Three Phase Inverters, Six-step PWM
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces the concept of three-phase inverters and discusses the six-step control technique commonly used in applications like variable frequency drives and photovoltaic inverters. The focus is on the basic operation of three-phase inverters, the configuration of the transistors, and their switching actions. The script explains how the six-step inverter works with BLDC motors, highlighting the switching states, voltage characteristics, and current flow. Additionally, the importance of minimizing switching losses and managing harmonics in the system is emphasized, alongside an overview of related PWM techniques and their applications.
Takeaways
- 😀 Three-phase inverters are widely used in industrial applications such as variable frequency drives, photovoltaic inverters, and motor drive systems.
- 😀 A three-phase inverter is typically made using six transistors, which are arranged in three legs, each consisting of two transistors with anti-parallel diodes.
- 😀 The primary function of a three-phase inverter is to convert DC voltage to AC and supply it to loads like motors or the electrical grid.
- 😀 Six-step PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) is a basic control technique for three-phase inverters, commonly used in BLDC motor drives and other applications.
- 😀 In a six-step inverter, the switching occurs at a fundamental frequency with each switching state lasting 60 degrees, creating a step-like waveform.
- 😀 The switching losses in a six-step inverter can be minimized by using slower switching transistors, resulting in cost savings by using cheaper MOSFETs.
- 😀 A six-step inverter produces a square wave with a three-level voltage source, with line-to-line voltages taking values like Vdc, -Vdc, and zero, depending on the switching state.
- 😀 The six-step technique uses a sequence of six different switching states, corresponding to six rotor positions, creating a rotating magnetic field in the motor.
- 😀 In the six-step inverter, each switching action changes only one transistor, keeping the system efficient by minimizing unnecessary switching and reducing losses.
- 😀 A key feature of the six-step inverter is the elimination of third-order harmonics from the output voltage, which improves performance compared to a standard square wave inverter.
Q & A
What are three-phase inverters commonly used for?
-Three-phase inverters are commonly used in industrial applications such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) to drive three-phase electrical machines. They are also used in photovoltaic inverters, wind turbines, and back-to-back converters.
What is the main difference between a single-phase and three-phase inverter circuit?
-In a single-phase inverter, you have one leg or half-bridge with two transistors. In a three-phase inverter, there are three legs, each containing two transistors. This configuration allows for three-phase output to drive motors or connect to the grid.
What is the significance of anti-parallel diodes in a three-phase inverter?
-Anti-parallel diodes are crucial in three-phase inverters, particularly for inductive loads. When the transistors are turned off, these diodes provide a path for the current to flow, ensuring the circuit remains functional without causing damage to the components.
What is a six-step PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) technique, and where is it typically used?
-The six-step PWM technique is commonly used in BLDC (Brushless DC) motor drives. It is characterized by six different switching states, which correspond to six rotor positions, creating a rotating magnetic field that drives the motor. It is simple and efficient, typically used in applications like drones, small electronics, and robotics.
How does the six-step PWM reduce switching losses in an inverter?
-The six-step PWM reduces switching losses by switching less frequently. Instead of switching at very high frequencies (e.g., kilohertz), it switches at the fundamental frequency, which means fewer transitions and less energy lost during switching.
What are the primary advantages and disadvantages of the six-step inverter technique?
-The main advantage of the six-step inverter is its simplicity and reduced switching losses, making it cost-effective for applications with lower-speed motors. The disadvantage is that it produces a square waveform, leading to higher harmonic content and less smooth operation compared to other PWM techniques like sinusoidal PWM.
How do the phase voltages behave in a six-step inverter configuration?
-In a six-step inverter, the phase voltages are not constant. The voltage steps alternate between positive and negative values, with each phase stepping through three voltage levels (Vdc/3, 2Vdc/3, and -Vdc/3) during the switching process, resulting in a square wave for the line-to-line voltage.
What is the role of the neutral point in a six-step inverter system?
-The neutral point in a six-step inverter is typically floating and not connected back to the DC source. It plays a role in the calculation of phase voltages and in ensuring the motor phases are properly aligned with the DC link during operation.
What is the importance of the motor's rotor position in a six-step inverter system?
-The rotor position is critical in a six-step inverter system, as the switching sequence depends on the rotor's position to create a rotating magnetic field. This alignment ensures efficient motor control, especially in applications like BLDC motors, where precise positioning is needed for smooth operation.
How are harmonics managed in a six-step inverter?
-In a six-step inverter, the third harmonic is eliminated because the waveform is a square wave. The fundamental component is lower than in a pure square wave, and the harmonics are distributed in odd multiples (5th, 7th, 11th, etc.). This results in a reduction of unwanted harmonics but still leads to higher harmonic distortion compared to more sophisticated PWM techniques.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

