BLOK 18 KP 2.4
Summary
TLDRThis transcript covers a comprehensive dental trauma and fracture management lecture, detailing types of injuries commonly caused by accidents and sports. The focus is on diagnosing and treating dental fractures, from crown to root fractures, as well as managing avulsed teeth through replantation. Various fixation techniques, including wire binding and intermaxillary fixation, are explored, along with tools used in the process. Post-treatment care, such as monitoring tooth vitality and occlusion, is emphasized. The lecture highlights the importance of early intervention, proper treatment, and ongoing care in ensuring successful outcomes for dental trauma patients.
Takeaways
- 😀 Fractures and trauma to the teeth and jaw are common in sports accidents, falls, and fights, especially in children and athletes.
- 😀 Soccer injuries are often associated with fractures to the teeth, jaw, and face, requiring specific trauma care.
- 😀 Immediate intervention is critical for avulsed teeth, with replantation recommended within 8 hours to maximize the chances of tooth vitality.
- 😀 Handling an avulsed tooth carefully is crucial; always hold the crown, never the root, to preserve the tooth's vitality.
- 😀 Replantation involves cleaning the tooth and socket, irrigating with saline or NaCl, and using fixation devices like wires to stabilize the tooth.
- 😀 In cases of crown fractures, the tooth's edges should be smoothed and conservation treatments like crowns should be considered.
- 😀 Root fractures should be evaluated based on their location; if the fracture is more than one-third of the root, extraction is usually the best option.
- 😀 Root canal treatment may be necessary if the pulp is affected, and apicotomy may be performed alongside root canal therapy.
- 😀 Various fixation methods, such as wire binding and intermaxillary fixation (IMF), are used to secure displaced teeth and restore occlusion.
- 😀 Regular follow-ups, including clinical and radiographic evaluations, are essential to monitor the success of treatments and the vitality of the teeth after replantation or fracture management.
Q & A
What are the common causes of dental trauma and fractures mentioned in the transcript?
-The common causes of dental trauma and fractures include sports accidents, falls, and other external factors such as fights or pushing between children.
What is the recommended treatment for a crown fracture that does not involve the pulp?
-For a crown fracture without pulp involvement, the recommended treatment is to smooth the edges of the fractured tooth, carry out conservation treatment, and then make a crown.
What should be done if a tooth root fracture is slightly below the cervical margin?
-If the tooth root fracture is slightly below the cervical margin, it can be restored. However, if the fracture extends to about one-third of the root, it is best to extract the tooth.
What is the process for replanting an avulsed tooth, and what is the maximum time frame for this procedure?
-The process for replanting an avulsed tooth involves soaking the tooth in saline or milk, cleaning the socket, and performing curettage. Replantation should ideally happen within 48 hours, with 8 hours being the best window for preserving tooth vitality.
How should the avulsed tooth be handled to prevent damage to its vitality?
-The avulsed tooth should be handled by the crown, not the root, as touching the root could damage the tooth's vitality.
What type of fixation is used to stabilize a replanted tooth?
-A fixation device, often using wires, is used to stabilize a replanted tooth. The wire may be tied between two or more teeth to maintain the position of the replanted tooth.
What are the key factors to evaluate during the first week after replantation of a tooth?
-During the first week after replantation, key evaluations include checking the location of the wire, the occlusion (bite), and whether any sharp wire edges need to be bent to avoid discomfort.
What is the purpose of radiographic examinations after dental trauma, and when should they be conducted?
-Radiographic examinations are conducted to assess any pathological conditions in the teeth that have been bonded or fixed with wire. They should be done after six weeks, alongside clinical evaluations.
What is the recommended method for cleaning a replantable avulsed tooth before replantation?
-The recommended method for cleaning a replantable avulsed tooth involves gently cleaning it with gauze or cotton, removing any dirt, and then soaking the tooth in saline or milk to preserve its vitality.
What is the significance of using an asbar tool in dental trauma cases, particularly with fractures?
-The asbar tool is used in dental trauma cases, especially for fractures, to reposition the teeth and ensure proper occlusion. It helps stabilize the fractured teeth by tying them together using wire, forming an intermaxillary fixation.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Cinemática do Trauma

XABCDE no trauma: APRENDA NA PRÁTICA!

Klasifikasi, penyebab, dan Penanganan pada Cedera Olahraga

General Trauma ,Management of Polytrauma Patients - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim

Initial assessment correct method
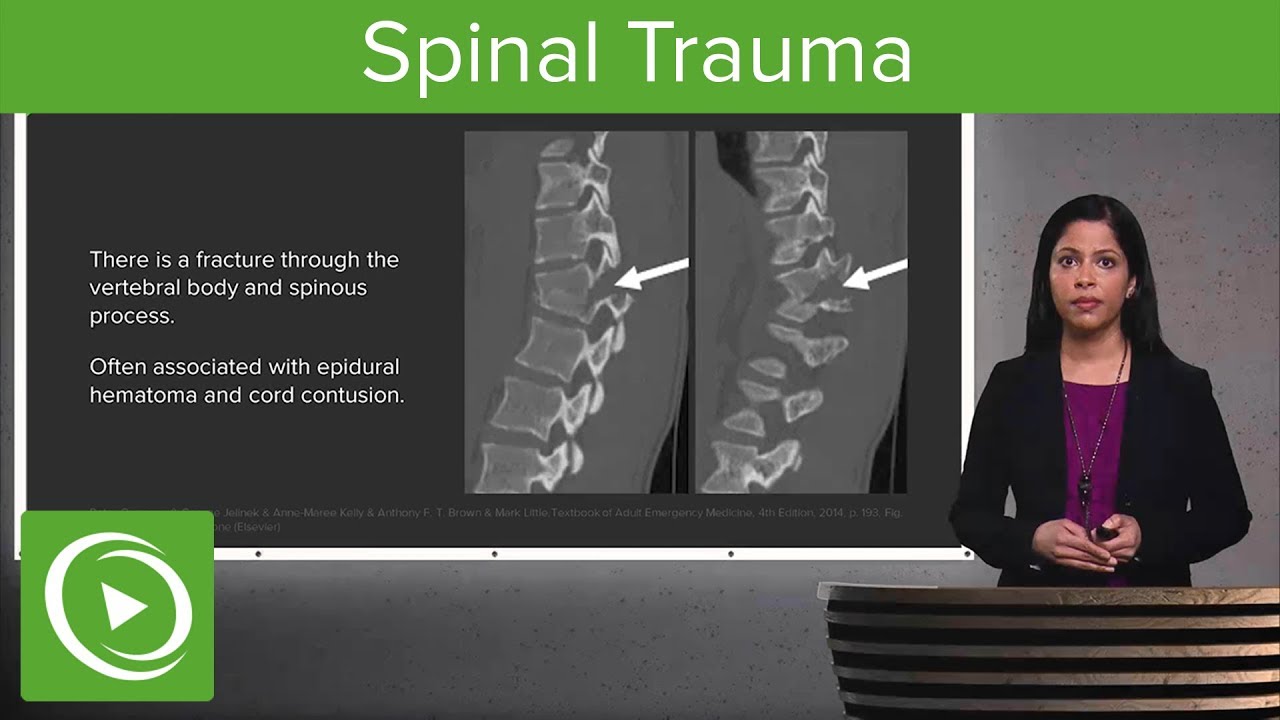
Spinal Trauma: Cervical Trauma Protocol, Common Spinal Fractures – Radiology | Lecturio
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
