V-I Characteristics of PN Junction Diode in Hindi | TECH GURUKUL By Dinesh Arya
Summary
TLDRThe script is a technical lecture on semiconductor diodes, focusing on the PN junction and its behavior under different conditions. It discusses the intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductor properties, the role of temperature, and the impact of voltage on diode performance. The lecture includes practical demonstrations, such as measuring current and voltage characteristics, and explores the effects of reverse bias conditions. It also touches on the concepts of depletion region and leakage current, providing a comprehensive understanding of diode functionality.
Takeaways
- 💡 The video discusses the characteristics of a semiconductor diode, focusing on P-N junctions and their behavior under various conditions.
- 🔋 Forward bias in a P-N junction diode reduces the depletion layer, allowing current to flow more easily as voltage increases.
- 📉 Reverse bias creates a depletion layer that prevents current flow, with only leakage current being observed until breakdown voltage is reached.
- ⚡ Breakdown voltage is the point where a strong reverse voltage causes a large current to flow due to electron-hole pairs breaking free.
- 🔧 The video describes practical circuit diagrams for testing diodes, including the use of variable resistors and voltmeters to measure current and voltage.
- 🔬 Intrinsic semiconductors become either N-type or P-type when doped with pentavalent or trivalent impurities, respectively.
- 📊 Graphs of voltage versus current can help illustrate the characteristics of diodes in both forward and reverse bias conditions.
- 💻 The video explains how to calculate diode current using formulas involving voltage and leakage current, particularly under reverse bias.
- 🌡️ Temperature has an effect on diode behavior, influencing the voltage-current relationship and the point at which breakdown occurs.
- 🧑🏫 The video invites viewers to ask questions and provide suggestions in the comment section, indicating an educational intent.
Q & A
What is a PN junction diode?
-A PN junction diode is a semiconductor device formed by joining P-type and N-type semiconductors together. It allows current to flow predominantly in one direction and is the fundamental building block of many electronic components.
What is the function of an intrinsic semiconductor?
-An intrinsic semiconductor is a pure semiconductor material, undoped, that exhibits electrical conductivity due to its own electrons and holes. It's used in devices like diodes to control the flow of current.
What is meant by the term 'drift current' in the context of semiconductors?
-Drift current refers to the flow of charge carriers (electrons and holes) within a semiconductor material due to an applied electric field, which is a key component in the operation of diodes and transistors.
What is the significance of the term 'depletion region' in a PN junction?
-The depletion region is the area in a PN junction where the majority of charge carriers are depleted due to the movement of electrons and holes across the junction. It acts as a barrier to further current flow and is crucial for the diode's rectifying properties.
How does the forward bias affect the current in a diode?
-Forward biasing a diode reduces the potential barrier at the PN junction, allowing more charge carriers to cross the junction and thus increasing the current flow through the diode.
What is the role of the reverse bias in a diode?
-Reverse biasing a diode increases the potential barrier at the PN junction, which opposes the flow of current. This makes the diode less conductive and is used to block current in one direction.
What is the significance of the 'breakdown voltage' in a diode?
-The breakdown voltage is the maximum reverse voltage a diode can withstand before it starts conducting in the reverse direction. It's a critical parameter for ensuring the diode's reliability and preventing damage.
What is meant by the term 'reverse saturation current' in the context of diodes?
-Reverse saturation current is the minimal current that flows in the reverse-biased condition of a diode. It's determined by the thermal generation of electron-hole pairs in the depletion region and is a key parameter in diode characteristics.
How does temperature affect the characteristics of a diode?
-Temperature affects the characteristics of a diode by influencing the intrinsic carrier concentration and the rate of thermally generated electron-hole pairs. An increase in temperature generally increases the reverse saturation current and can lead to higher leakage currents.
What is the role of a variable resistor in a diode testing circuit?
-A variable resistor, or rheostat, in a diode testing circuit is used to adjust the current flowing through the circuit, allowing for the measurement of the diode's voltage-current characteristics under different conditions.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
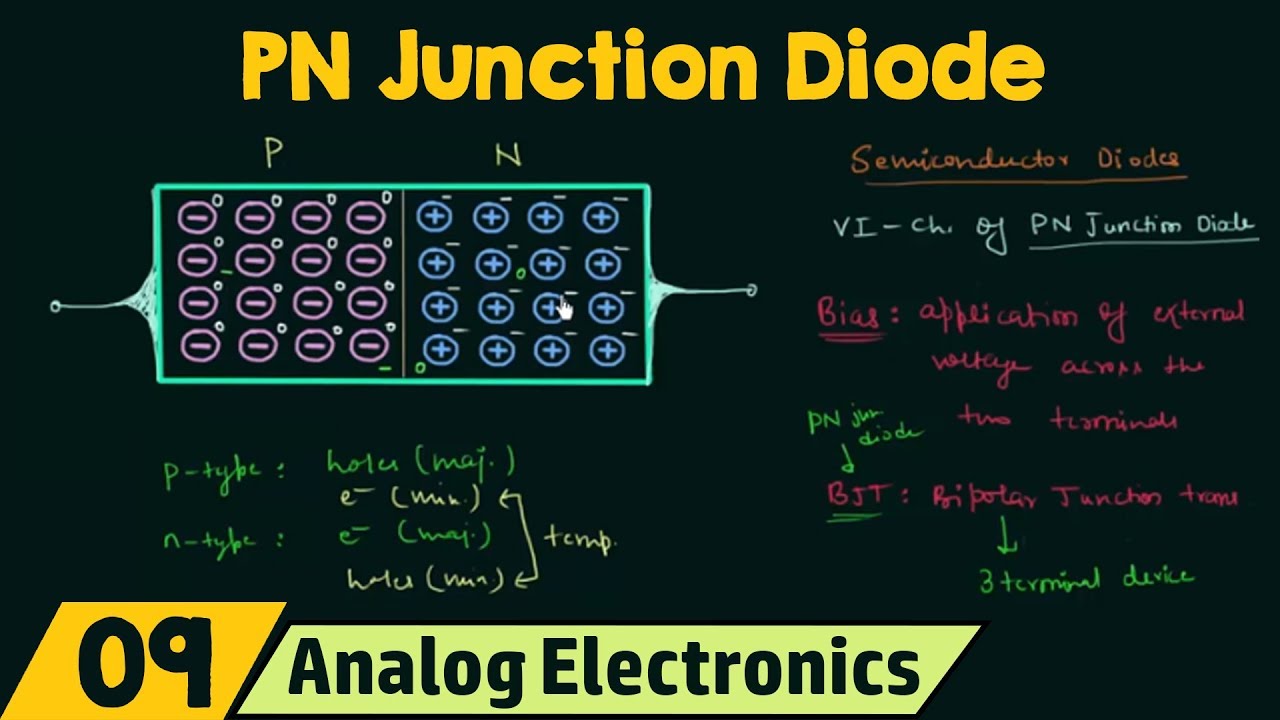
PN Junction Diode (No Applied Bias)

Varactor (Construction & Working) Special Purpose Diode (Basic Electronics) BE/BTech 1st year

Schottky Diode (Construction & Working) Special Purpose Diodes (Basics Electronics)

Semiconductor PN Junctions, The Depletion Region and Diode Characteristics

U1_L2_P-N Junction Diode | Electronics Engineering (BEC101/201)| Hindi

Types of Diodes - The Learning Circuit
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
