Lab Safety 3 Hazardous Waste
Summary
TLDRThe video script emphasizes the importance of laboratory safety, particularly avoiding contact with hazardous chemicals. It highlights the use of fume hoods to manage volatile chemicals and prevent inhalation. The script also discusses proper waste disposal, stressing the need to collect hazardous waste—both liquid and solid—using designated containers. It concludes with a reminder to always follow instructor guidance on waste disposal to minimize environmental impact.
Takeaways
- 🧪 Safety in the laboratory is crucial to avoid contact with hazardous chemicals.
- 👃 Breathing in volatile chemicals is a significant hazard, and fume hoods are used to mitigate this risk.
- 🌪️ Fume hoods maintain negative pressure to draw in air and prevent hazardous gases from escaping into the room.
- 🔬 When working with volatile chemicals, always follow your instructor's guidance on using fume hoods.
- 🧼 Treat the fume hood space with the same respect for cleanliness as you would a lab bench.
- 💨 Closing the fume hood sash is important to conserve energy and prevent unnecessary air loss.
- 🚮 Proper waste disposal is essential; never throw hazardous waste in the garbage or down the sink without instruction.
- 🗑️ Solid waste should be placed in designated containers provided by the instructor.
- 💧 Liquid waste requires careful handling, using containers with locking lids to prevent leaks and spills.
- 🛡️ The instructor will provide guidance on the proper disposal of different types of waste to protect the environment.
Q & A
What is the primary goal of safety in the laboratory?
-The primary goal of safety in the laboratory is to avoid contact of hazardous chemicals with one's skin, eyes, or ingestion, and to prevent their release into the environment.
How can breathing in hazardous chemicals be harmful?
-Breathing in hazardous chemicals can be harmful as it can lead to health issues due to the inhalation of volatile and toxic substances.
What are fume hoods and what is their purpose?
-Fume hoods are safety cabinets designed to protect users from hazardous gases by drawing in air from outside, circulating it, and then exhausting it outside, preventing the release of harmful gases into the laboratory environment.
What is the sash in a fume hood and how does it function?
-The sash is the window in a fume hood that can be opened or closed. It is designed to maintain a negative pressure inside the hood, ensuring that air and hazardous gases are drawn in and expelled outside.
Why is it important to keep the fume hood sash closed when not in use?
-Keeping the fume hood sash closed when not in use is important to maintain the negative pressure inside the hood and to prevent unnecessary air and heat loss from the laboratory, which can be costly, especially in winter.
How should one prepare and clean a fume hood before and after use?
-One should treat the space in a fume hood similarly to a common lab bench, ensuring it is clean before starting work and cleaned thoroughly after use.
What are the two main types of chemical waste that need to be managed in a laboratory?
-The two main types of chemical waste that need to be managed are liquid and solid hazardous waste.
How should solid waste be disposed of in a laboratory setting?
-Solid waste should be placed in a designated container, similar to a large mason jar, provided by the instructor for the collection of solid hazardous waste.
What is the procedure for handling liquid waste in a fume hood?
-Liquid waste should be poured into a container with a locking lid within the fume hood, ensuring the lid is open and locked while pouring, and then closed securely after use.
Who is responsible for collecting and handling hazardous waste in the laboratory?
-Hazardous waste is collected by the hazardous waste staff who are responsible for its proper handling and disposal.
What is the most important rule regarding waste disposal in the laboratory as per the script?
-The most important rule is to never throw any waste in the garbage or down the sink without being instructed by the instructor that it is safe to do so.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

PENGENALAN ALAT-ALAT LABORATORIUM KIMIA DAN KEAMANAN & KESELAMATAN KERJA (K3) DI LABORATORIUM KIMIA

3D Chemical Handling Safety Animation Videos| Chemical Handling Guidelines|3D Safety Animation Video
Keselamatan Kerja di Laboratorium IPA Mata Kuliah Pendalaman Materi IPA

Bab 1 Hakikat Ilmu Sains dan Metode Ilmiah #2 (Laboratorium IPA) | IPA SMP 7 | Sekolah Penggerak

Chemical Safety in the Laboratory
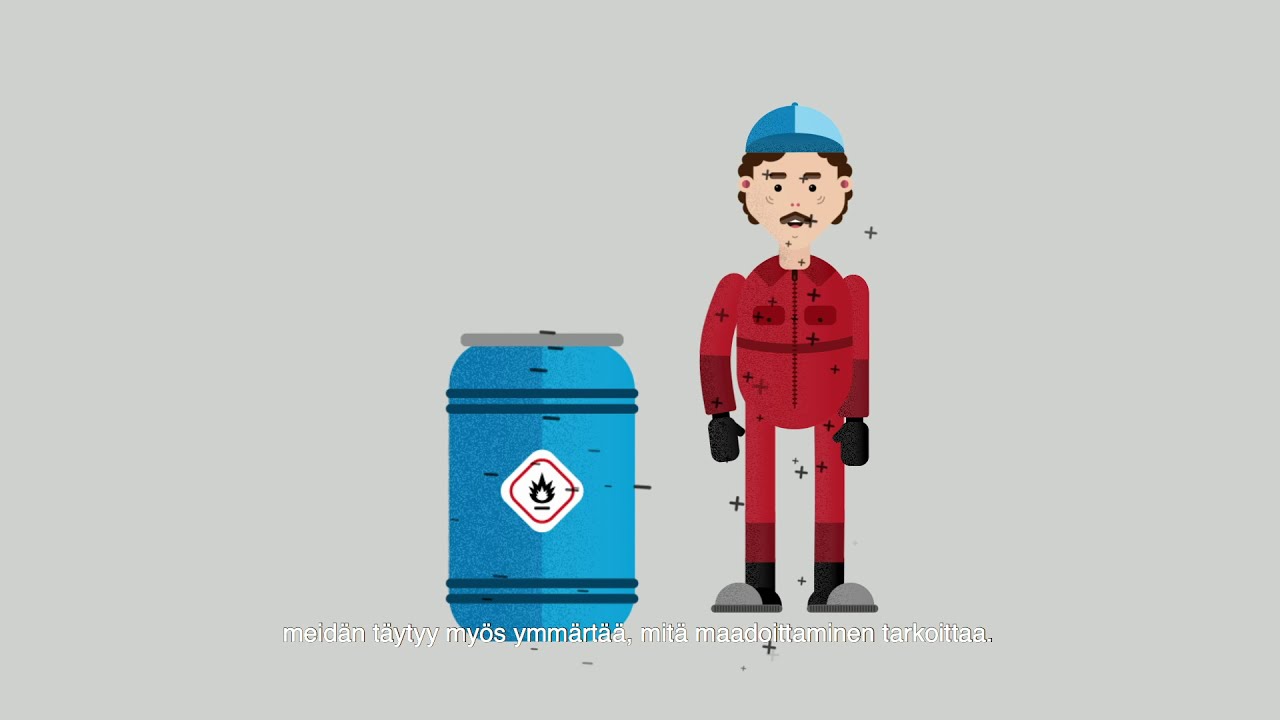

Workplace safety - Paint worker died after a solvent barrel exploded
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
