The Plant Kingdom
Summary
TLDRThis script offers an insightful exploration into the world of plant biology, comparing animal and plant cells and highlighting the unique characteristics of plant cells such as the central vacuole, chloroplasts, and cellulose cell wall. It delves into the autotrophic nature of plants, their role as producers in ecosystems, and their importance as a food source and for various materials like fuel and medicines. The script also discusses plant evolution, from simple mosses to complex flowering plants, and the ecological process of succession, illustrating how a barren parking lot can transform into a mature forest over time. It emphasizes the adaptability and diversity of plants, concluding with an encouragement to appreciate and further explore the plant kingdom.
Takeaways
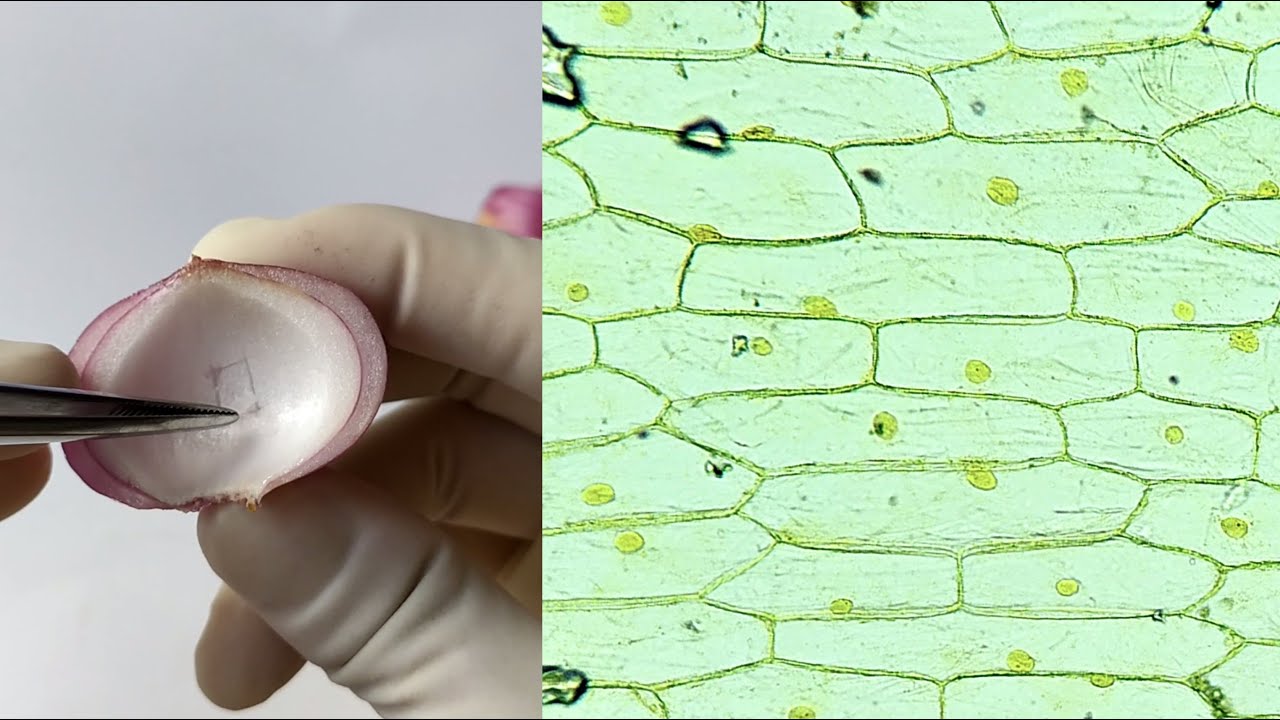
- 🌿 The video discusses the differences between animal and plant cells, highlighting the large central vacuole, chloroplasts, and cell wall made of cellulose in plant cells.
- 🌱 Plants are autotrophic, meaning they obtain energy from inorganic sources like sunlight, and are crucial as producers in terrestrial food webs.
- 🌳 Plants have evolved to maximize light exposure through mechanisms like phototropism and the development of specialized structures like tendrils.
- 🌞 Photosynthesis allows plants to convert sunlight into stored energy in the form of starch, composed of glucose units.
- 🌲 The importance of plants extends beyond food and includes uses in fuel, plastics, wood, paper, cotton, and medicines.
- 🌿 The video uses the analogy of a parking lot to explain the process of ecological succession, where a barren area gradually becomes a mature forest over time.
- 💧 Terrestrial plants face challenges like water loss, which they overcome by developing a waxy cuticle and stomata for gas exchange.
- 🌱 Mosses, as simple terrestrial plants, are among the first to colonize new areas during succession due to their reliance on water for reproduction.
- 🌳 Ferns represent a more evolved group of plants with specialized transport structures like roots, stems, and leaves, allowing them to live in less wet environments.
- 🌲 Seed-producing plants, including gymnosperms and angiosperms, have evolved to reproduce without the need for water, with the latter group making up over 90% of plant species.
- 🌼 The video emphasizes the diversity and success of angiosperms, which range from grasses to giant trees, and their role in pollination through attractive flowers and pollen.
Q & A
What is the primary difference between animal cells and plant cells?
-Plant cells have a large central vacuole, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and a cell wall composed of cellulose, which are not present in animal cells.
How do plants obtain their energy as autotrophs?
-Plants, being autotrophic, obtain their energy from inorganic sources like sunlight through the process of photosynthesis.
What is the role of tendrils in plants?
-Tendrils are specialized structures that allow plants to move up materials, such as climbing ivy, to position themselves for better sunlight exposure.
