How did The Silk Road Actually Work?
Summary
TLDRThe script narrates the historical significance of the Silk Road, initiated by the Han Dynasty in 130 BC to counter the Xiongnu threat and later expanded for trade. It facilitated the exchange of goods like silk, tea, and gunpowder, and ideas between East and West, influencing cultures and sparking the Age of Discovery. The route's closure by the Ottoman Empire led to European sea explorations, shaping global history.
Takeaways
- 🏰 The Han Dynasty, aiming to resolve conflicts with the Xiongnu, initiated contact with the Yuezhi in 138 BC, leading to the discovery of the superior Da-yuan horses.
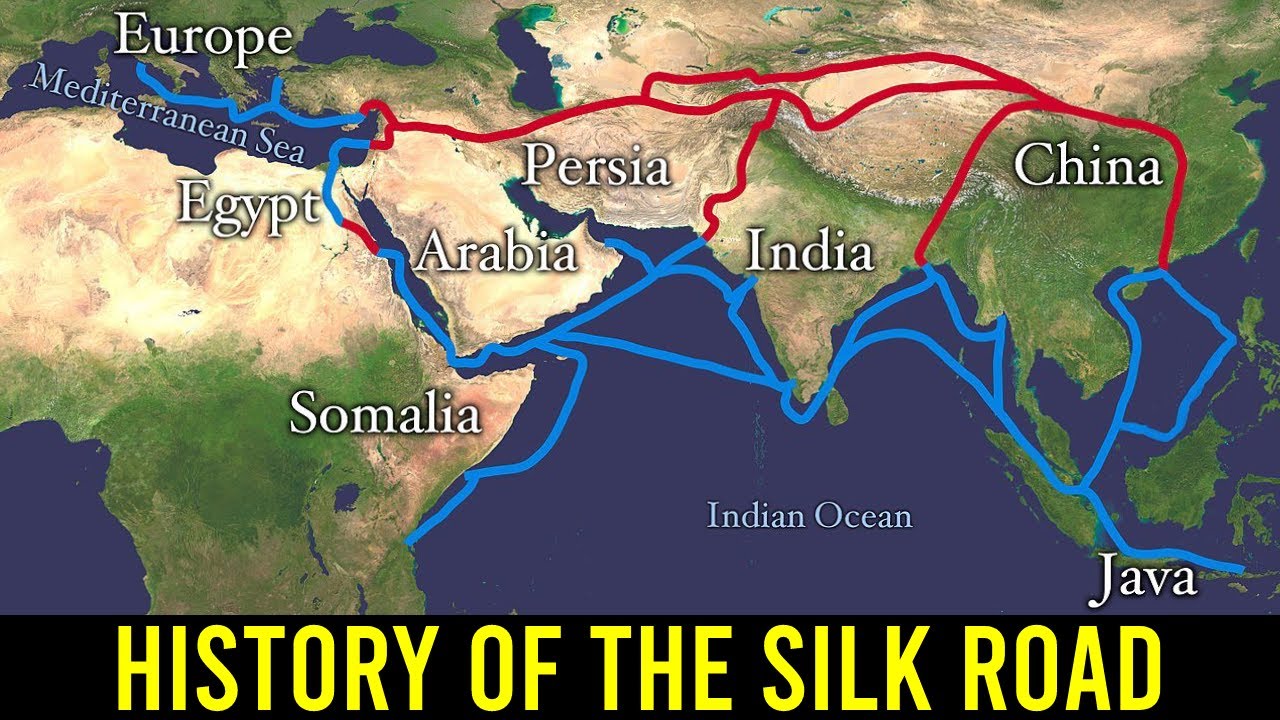
- 🌏 Emperor Wu of Han was inspired by Zhang Qian's reports and opened the Silk Road in 130 BC, establishing a vast trade network connecting China to Europe.
