The Silk Road: A Story of Trade, Travel, and Cultural Exchange
Summary
TLDRThis episode explores the origins and impact of the Silk Road, initiated by Emperor Wu of the Han Dynasty to form alliances and counter the Xiongnu. Zhang Qian's journey led to the discovery of the Dayuezhi's powerful horses and the establishment of trade routes that facilitated cultural and technological exchange between the East and West. The Silk Road's influence extended from the spread of silk and spices to the transmission of ideas and diseases, shaping global civilization and ultimately leading to the Age of Discovery and the Colombian Exchange.
Takeaways
- 🚀 Emperor Wu of the Han Dynasty initiated the Silk Road to form alliances and expand trade.
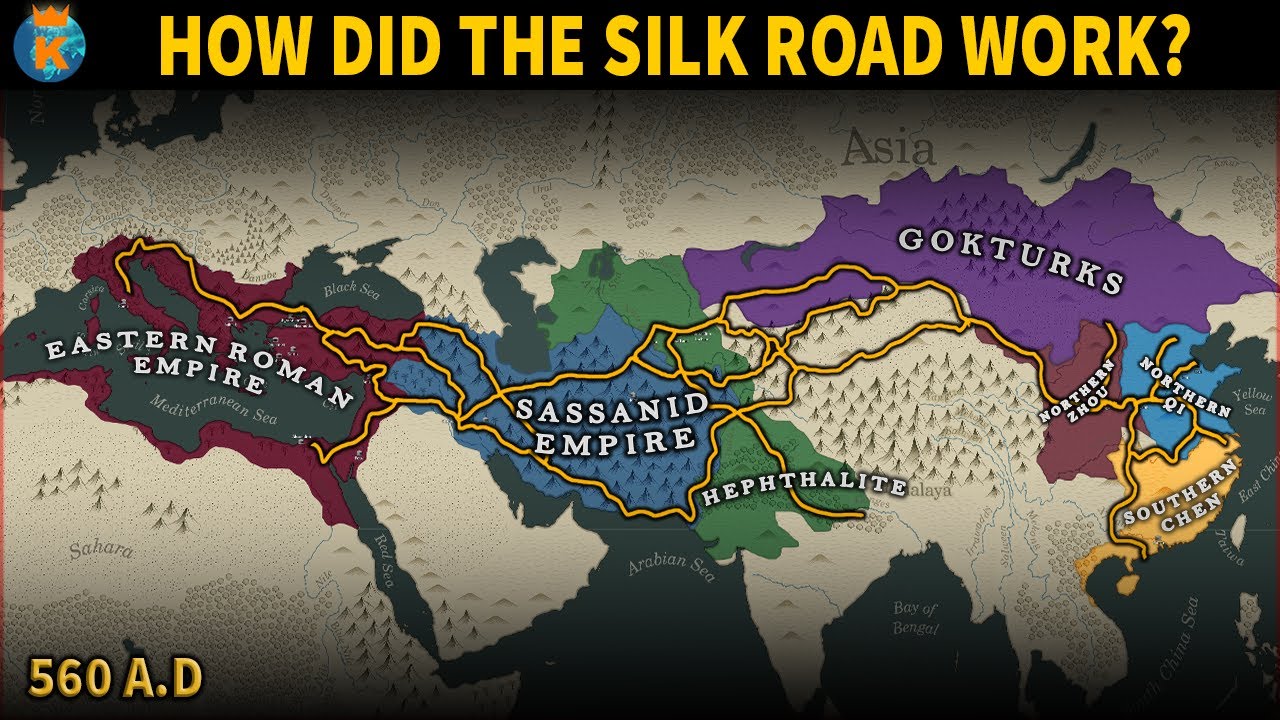
- 🌍 The Silk Road was a vast network of trade routes connecting China with Central Asia, Europe, and Africa.
- 🐎 The Dayuan horses, discovered by Zhang Qian, played a key role in strengthening China's military against the Xiongnu.
- 💰 The trade routes facilitated not only the exchange of goods like silk and spices but also cultural exchanges, shaping civilizations across continents.
- 📜 The term 'Silk Road' was coined by German geographer Ferdinand von Richthofen in 1877, though the network existed long before.
- ⚔️ The closure of the Silk Road by the Ottoman Empire in 1453 led Europeans to explore new maritime trade routes, sparking the Age of Discovery.
- 🏛️ The Silk Road also served as a conduit for art, religion, philosophy, technology, and language, profoundly impacting global civilization.
- 🦠 Diseases like the Bubonic Plague spread along the Silk Road, influencing historical events such as the fall of empires.
- 🧵 The Byzantine Empire, after learning the secret of silk production, started its own silk industry, which flourished until its fall to the Turks.
- 🌍 The Silk Road's legacy continues to influence modern global trade and cultural exchanges, making it a cornerstone of world history.
Q & A
Who was the first Chinese explorer to embark on a voyage that would eventually lead to the creation of the Silk Road?
-Zhang Qian was the first Chinese explorer to embark on a voyage in pursuit of alliances against the Xiongnu, which eventually led to the creation of the Silk Road.
What significant event marked the formal start of the Silk Road?
-The formal start of the Silk Road is marked by the trade that began with the West in 130 BC under the Han Dynasty.
Who were the Dayuezhi and how did they contribute to the Silk Road?