What is phototropism and how does it relate to plant growth?
-Phototropism is the phenomenon where plants orient themselves towards the source of light, often appearing as if they are moving towards the Sun, due to chemical compounds called auxins.
How do plants convert sunlight into a storable form of energy?
-Plants convert sunlight into a storable form of energy through photosynthesis, creating a carbohydrate called starch, which is composed of glucose units formed from the sun's energy.
Why are plants important in terrestrial food webs?
-Plants are important in terrestrial food webs as they are primary producers, converting inorganic energy into organic matter that serves as a food source for other organisms.
What is the process of succession and how does it relate to plant growth?
-Succession is the process by which an area that was previously devoid of vegetation gradually becomes populated by plants, evolving from simple to more complex ecosystems over time.
How do plants adapt to life on land as opposed to aquatic environments?
-To adapt to life on land, plants have developed a waxy cuticle to reduce water loss and stomata to regulate gas exchange, overcoming the challenges of water loss and gas exchange without being submerged in water.
What are the characteristics of bryophytes, the simplest terrestrial plants?
-Bryophytes, or mosses, are simple terrestrial plants that lack transport systems, roots, stems, or proper leaves but possess specialized cells for photosynthesis and are often found in damp environments.
How do the reproductive needs of ferns differ from those of bryophytes?
-Ferns, unlike bryophytes, have specialized transport structures like roots, stems, and leaves, but still require water for reproduction, unlike more evolved plants that can reproduce without water.
What are the key features of gymnosperms and angiosperms?
-Gymnosperms, like conifers, have naked seeds and are often evergreen with adaptations for drought and cold tolerance. Angiosperms, or flowering plants, have enclosed seeds and make up over 90% of the world's plant species, with a wide range of adaptations for pollination.
How do the characteristics of a plant's flowers relate to its pollination method?
-Plants that rely on wind for pollination often have less showy flowers, while those that require animal pollinators tend to have more attractive flowers with colors, scents, and nectar to attract pollinating organisms.
What is the significance of the number of cotyledons in a seed for plant classification?
-The number of cotyledons in a seed distinguishes monocots and dicots, which have one and two cotyledons respectively, and influences the developmental patterns of stems, leaves, root systems, and flower structures.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Plant Cell vs Animal Cell | 3 Key Differences

CÉLULA ANIMAL E CÉLULA VEGETAL - DIFERENÇAS | Biologia com Samuel Cunha

生命科學(一) Ch7-2 A Tour of the Cell

Types of Cells | Don't Memorise
Onion Epidermal Cell Peel Slide Preparation Practical Experiment

Overview of animal and plant cells | Biology | Khan Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
