Sino talagang makikinabang sa rice price cap ni BBM?
Summary
TLDRThe video discusses the removal of an undersecretary from the Department of Finance after posting a graph illustrating the effects of price ceilings on supply and demand. The speaker explains how price caps can lead to unintended consequences like shortages, hoarding, and a black market, emphasizing that these policies harm low-income consumers and farmers. The post sparked controversy and led to the speaker’s dismissal, though they argue that transparency and standing by economic principles are crucial. They reflect on their experience in government and the lack of consultation on such impactful decisions.
Takeaways
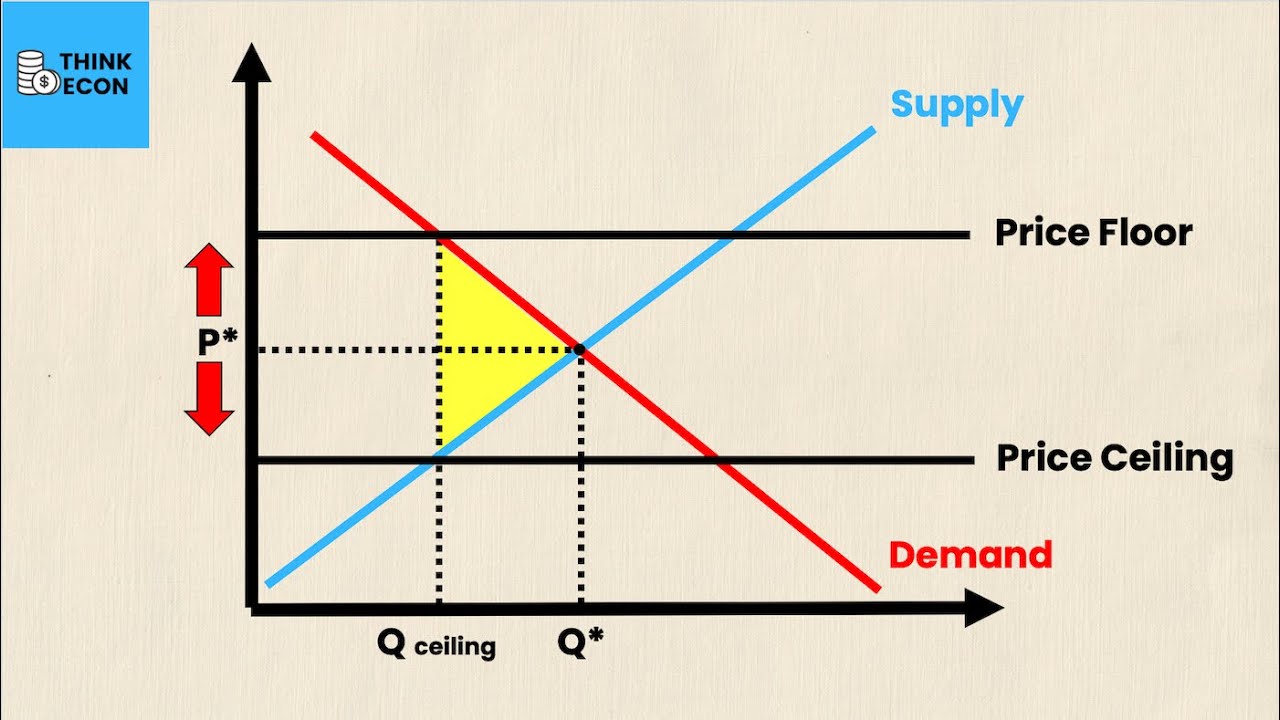
- 📊 The speaker posted a graph about the law of supply and demand to show the effects of a price ceiling or price cap.
- 😲 The graph's purpose was to highlight human behavior, explaining how middle-class consumers would buy more when prices are capped.
- 📉 A price cap leads to increased demand but a reduced supply, resulting in a shortage, where wealthier consumers have better access to goods like rice.
- 💰 Small retailers suffer under price caps, as they may need to sell at a loss or hoard products to avoid further financial damage.
- ⚠️ Price caps can lead to unintended consequences, such as the emergence of a black market where rice is sold at higher prices.
- 💼 Farmers may face reduced earnings as buyers offer lower prices for their crops due to the imposed price caps.
- 🚫 The government did not consult its economic managers before imposing the price cap, leaving many surprised and without input.
- 👎 The policy, while aimed at reducing rice prices, fails to solve the shortage issue and exacerbates problems in the market.
- 🔍 The speaker previously faced issues due to political posts and knew posting the graph could lead to repercussions, but did it to raise awareness.
- 🔒 Despite the negative impact of price caps, the government’s decision appears to be driven by short-term solutions without considering long-term effects.
Q & A
Why did the speaker post a graph of supply and demand?
-The speaker posted the graph to explain the effects of price ceilings, especially on the supply and demand of rice, showing how human behavior interacts with economic policies like price controls.
What does the speaker suggest happens to demand when a price cap is introduced?
-The speaker suggests that a price cap increases demand, as middle-class consumers tend to buy more since they can afford it. Meanwhile, lower-income consumers may buy only what they need for the day, leading to increased demand overall.
How does a price cap affect suppliers, according to the speaker?
-Suppliers, especially those with large storage capabilities, may hoard their products instead of selling at a loss under the price cap, waiting for the cap to be lifted. Smaller sellers may struggle to break even, leading to decreased supply.
What is the term used to describe the gap between supply and demand when a price cap is imposed?
-The speaker refers to this gap as a 'shortage,' where demand exceeds supply due to the price cap, leading to reduced availability of goods.
Who benefits from the price cap, according to the speaker?
-According to the speaker, the middle-class consumers who can afford to buy in bulk and those who operate in the black market benefit from the price cap. However, it does not benefit lower-income consumers, small sellers, or farmers.
How does the speaker explain the potential rise of a black market for rice?
-As the supply of rice diminishes due to the price cap, a black market may emerge where people are willing to pay more than the capped price to obtain rice. Those selling on the black market can benefit from higher prices.
What unintended consequences might result from the price cap, as mentioned by the speaker?
-Unintended consequences include reduced supply, lower-quality rice due to adulteration (mixing with cheaper varieties), and the rise of a black market where rice is sold at a higher price.
Why was the timing of the price cap implementation considered problematic by the speaker?
-The timing was problematic because it coincided with the harvest season for rice. The speaker also mentions that the government had previously assured there was enough rice supply, making the sudden imposition of a price cap surprising.
Why did the speaker expect to be removed from their position after posting the graph?
-The speaker anticipated being removed from their position because they had previously posted critical comments about economic policies and had already been warned once in July. Despite knowing the risk, they chose to post the graph to highlight important issues.
How does the speaker feel about the lack of consultation with economic managers regarding the price cap policy?
-The speaker feels disappointed and surprised that economic managers were not consulted, especially since such a significant policy affecting millions of Filipinos was implemented without their input.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Quarter 3 - Module 10: Government Intervention in Market Prices: Price Ceiling
Price Ceiling and Price Floor | Think Econ

Penawaran, Permintaan, dan Efisiensi Pasar: Surplus Konsumen, Produsen, Deadweight Loss (Part 30)

Price Ceilings and Floors- Micro Topic 2.8

Supply, Demand, and Market Equilibrium - Mikroekonomi #EP101

Micro: Unit 1.4 -- Government Intervention: Price Controls, Quotas, and Subsidies
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
