How China Is Preparing for a Conflict With India
Summary
TLDRChina's massive infrastructure projects in Tibet are reshaping the region, with roads, airports, and hydroelectric dams being constructed at unprecedented scales. These developments are not only about enhancing civilian infrastructure but also have strong military and strategic implications, strengthening China's position near contested borders with India. With dual-use facilities, railways, and energy hubs, China is positioning itself to control vital resources and power future technologies, like AI. The buildup is a calculated move to deter potential conflicts, especially with India, signaling a readiness to defend its sovereignty while raising tensions in the region.
Takeaways
- 😀 China is rapidly transforming the remote and inhospitable Himalayan region with infrastructure projects, reshaping both the landscape and geopolitical dynamics.
- 😀 Dual-use infrastructure projects, such as roads, airports, and railways, are being built in Tibet to strengthen China's military and strategic positioning near the India-China border.
- 😀 Beijing's development efforts include not just roads, but the construction of military air bases, such as the ones at Shigata Heping and others, which have been upgraded with fighter jets, air defense systems, and longer runways.
- 😀 China has expanded its infrastructure and military reach in Tibet, including the construction of two mega dams that could potentially be used for hydro-power as leverage in South Asia's geopolitical struggles.
- 😀 The Medog Dam project is poised to become the largest dam in the world, providing 60 gigawatts of electricity and strategically giving China control over vital water sources in the region.
- 😀 Tibet plays a crucial role in China's energy plans due to its significant hydroelectric potential, essential for the country's growing power demands driven by AI and data centers.
- 😀 The Chinese government's focus on building strategic infrastructure in Tibet is seen not only as a military move but also as part of the larger plan to ensure energy security in the face of rapid technological growth.
- 😀 China's infrastructure developments also aim to increase its control over the headwaters of major rivers like the Brahmaputra, Mekong, and Salwin, which flow into downstream countries like India and Bangladesh.
- 😀 With a growing military presence and infrastructure in Tibet, China is sending a message of deterrence, ensuring that India cannot act opportunistically along the border while China focuses on the eastern theater, especially Taiwan.
- 😀 The military build-up along the Himalayas creates a paradox: what China views as a defensive strategy to prevent Indian aggression, India perceives as a growing encroachment on its territory.
- 😀 The technological gap between China and India, especially in air power, is a critical factor. China's development of fifth and sixth-generation fighter jets puts it at a significant advantage over India's current fourth-generation capabilities.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of China's infrastructure projects in Tibet?
-China's infrastructure projects in Tibet focus on enhancing dual-use facilities, improving military mobility, and strengthening energy capabilities, particularly through the construction of roads, railways, airports, and dams. These projects aim to secure China's geopolitical position and bolster its energy output, particularly hydro power.
How does China’s infrastructure in Tibet affect the region's military dynamics?
-China's infrastructure in Tibet facilitates rapid military movements by upgrading highways, airports, and constructing new railways, transforming the region into a strategic military hub. Airports and facilities along the border are being expanded for dual-use, which increases China's ability to deploy military forces quickly.
What is the significance of the Medog Dam project in Tibet?
