Inversor de Frequências _ Aula 1_ Conceitos Básicos
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the function and operation of frequency inverters (VFDs) in controlling the speed and torque of three-phase induction motors. It covers the conversion of AC to DC, smoothing the DC signal, and then converting it back to AC using IGBTs controlled by Pulse Width Modulation (PWM). The script breaks down how varying the frequency adjusts the motor’s speed and emphasizes the internal components of the inverter, like the rectifier bridge and filters. Ideal for professionals and trainees in the electrical field, this lesson offers a foundational understanding of motor control systems and the principles behind frequency inverters.
Takeaways
- 😀 Frequency inverters, or variable frequency drives (VFDs), control the speed and torque of induction motors by adjusting their frequency.
- 😀 The motor's RPM (rotations per minute) is determined by the formula: RPM = (Frequency × 120) ÷ Number of Poles.
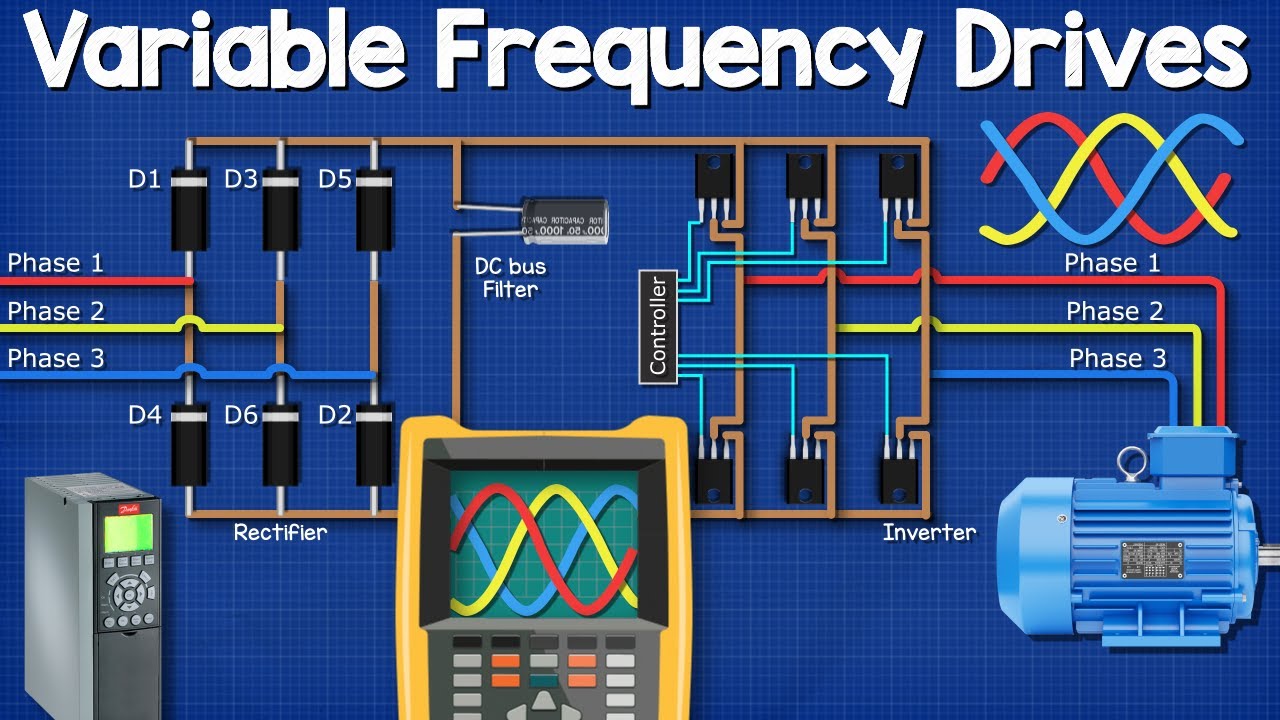
- 😀 The inverter receives a three-phase AC input and converts it into a pulsating DC signal using a bridge rectifier made up of diodes.
- 😀 After rectification, the DC signal is filtered to remove ripples, creating a smoother DC signal for the inverter to work with.
- 😀 The inverter then converts the DC signal back into AC using IGBTs (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors), creating a square wave output.
- 😀 The frequency of the AC signal can be controlled by adjusting the pulse width in a technique called Pulse Width Modulation (PWM).
- 😀 By altering the width of the pulse in PWM, the inverter can change the frequency and therefore the motor speed and torque.
- 😀 The number of poles and the constant 120 in the RPM formula cannot be changed, so the only adjustable factor for speed control is the frequency.
- 😀 Inverters are capable of controlling both the speed and torque of motors, which is essential in many industrial applications.
- 😀 The key takeaway is that inverters convert AC to DC, smooth the DC, and then invert it back to a modified AC signal to control motor speed and torque.
Q & A
What is the primary function of a frequency inverter?
-A frequency inverter primarily controls the speed and torque of an induction motor by adjusting the frequency of the electrical power supplied to it.
How is motor speed calculated using a frequency inverter?
-Motor speed (RPM) is calculated using the formula: RPM = (120 * Frequency) / Number of Poles. By altering the frequency, the inverter changes the motor's speed.
What is the relationship between frequency and motor speed?
-The motor's speed is directly proportional to the input frequency. Increasing the frequency increases the motor's speed, and decreasing the frequency reduces the speed.
What is a frequency inverter also known as?
-A frequency inverter is also known as a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD).
What happens when an AC power supply is fed into a frequency inverter?
-When an AC power supply is fed into a frequency inverter, it first passes through a **rectifier**, which converts the AC to pulsating DC. The inverter then smooths the DC signal and converts it back to controlled AC at the desired frequency using IGBTs.
What role do IGBTs play in a frequency inverter?
-IGBTs (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors) are used to switch the DC voltage back into AC with variable frequency. They act as electronic switches, enabling precise control over the output frequency.
What is the purpose of the DC filter inside a frequency inverter?
-The DC filter inside a frequency inverter smooths out the pulsating DC signal, removing ripple and improving the quality of the DC voltage, which is crucial for stable motor operation.
How does Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) work in a frequency inverter?
-PWM controls the output frequency by adjusting the width of the pulses sent to the motor. This modulation of pulse width determines the motor's speed and allows for fine control over its operation.
What happens when the frequency is lowered in a motor controlled by an inverter?
-When the frequency is lowered, the motor's speed decreases. At very low frequencies, the motor can run at much slower speeds or even stop, depending on the inverter settings.
Can the number of poles of the motor affect its speed calculation?
-Yes, the number of poles in the motor affects the speed calculation. The number of poles is used in the formula to calculate RPM, and different motors with different pole numbers will have different speed ranges at the same frequency.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Variable Frequency Drives Explained - VFD Basics IGBT inverter
Single Phase Induction Motor (Capacitor Induction Motor or AC Motor) explained

Single phase Induction Motor / Capacitor start capacitor run motor / Capacitor start induction motor

Motor Basics

Three Phase Inverters, Six-step PWM

What Is A VFD? (Variable Frequency Drive) HVAC VFD BASICS
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)