What Is A VFD? (Variable Frequency Drive) HVAC VFD BASICS

SPWM (Sinusoidal PWM) Three Phase Inverters

Kuliah Elektronika Daya Pokok Bahasan Rangkaian Inverter

Inversor de Frequências _ Aula 1_ Conceitos Básicos

Module: Power Converter I BEE I 1Ph VSI (Half Bridge)
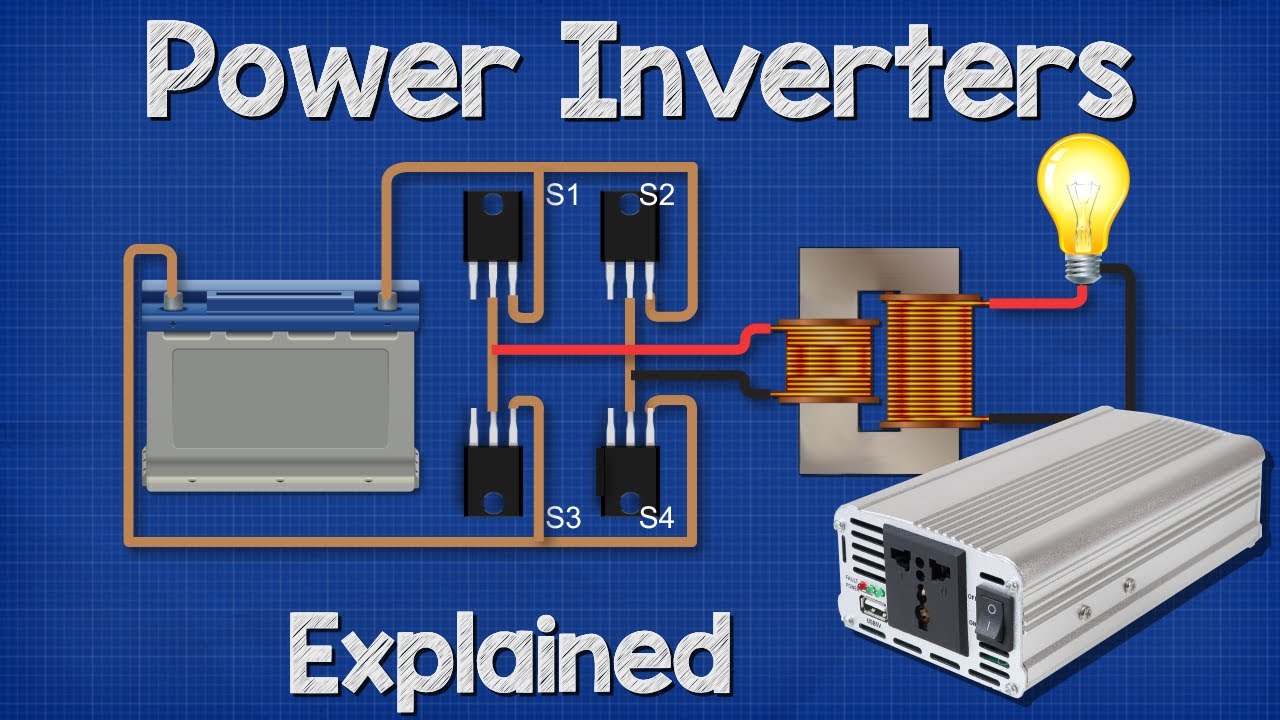
Power Inverters Explained - How do they work working principle IGBT
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
