Kuliah Elektronika Daya Pokok Bahasan Rangkaian Inverter
Summary
TLDRThis video script provides an in-depth exploration of DC to AC inverters, explaining their function, components, and applications in modern power systems. The presenter discusses various inverter types, including single-phase and three-phase systems, and their use in industries like motor control, solar power, and UPS backup. Key concepts such as waveform quality, including square and sinusoidal waveforms, are highlighted for ensuring efficient operation. Practical applications in homes, offices, hospitals, and factories are also covered, emphasizing the importance of inverters in powering critical equipment and maintaining reliable electricity supply.
Takeaways
- 😀 Inverters are electronic circuits that convert DC to AC electricity, essential in various applications where AC power is needed but only DC power is available.
- 😀 The primary function of an inverter is to change DC electricity (from sources like batteries, solar panels, or wind turbines) into AC power for household, industrial, and other equipment.
- 😀 Inverters can be used for both single-phase and three-phase power conversion, with controls that adjust the output voltage and frequency.
- 😀 Inverters are crucial in areas without a direct AC power source, such as rural areas, remote locations, or in vehicles, where DC power is the only option available.
- 😀 A popular application of inverters is in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), which provide backup AC power during grid outages, using a DC source like batteries.
- 😀 Inverters are available in different capacities, ranging from small units for home use to large industrial systems for critical equipment like motors and servers.
- 😀 There are three main types of waveforms for inverter output: square wave, modified sine wave, and pure sine wave, with sine waves being preferred for sensitive equipment.
- 😀 To ensure efficient operation and prevent damage to electrical equipment, inverters often incorporate pulse-width modulation (PWM) to smooth the waveform and reduce harmonic distortion.
- 😀 Inverters can be designed for specific industrial uses like variable speed drives (VSD), which control motor speeds by adjusting the frequency of the AC output.
- 😀 Examples of inverter applications include solar power systems, variable speed drives for compressors, air conditioning systems, and emergency lighting systems, where reliable and controlled AC power is critical.
Q & A
What is the main function of an inverter in electronics?
-An inverter is a power electronics circuit that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC).
What types of circuits are commonly used for power conversion?
-The four main types of power conversion circuits are: AC to DC (converter), DC to DC (chopper), AC to AC (AC regulator), and DC to AC (inverter).
What are the typical applications of inverters in daily life?