-The Medog Dam is one of China's largest infrastructure projects, located on the Yarlung Tsangpo River in Tibet. It is designed to generate 60 gigawatts of electricity, making it a crucial element in China's energy strategy. The dam also gives China control over water flow in the region, which could be used as leverage in geopolitical negotiations with downstream nations like India and Bangladesh.
What is the strategic importance of Tibet’s rivers for China?
-Tibet's rivers are vital for China's hydroelectric power production and energy strategy. They provide a renewable and powerful source of electricity, which is essential for fueling China's rapidly growing tech and AI sectors. Additionally, China controls the headwaters of major rivers like the Brahmaputra, which could potentially be used as a geopolitical tool to influence downstream countries.
What role does uranium play in China's geopolitical and economic strategy?
-Uranium is a key resource for China, especially as the demand for nuclear energy grows worldwide. China’s control over uranium deposits in regions like Tibet and partnerships with companies like F3 Uranium are part of its broader energy strategy to secure resources necessary for nuclear power generation, which is essential for both economic development and energy security.
How does the expansion of airports in Tibet impact China’s military readiness?
-The expansion of airports like Shigatse Heping into dual-use facilities enhances China's ability to project military power. These airports are being equipped with advanced military infrastructure such as longer runways, missile systems, and fighter jets, making them capable of sustaining high-altitude air operations along the India-China border.
What is the role of railways in China’s strategy in Tibet?
-Railways in Tibet, such as the Sichuan-Tibet line, are being constructed to enhance the rapid movement of troops, equipment, and ammunition across the region. Once completed, this railway will significantly reduce travel time between key locations, allowing China to maintain military and logistical superiority along its contested borders.
How does China’s dual-use infrastructure strategy affect India’s perception of its actions?
-India perceives China's dual-use infrastructure in Tibet as a strategic encroachment rather than a defensive measure. China’s development of military-capable roads, airports, and dams near contested borders heightens India’s concerns over territorial security, particularly in regions like Arunachal Pradesh and the Kashmir area.
Why is the construction of dual-use infrastructure in Tibet seen as a deterrent by China?
-China’s dual-use infrastructure is seen as a deterrent because it is designed to prevent India from taking advantage of perceived vulnerabilities along the Himalayan border. By enhancing logistics and fortifying military positions, China aims to dissuade India from acting opportunistically, especially in light of potential conflicts elsewhere, such as in Taiwan.
How does the energy demand related to AI influence China's infrastructure projects in Tibet?
-The global surge in AI-related energy demand is driving China to expand its energy capacity, particularly through hydroelectric projects in Tibet. As AI requires massive data centers that consume vast amounts of electricity, China's infrastructure developments in Tibet are intended to ensure a stable and scalable energy supply to support its growing tech and AI sectors.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
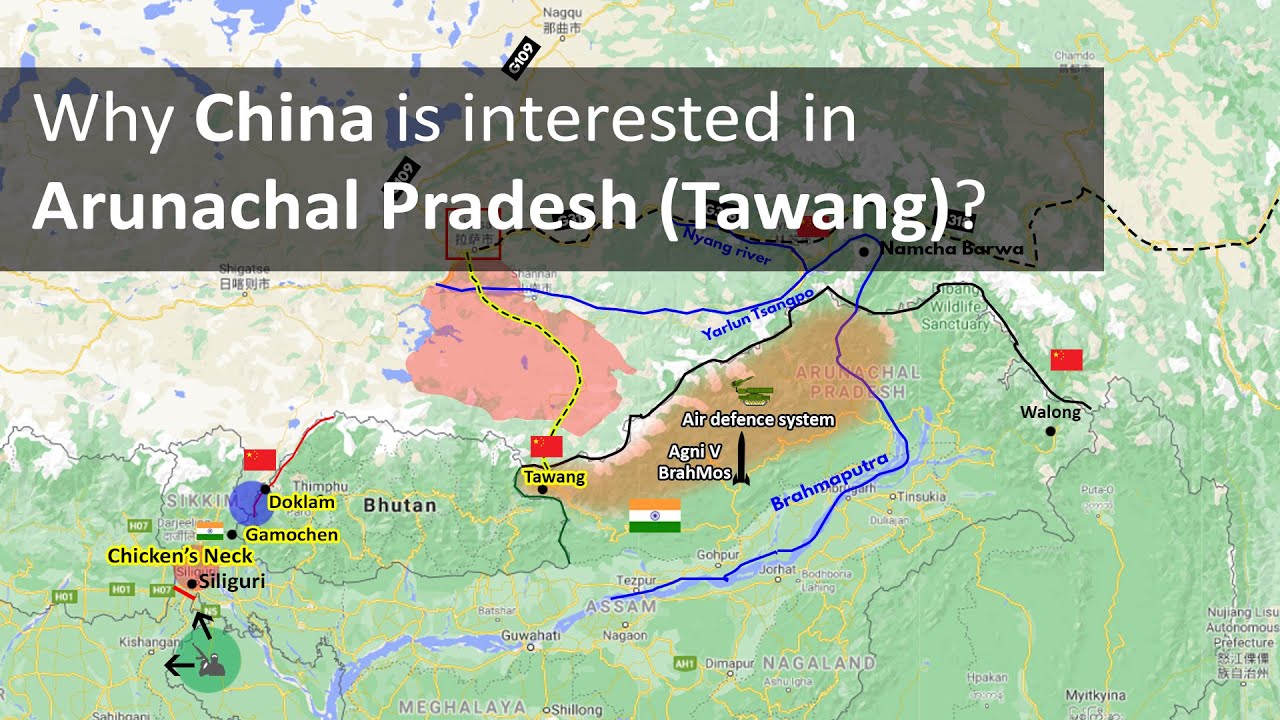
Why China is interested in Arunachal Pradesh (Tawang) | India China border conflict / Tawang clash

China's Rush Into Africa, Explained.

A Day in the Life - Civil Engineer

How China Is Quietly Bracing for Conflict With India | WSJ Coordinates

PENGANTAR GEOGRAFI PARIWISATA - Materi 1 Kuliah Online GeoPar - Sekolah Tinggi Pariwisata Ambarrukmo

Perkembangan Jasa Industri Konstruksi di Indonesia
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
