Animal Tissues
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the four primary types of animal tissues: epithelial, nervous, connective, and muscle tissues. It explains the specific functions and structures of each tissue, including the protective role of epithelial tissues, the signal-conducting function of nervous tissues, the supportive role of connective tissues, and the movement-enabling muscle tissues. The script also breaks down the different subtypes of each tissue, such as squamous, columnar, and cuboidal epithelia, sensory and motor neurons, and various connective tissues like areolar, fibrous, and cartilage. It provides a foundational understanding of the complex biological systems that support life.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Epithelial tissue is the body's protective layer, with cells often organized in a single or multi-layered structure, attached by a basement membrane.
- 🔍 Epithelial tissues can be identified by their geometric shapes, such as squamous, columnar, and cuboidal, each serving specific functions like protection, secretion, and absorption.
- 💡 Nervous tissue is responsible for conducting electrochemical signals and includes sensory neurons for sensing, motor neurons for movement, and interneurons for decision-making.
- 🧠 Nerve cells have four basic components: dendrites, cell body, axon, and axon terminals, with the position of the cell body determining the division between dendrites and axon.
- 🔗 Connective tissue supports, stabilizes, and protects the body's organs, and includes a variety of types such as areolar, fibrous, cartilage, blood, adipose, and bone tissue.
- 🩹 Areolar tissue is a basic form of connective tissue that binds epithelium and provides a loose connection between organs.
- 💪 Fibrous connective tissue is dense and strong, found in tendons and ligaments, providing flexibility without stretch.
- 🩸 Blood is the only liquid connective tissue, composed of lymphocytes, erythrocytes, and platelets, and is responsible for transporting nutrients, waste, and hormones.
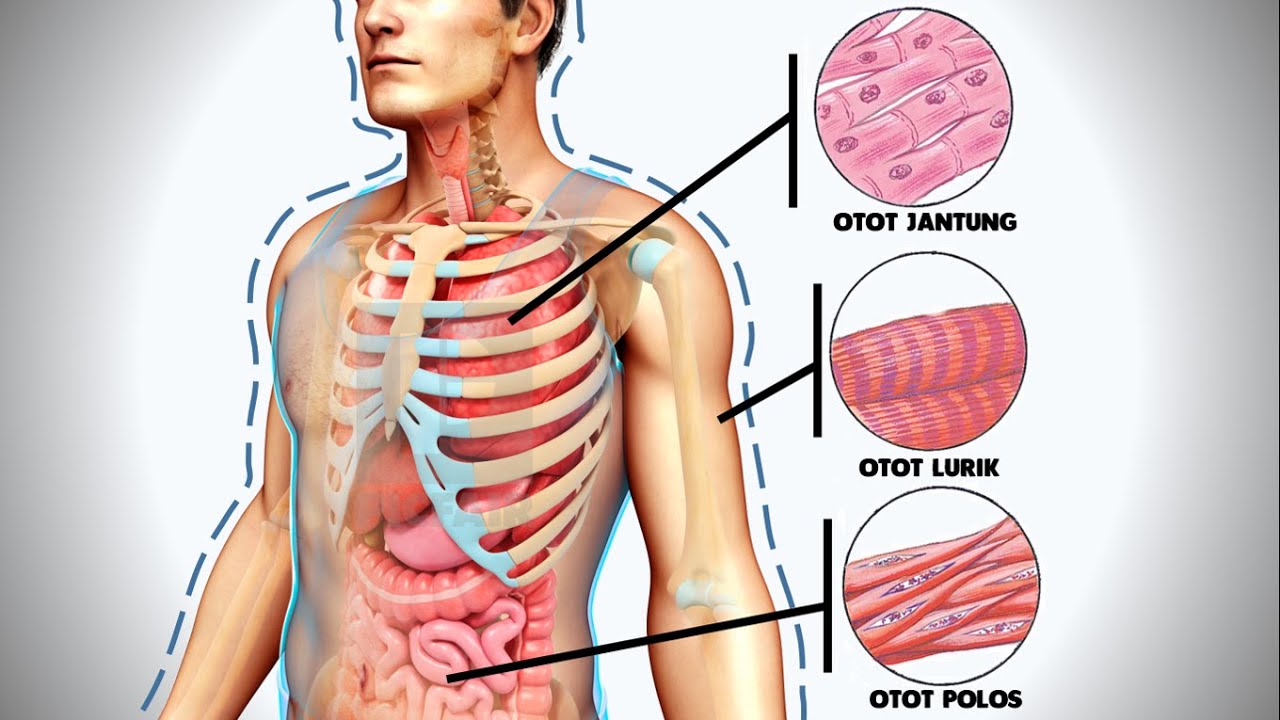
- 🏋️♂️ Muscle tissue allows for movement and is categorized into skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle, each with distinct characteristics and functions.
- 🦴 Skeletal muscle is striated and under voluntary control, attached to bones for movement.
- 🌀 Smooth muscle is found in the digestive system and blood vessels, responsible for involuntary movements like peristalsis and blood flow regulation.
- ❤️ Cardiac muscle is unique, found only in the heart, and moves involuntarily without instructions from the brain.
Q & A
What is the primary function of epithelial tissue?
-Epithelial tissue serves as a protective layer and lines the internal and external surfaces of the body, preventing unwanted substances from entering the body.
What is the role of the basement membrane in epithelial tissue?
-The basement membrane acts as a sticky surface that helps attach epithelial cells to the underlying tissue, ensuring they stay close together for protection.