-Inverters are used in various applications such as in homes, offices, and industries to convert DC power from sources like batteries or solar cells into AC power, which is needed to operate many electrical devices like refrigerators, air conditioners, and lighting.
What are some common sources of DC power for inverters?
-Common sources of DC power for inverters include batteries, solar cells (PLTS), wind power generators, and AC power that has been rectified.
How does an inverter contribute to the functioning of a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply)?
-In a UPS, when the main power source (grid) fails, the battery inside the UPS provides DC power, which the inverter then converts into AC power to keep critical equipment running.
Why is it necessary to convert DC to AC in industrial applications?
-Many industrial devices, including motors and other electrical equipment, require AC power to operate, even though DC power might be available from sources like batteries or solar panels.
What is the difference between a single-phase and a three-phase inverter?
-A single-phase inverter converts DC power into a single-phase AC output, whereas a three-phase inverter produces a three-phase AC output, which is typically used for more power-intensive industrial applications and provides smoother power delivery.
What types of waveforms can be produced by an inverter, and why does it matter?
-Inverters can produce several types of waveforms, including square wave, modified sine wave, and pure sine wave. The quality of the waveform is crucial because poor waveforms (like square waves) can damage sensitive equipment like motors due to heat generation, while pure sine waves are ideal for minimizing such risks.
What role does Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) play in improving inverter output?
-PWM is used in inverters to modulate the width of pulses in the output signal, effectively transforming a square waveform into a more sinusoidal shape. This improves the quality of the AC output, reducing harmonic distortion and preventing damage to connected equipment.
How does an inverter contribute to energy efficiency in variable speed drives (VSD)?
-In variable speed drives (VSD), an inverter controls the frequency and speed of the AC motor, allowing for more efficient operation by adjusting the motor speed to match the load. This can save energy, especially in applications like escalators and air conditioning compressors where speed regulation is crucial.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Types of Power Electronic Circuits | Power Electronics | Lecture 4
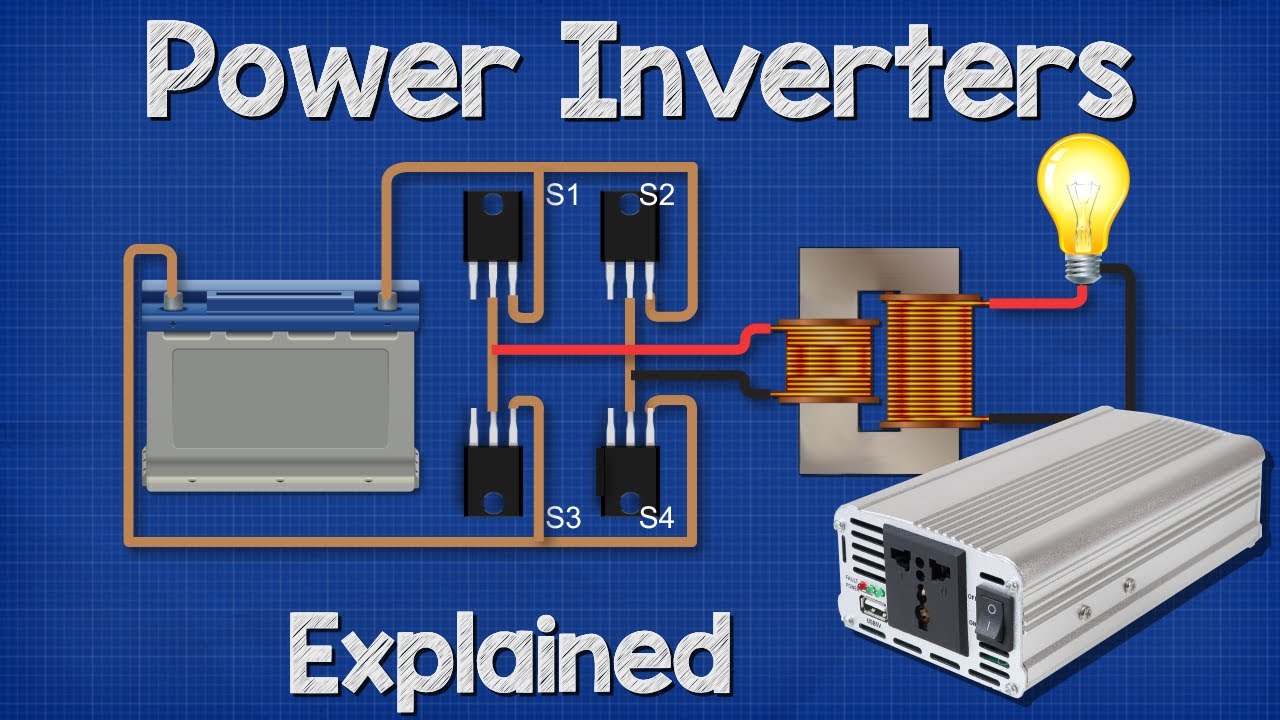
Power Inverters Explained - How do they work working principle IGBT
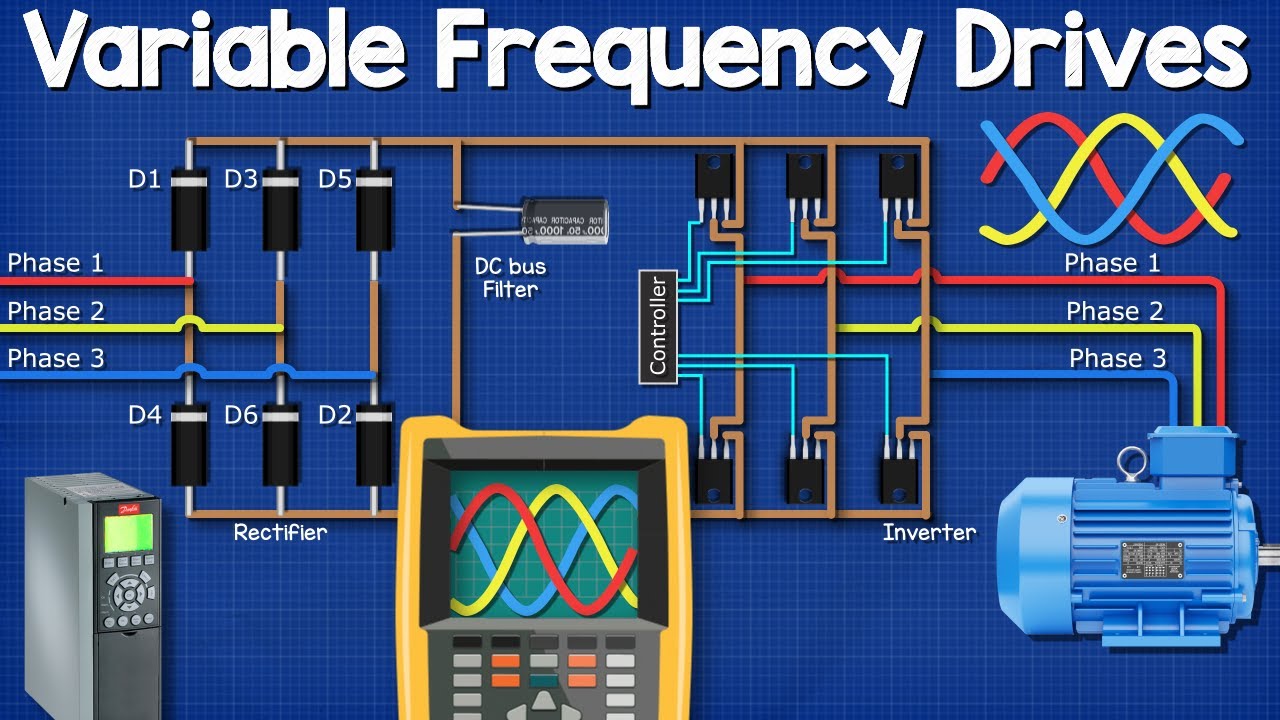
Variable Frequency Drives Explained - VFD Basics IGBT inverter

AC and DC Electricity basics

Silicon Controlled Rectifier

Inversor de Frequências _ Aula 1_ Conceitos Básicos
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)