Your Hormones - Working Hard Everyday!
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the crucial role of hormones in the human body, showcasing how the endocrine system and over 200 hormones regulate vital functions like metabolism, mood, growth, and reproduction. It highlights the impact of hormonal imbalances on health, such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, and stress-related issues. The video emphasizes the importance of maintaining hormone balance through a healthy lifestyle—balanced nutrition, regular exercise, quality sleep, and stress management. Special focus is given to sex hormones like estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone, with recommendations for seeking medical advice if imbalances occur.
Takeaways
- 😀 Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate the body's organs and functions, working around the clock to keep the body in balance.
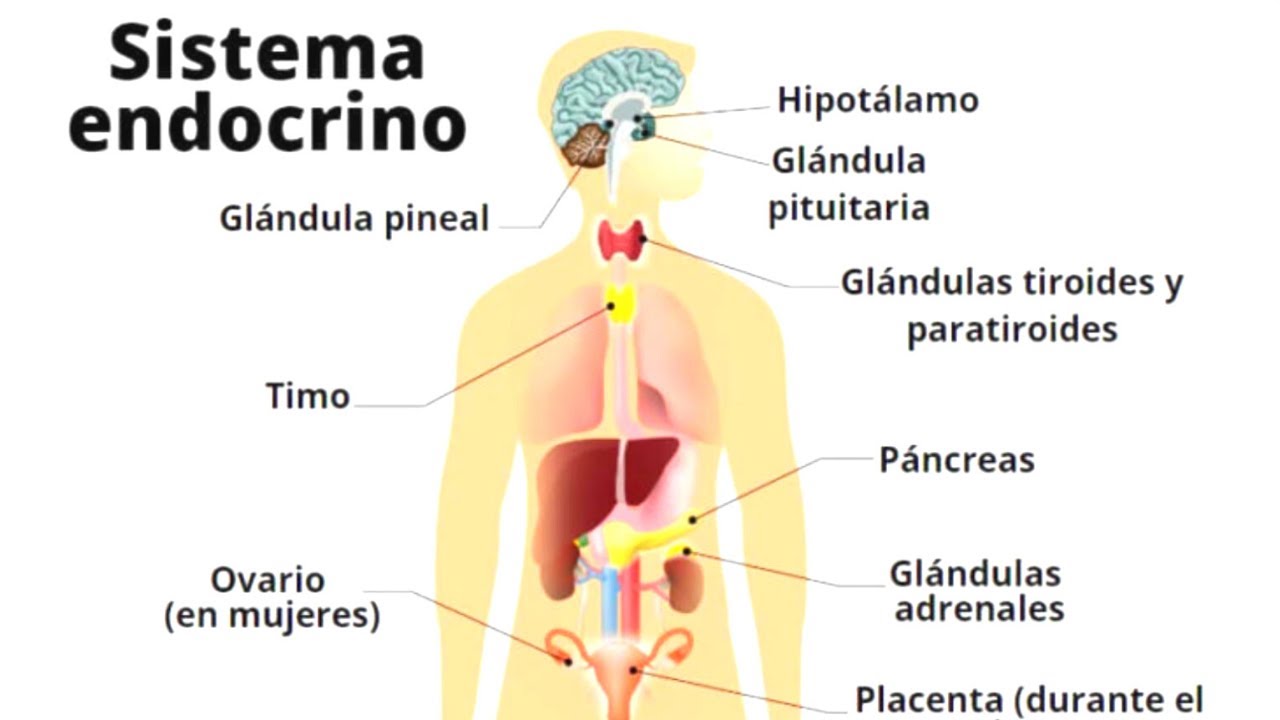
- 😀 The endocrine system consists of glands throughout the body that produce hormones, including the pancreas, thyroid, adrenal glands, and hypothalamus.
- 😀 Hormones affect every part of your life, from metabolism and mood to heart rate and blood sugar levels.
- 😀 Maintaining hormone balance is crucial for overall health and can prevent conditions like diabetes, thyroid disorders, heart disease, and stress-related problems.
- 😀 Hormonal fluctuations naturally occur during puberty, pregnancy, menopause, and aging, but imbalances outside these phases can lead to health issues.
- 😀 Lifestyle factors, such as stress, sleep, diet, exercise, and exposure to chemicals, play a significant role in hormone health.
- 😀 To keep hormones balanced, aim for a healthy weight, eat nutritious foods, limit added sugars and processed foods, and stay active with regular exercise.
- 😀 Quality sleep and stress management are essential to maintaining hormone health and overall well-being.
- 😀 In women, estrogen and progesterone regulate menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, and imbalances can lead to issues like heavy periods, infertility, and hot flashes.
- 😀 In men, testosterone is the main sex hormone, influencing sex drive, muscle mass, and bone health. Low testosterone can lead to mood changes, reduced sex drive, and muscle weakness.
- 😀 If you experience symptoms of hormone imbalances, consult a healthcare team to evaluate the cause and explore treatment options, including medication or therapy.
Q & A
What is the role of hormones in the human body?
-Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate most major body functions by sending signals to organs and tissues, telling them what to do, when to do it, and for how long, ensuring the body functions like a finely tuned machine.
How do hormones affect daily life?
-Hormones influence various aspects of daily life, from regulating your sleep-wake cycle to controlling your mood, hunger, body temperature, and even your ability to respond to stress or danger, all while keeping the body's systems in balance.
What organs produce hormones, and where are they located?