How do squamous epithelial cells differ from columnar and cuboidal epithelial cells in terms of shape and function?
-Squamous epithelial cells are thin and irregularly shaped, often found in areas that require rapid healing like the mouth and skin. Columnar epithelial cells are elongated and often associated with secretion and absorption, found in the intestines and gallbladder. Cuboidal cells are square-like and also involved in absorption and secretion, located in sweat glands and the lining of the kidney tubes.
What are the four main types of tissues covered in the script?
-The four main types of tissues are connective, epithelial, muscle, and nervous tissue, each with specific functions and structures.
What is the primary function of nervous tissue?
-Nervous tissue is responsible for conducting electrochemical signals between the organs of the body and the brain, acting as the message pathways for the body.
How do sensory neurons differ from motor neurons and interneurons in structure and function?
-Sensory neurons are responsible for sensing and receiving information from the environment, with the cell body often off to the side. Motor neurons control movement and have a centrally located cell body. Interneurons, or relay neurons, are found in the spinal cord and brain, relaying information between sensory and motor neurons.
What is the basic structure of connective tissue?
-Connective tissue is composed of cells suspended in a fluid, matrix, or solid substance that provides support, stability, and protection to the body's organs.
What are the characteristics of areolar connective tissue?
-Areolar connective tissue is loose and binds epithelium to other tissues. It is made mostly of collagen and elastic fibers, providing a flexible yet strong connection between tissues.
How does fibrous connective tissue differ from areolar tissue?
-Fibrous connective tissue is more neatly arranged with a dense network of non-elastic collagen fibers, providing strength and flexibility without stretchiness, commonly found in tendons and ligaments.
What is the role of adipose tissue in the body?
-Adipose tissue stores excess energy in the form of fat, provides insulation for heat retention, and cushions and protects organs due to its location around them.
What are the three types of muscle tissues and their primary functions?
-Skeletal muscle is striated and responsible for voluntary movements, attached to bones. Smooth muscle is non-striated and controls involuntary movements in the digestive system and blood vessels. Cardiac muscle is also involuntary and striated, found only in the heart, responsible for its rhythmic contractions without brain instruction.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

jaringan hewan (bahasa indonesia)

Tissues of Human Body | Animation | Simple Explanation

IMAT Biology Lesson 6.1 | Anatomy and Physiology | Animal Tissues Part I

Jaringan Hewan

what are tissues in human body, what are tissues made of, what are tissues class 9, Human tissues,
Media Pembelajaran Jaringan Hewan - Kelas Daring Biologi SMA Kelas XI
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
