Lesson 9: Incomplete Dominance
Summary
TLDRThis educational video introduces non-Mendelian inheritance, focusing on incomplete dominance. It explains how traits do not always follow Mendel's laws, leading to phenotypes that are a blend of both parental traits, such as pink flowers from red and white parents. Examples like 4 o'clock flowers and Andalusian chickens illustrate this concept, and the video guides viewers to use Punnett squares to predict genotypic and phenotypic ratios for such inheritance patterns.
Takeaways
- 🌟 The video introduces non-Mendelian inheritance, which includes patterns that do not follow Mendel's laws of inheritance.
- 🔍 It focuses on the concept of incomplete dominance, where the phenotype of the offspring is a blend of the parents' traits.
- 🌺 An example of incomplete dominance is given with flowers, where a cross between red and white flowers results in pink flowers.
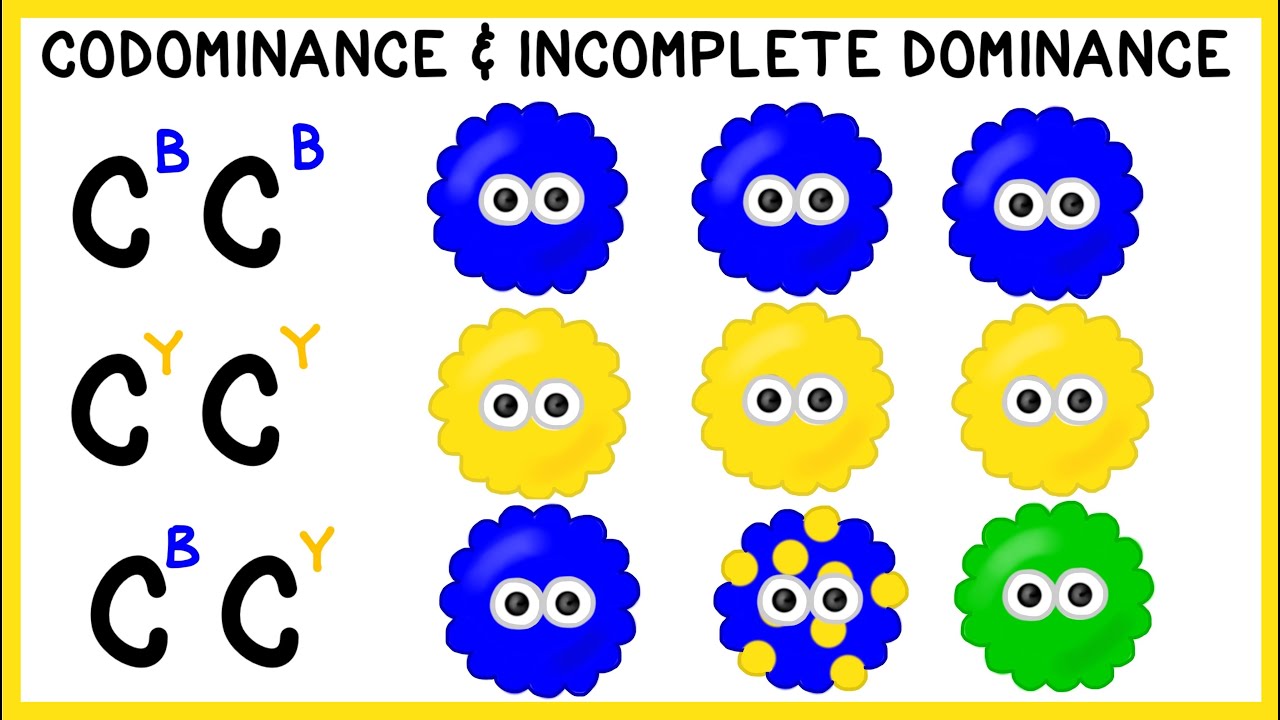
- 🐔 The Andalusian chicken is used as another example, where black and white feathered parents produce blue-feathered offspring, illustrating co-dominance.
- 🧬 The video explains that in co-dominance, both alleles are expressed in the phenotype, unlike typical Mendelian dominance.
- 📊 Viewers are expected to use a Punnett square to solve for non-Mendelian inheritance problems by the end of the video.
- 📚 A review of Mendelian inheritance terminologies is prompted, including dominant traits, homozygous, recessive traits, monohybrid cross, heterozygous, and phenotype.
- 🌼 The video script includes a sample problem using a Punnett square to determine the genotypic and phenotypic ratios for flower color crosses.
- 🔢 The genotypic ratio for a cross between a pink and a white flower is 50% heterozygous pink and 50% homozygous recessive white, resulting in a 1:1 ratio.
- 🎨 For a cross between two pink flowers, the genotypic ratio is 25% homozygous dominant red, 50% heterozygous pink, and 25% homozygous recessive white, leading to a 1:2:1 ratio.
- 📈 The phenotypic ratio for the cross between two pink flowers is 25% red, 50% pink, and 25% white, also reflecting a 1:2:1 ratio.
- 👋 The video concludes with an invitation to subscribe for more science educational content.
Q & A
What is non-Mendelian inheritance?
-Non-Mendelian inheritance refers to any pattern of inheritance where traits do not segregate according to Mendel's laws, which describe the inheritance of traits linked to single genes on chromosomes in the nucleus.
What are the types of inheritance patterns that fall under non-Mendelian inheritance?
-Incomplete dominance, sex-linked traits, and multiple alleles are the patterns of inheritance that fall under non-Mendelian inheritance, although the script focuses only on incomplete dominance.
What is incomplete dominance?
-Incomplete dominance is a genetic phenomenon where neither allele is completely dominant over the other, resulting in a phenotype that is a blend of both parental traits.
