Antibiotic Choices for Common Infections: Antibiotics Mnemonic + How to Choose an Antibiotic
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the speaker provides a comprehensive overview of common infections and the antibiotics used to treat them. Using a mnemonic, 'Antibiotics Can Protect the Queen’s Men Servants and Guards,' the script covers a variety of antibiotic classes including aminoglycosides, cephalosporins, penicillins, and more. For each class, the video explains their mechanisms, side effects, and clinical indications. The speaker also walks through common infections like UTIs, respiratory and skin infections, and even central nervous system infections, offering treatment guidelines based on the pathogens involved.
Takeaways
- 😀 Antibiotics are classified into several categories, each with specific uses, mechanisms, and side effects.
- 😀 Aminoglycosides like gentamicin are used for UTIs, endocarditis, and pneumonia but can cause nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity.
- 😀 Cephalosporins have five generations, each with a varying spectrum of activity, from narrow to broad, and are used for conditions like respiratory infections and bacterial meningitis.
- 😀 Carbapenems, including meropenem, are last-line antibiotics that work against resistant bacteria and cover gram-positive, gram-negative, and anaerobic organisms.
- 😀 Penicillins like amoxicillin are widely used for respiratory infections, neurosyphilis, and soft tissue infections, but can cause hypersensitivity reactions and neurotoxicity.
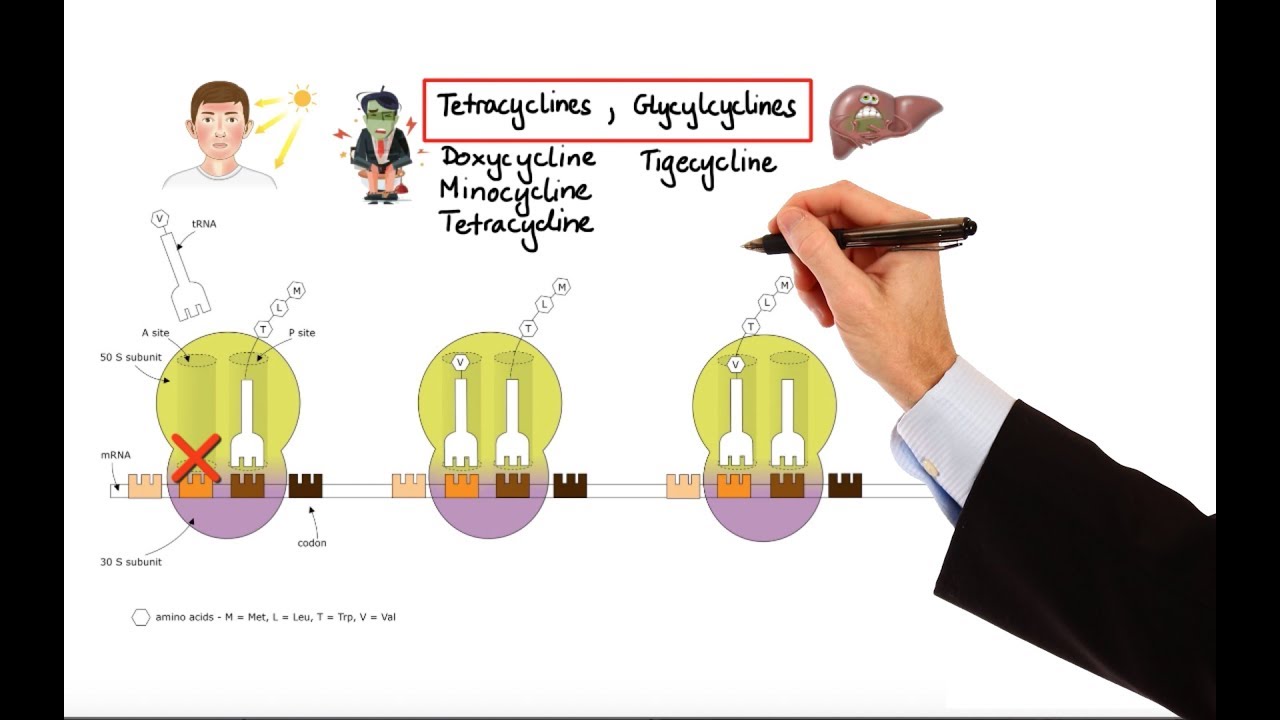
- 😀 Tetracyclines, such as doxycycline, inhibit protein synthesis and are used for conditions like anthrax and pneumonia, but are contraindicated in pregnant women and children under 8.
- 😀 Quinolones like ciprofloxacin target DNA synthesis and are effective against urinary tract infections, gastroenteritis, and respiratory pathogens.
- 😀 Macrolides, including azithromycin, are often used for respiratory infections, STIs, and atypical pneumonia but can cause GI upset and QT prolongation.
- 😀 Sulfonamides, like sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim, are effective for MRSA and UTIs but can lead to serious side effects such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and nephrotoxicity.
- 😀 Vancomycin, a glycopeptide, is used for MRSA infections and is effective in cases of endocarditis or C. difficile infections, but it can cause nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity if administered too quickly.
Q & A
What are the key classes of antibiotics discussed in the video?
-The key classes of antibiotics discussed in the video include Aminoglycosides, Cephalosporins, Carbapenems, Penicillins, Tetracyclines, Quinolones (Fluoroquinolones), Macrolides, Sulfonamides, and Glycopeptides.
How do Aminoglycosides work and what are their main side effects?
-Aminoglycosides work by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria, specifically by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit. Their main side effects include nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity, affecting 10-20% of patients.