- 📜 The Silk Road predated by the Persian Royal Road, which was established by Darius I, stretching from Susa to Sardis and influencing later trade routes.
- 🐛 The secret of silk production was a Chinese monopoly until the Byzantine Empire, under Emperor Justinian, stole silkworms to balance trade.
- 🌈 The Silk Road was instrumental in the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures, including the spread of paper and gunpowder to the West.
- 🛣️ The trade along the Silk Road was not conducted by individual merchants traversing the entire route but through a series of middlemen and local trades.
- 📚 Marco Polo's travels and writings about his experiences along the Silk Road brought significant attention to the trade routes and their cultural impact.
- 🔄 The Silk Road facilitated not only the trade of physical goods but also the spread of religions, languages, and even diseases like the Black Death.
- 🚢 The decline of the Silk Road due to the Ottoman Empire's control led to the European Age of Discovery and the search for sea routes to the East.
- ⚓️ The Silk Road's influence extended beyond trade, inspiring exploration and the eventual European colonization of the Americas.
Q & A
When was the Han Dynasty established and what was its initial ambition?
-The Han Dynasty was established in the 2nd century BC. Its initial ambition was to resolve the recurrent issue of conflict with the Xiongnu tribes along the north and west borders.
Who was the Han emperor that sent an envoy to form an alliance with the Yuezhi?
-Emperor Wu was the Han emperor who decided in 138 BC to send an envoy to try and form an alliance or garner support from the Yuezhi in the west.
What was Zhang Qian's significant discovery during his journey through Central Asia?
-Zhang Qian was particularly fascinated by the Da-yuan people and their horses, which he found to be far superior to those bred in China in terms of size, strength, and speed.
How did the Han Dynasty utilize the horses of Da-yuan?
-The Han Dynasty purchased some of the western horses from Da-yuan, which helped them address the Xiongnu threat and improve their military capabilities.
What was the impact of Zhang Qian's journey on the opening of the Silk Road?
-Impressed by the success of Zhang Qian's journey and the collaboration it inspired, Emperor Wu decided to open the Silk Road in 130 BC, connecting the East to the West through a network of trade routes.
Who created the original international trade route known as the Royal Road?
-The Persians under Darius I and the Persian Empire created the original international trade route known as the Royal Road, which stretched from Susa in modern-day Iran to Sardis in what is now Turkey.
What was the primary commodity traded along the Silk Road and why was it so valuable to the Romans?
-Silk was the primary commodity traded along the Silk Road. The Romans developed a near-obsession with silk, which led to an unfavorable balance of trade for Rome due to the high demand for this luxurious Chinese commodity.
How did the Eastern Roman Empire, or the Byzantines, address the trade imbalance caused by the high cost of silk?
-Emperor Justinian sent two men undercover as monks into China to steal silkworms, which allowed the Eastern Roman Empire to start their own silk production and save itself from the high-priced silk-induced trade imbalance.
What other products besides silk were frequently traded along the Silk Road?
-Besides silk, products such as teas, dyes, spices, porcelain, paper, gunpowder, and medicine were frequently traded along the Silk Road.
How did the Silk Road facilitate cultural exchange between the East and the West?
-The Silk Road allowed for the exchange of goods, cultures, languages, religions, and ideas. It also enabled the spread of significant inventions like paper and gunpowder to the West, and brought Western goods and influences to the East.
Who was the famous traveler that documented his journey along the Silk Road, and what was the impact of his travels?
-Marco Polo was the famous traveler who documented his journey along the Silk Road. His travels and the subsequent book, 'The Travels of Marco Polo', shared his experiences and knowledge of Asia with the European world, contributing to a greater understanding and desire for exploration and global trade.
What event led to the decline of the Silk Road and the subsequent Age of Discovery?
-The decline of the Silk Road began when the Ottoman Empire conquered Byzantium and cut off trade with the West, leading Europeans to explore the seas in the Age of Discovery, which eventually led to expeditions to the New World.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)