-The Dayuezhi, also known as the Great Ionians, were the Greco-Bactrians descended from Alexander the Great's forces. They possessed powerful horses that became a secret weapon in the fight against the Xiongnu and contributed to the establishment of the Silk Road.
What was the role of the Parthian Empire in the Silk Road?
-The Parthian Empire became the primary intermediary between China and Western regions, controlling Mesopotamia and the Silk Road, which facilitated trade and cultural exchange.
Why did the Silk Road decline and eventually close?
-The Silk Road declined and eventually closed due to the Ottoman Empire's imposition of a trade boycott with the West in 1453 CE, which compelled Europeans to seek new maritime trade routes.
What impact did the closure of the Silk Road have on Europe?
-The closure of the Silk Road led to the Age of Discovery, where Europeans ventured to seas and charted new maritime paths to replace overland trade, profoundly impacting global cultures.
Who was the first to document the Silk Road in a notable work?
-Marco Polo extensively documented his travels along the Silk Road in his notable work, although he did not name the routes as the 'Silk Road'.
Who first used the terms 'Silk Road' and 'silk routes'?
-The terms 'Silk Road' and 'silk routes' were first used by German geographer and traveler Ferdinand von Richthofen in 1877.
What was the significance of the Persian Royal Road in the history of the Silk Road?
-The Persian Royal Road, established during the Achaemenid Empire, was a vital route that extended from Northern Persia to the Mediterranean Sea and laid the foundation for the interconnected routes that would become part of the Silk Road.
What cultural exchanges were facilitated by the Silk Road?
-The Silk Road facilitated the exchange of art, religion, philosophy, technology, language, science, architecture, and other aspects of civilization, along with commercial merchandise.
How did the Byzantine Empire attempt to break China's monopoly on silk?
-Byzantine Emperor Justinian sent emissaries disguised as monks to steal silkworms from China and smuggle them back to the West, marking the beginning of the Byzantine silk industry.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
How did The Silk Road Actually Work?

The Rise & Fall of China's Han Dynasty Empire…and it’s Rise & Fall Again

The Han Dynasty Explained

Jalur yang menghubungkan dunia kuno lewat perdagangan, "JALUR SUTRA"

FILM KOLOSAL CHINA‼️ KISAH PERTEMPURAN 3 KERAJAAN ZAMAN DINASTI HAN TIONGKOK KUNO • ALUR CERITA FILM

Silk Road Virtual Tour
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