What is the role of Cephalosporins, and how do their generations differ?
-Cephalosporins inhibit cell wall synthesis and are categorized into five generations. The first generation has a narrow spectrum, while higher generations cover a broader range, including gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. The fifth generation is especially effective against MRSA.
What are Carbapenems used for, and why are they considered last-line agents?
-Carbapenems are used for serious infections like UTIs, meningitis, and sepsis. They are considered last-line agents because they can inhibit beta-lactamase, an enzyme that makes bacteria resistant to other beta-lactam antibiotics.
Which infections are commonly treated with Penicillins?
-Penicillins are used to treat infections like endocarditis, skin and soft-tissue infections, pneumonia, upper respiratory tract infections, and neurosyphilis.
What are the risks associated with Tetracyclines, and why are they contraindicated in children and pregnant women?
-Tetracyclines can cause GI issues, renal toxicity, and liver problems. They are contraindicated in children under 8 and pregnant women because they can cause teeth staining and hinder fetal bone growth.
How do Quinolones (Fluoroquinolones) work, and what are their key side effects?
-Quinolones work by inhibiting DNA gyrase and topoisomerase II, enzymes responsible for DNA replication. Key side effects include tendon rupture, cartilage toxicity, and an increased risk of peripheral neuropathy.
What are Macrolides used for, and what should be considered regarding their side effects?
-Macrolides, like azithromycin and clarithromycin, are used to treat respiratory infections and STIs like chlamydia. They can cause GI upset, hypersensitivity, QT prolongation, and cholestatic jaundice, particularly with erythromycin.
How do Sulfonamides work, and what are the risks associated with them?
-Sulfonamides, particularly when combined with trimethoprim, inhibit folic acid production in bacteria. Risks include hypersensitivity reactions, nephrotoxicity, hyperkalemia, and blood disorders like neutropenia and hemolytic anemia.
What is the primary use of Glycopeptides like Vancomycin, and what are their side effects?
-Vancomycin is primarily used to treat MRSA infections and other gram-positive bacteria. Its side effects include nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity (though rarer than with aminoglycosides), and hypotension if infused too quickly.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Antibiotic | एंटीबायोटिक | Antibiotic Tablet | Antibiotic Injection | Medicine | Nursing | Pharmacy

Fluoroquinolones (Quinolones) Pharmacology Nursing Mnemonic, Mechanism of Action NCLEX

Antibiotics classes and coverage in 7 minutes!!
Pharmacology – ANTIBIOTICS – DNA, RNA, FOLIC ACID, PROTEIN SYNTHESIS INHIBITORS (MADE EASY)

Pharmacology – ANTIBIOTICS – CELL WALL & MEMBRANE INHIBITORS (MADE EASY)

Bacterial Infections - Causes, Symptoms and Treatments and More
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