-Hormones are produced by glands in the endocrine system, which are located throughout the body. These glands include the pancreas, thyroid, adrenal glands, and hypothalamus, each responsible for producing specific hormones.
Can you explain the role of insulin in hormone regulation?
-Insulin is produced by the pancreas and helps control blood sugar levels. After eating, it enables cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream, which provides energy for bodily functions.
What happens when hormones are out of balance?
-When hormone levels are too high or low for extended periods, it can lead to various health issues, including diabetes, thyroid disorders, heart disease, cancer, weak bones, anxiety, and problems with sleep or appetite.
What factors can influence hormone health?
-Hormone health can be influenced by factors like infections, exposure to certain chemicals, family history, and lifestyle habits. Diet, exercise, stress levels, and sleep quality also play a significant role in maintaining hormonal balance.
How can one maintain balanced hormones?
-Maintaining balanced hormones involves maintaining a healthy weight, eating a nutritious diet, staying physically active, getting enough quality sleep, and managing stress effectively.
What are the primary sex hormones in women and their functions?
-In women, the primary sex hormones are estrogen and progesterone. They regulate menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause. Estrogen also helps control cholesterol levels and supports bone health.
What health issues can arise from hormonal imbalances in women?
-Hormonal imbalances in women can lead to symptoms like heavy or painful periods, infertility, vaginal bleeding, and hot flashes. The treatment may include medications or hormone therapies to restore balance and alleviate symptoms.
What is the main sex hormone in men, and what role does it play?
-Testosterone is the primary sex hormone in men. It influences sex drive, erections, sperm production, and helps maintain muscle strength and bone density.
How does testosterone imbalance affect men?
-Low testosterone levels in men can lead to a drop in sex drive, reduced sperm count, erectile dysfunction, loss of muscle strength, body hair, and mood changes. Testosterone replacement therapy may help manage these symptoms when prescribed by a doctor.
What should someone do if they suspect a hormonal imbalance?
-If someone suspects a hormonal imbalance, they should consult their healthcare provider for an evaluation. The healthcare team will help identify the cause of the imbalance and recommend appropriate treatment options based on the individual's needs and preferences.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Sistem Hormon_(Sistem Koordinasi Bagian 2 )_Biologi SMA XI
El SISTEMA ENDOCRINO explicado: cómo funciona, partes y hormonas🧠🧍

Sistema Endócrino: Introdução | Anatomia e etc

ENDOKRIN [BASIC, BIOMEDIK&FISIOLOGI DASAR]

Keterkaitan Struktur dan Fungsi Kelenjar Endokrin dan Peran Hormon dalam Reproduksi

Sistema endócrino - Introdução - Fisiologia veterinária - Aula 1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
