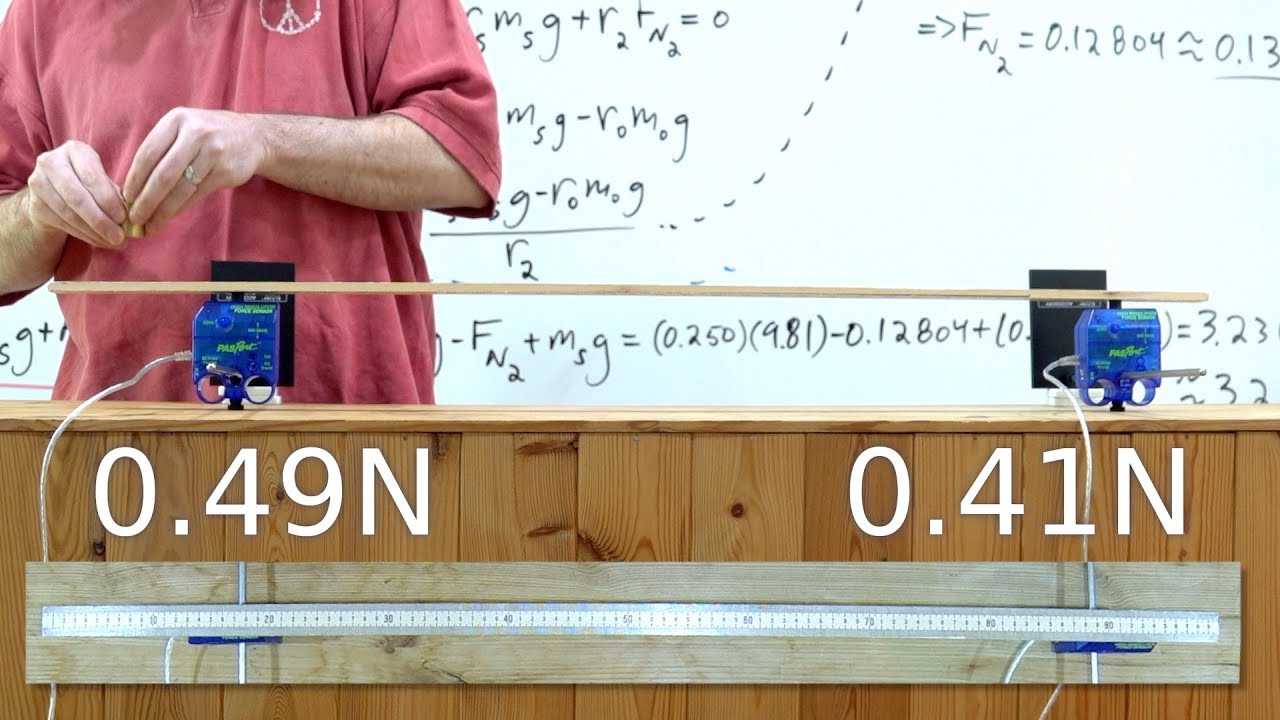
Introductory Rotational Equilibrium Problem

Part 1 Kesetimbangan Kimia: Reaksi Irreversible, Reaksi Reversible dan Konsep Kesetimbangan Dinamis.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