How does the phenotype of the F1 generation differ in incomplete dominance from Mendelian inheritance?
-In incomplete dominance, the F1 generation exhibits a phenotype that is intermediate between the phenotypes of the homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive parents, rather than expressing only the dominant trait as in Mendelian inheritance.
What is an example of incomplete dominance in flowers?
-An example of incomplete dominance in flowers is seen in 4 o'clock flowers, where a cross between a homozygous red flower and a homozygous white flower results in pink flowers due to the blending of the red and white alleles.
What is the concept of co-dominance mentioned in the script?
-Co-dominance is a genetic phenomenon where both alleles are expressed in the phenotype, neither being completely dominant or recessive. An example given is the Andalusian chicken, where black and white feathers result in blue offspring.
What is the purpose of using a Punnett square in the context of the video?
-A Punnett square is used to predict the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring in a genetic cross, helping to solve for non-Mendelian inheritance patterns such as incomplete dominance.
What is the genotypic ratio in the cross between a pink and a white flower, according to the script?
-The genotypic ratio in the cross between a pink and a white flower is 50% heterozygous pink and 50% homozygous recessive white, resulting in a 1:1 ratio.
What is the phenotypic ratio when a pink flower is crossed with another pink flower?
-The phenotypic ratio when a pink flower is crossed with another pink flower is 25% red, 50% pink, and 25% white, resulting in a 1:2:1 ratio.
What is the significance of the term 'heterozygous' in genetics?
-Heterozygous refers to an individual that has two different alleles for a particular gene, one inherited from each parent. In the context of incomplete dominance, a heterozygous individual will display a phenotype that is intermediate between the two homozygous parents.
What is the definition of 'homozygous dominant' and 'homozygous recessive' as per the script?
-Homozygous dominant refers to an individual with two dominant alleles for a trait, while homozygous recessive refers to an individual with two recessive alleles. In the script, these terms are used to describe the parental flowers in a genetic cross.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

NON-MENDELIAN GENETICS: INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE || GRADE 9 SCIENCE _ BIOLOGY

Incomplete Dominance and Codominance (Non- Mendelian Genetics)
Non-Mendelian Inheritance | Grade 9 Science Quarter 1 Week 4-5 | Maestrang Techy

S9Q1W4-5 | Non-Mendelian Inheritance
Codominance and Incomplete Dominance: Non-Mendelian Genetics

The DNA and Non-Mendelian Genetics (Incomplete Dominance): Knowledge Catalog Grade 9 Biology #7
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
