Sistema Endócrino: Introdução | Anatomia e etc
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the focus is on the endocrine system, which plays a crucial role in regulating various biological processes through hormones. Hormones, produced mainly by endocrine glands, act as chemical messengers in the bloodstream to target specific cells. The video explains the different types of hormones, their functions, and how they regulate processes like metabolism, growth, energy balance, and reproduction. It highlights key endocrine organs, such as the pineal gland, hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, pancreas, adrenal glands, ovaries, and testes, and sets the stage for further exploration of each in future lessons.
Takeaways
- 😀 The endocrine system plays a crucial role in regulating various biological processes through hormones.
- 😀 Hormones are chemical messengers released into the bloodstream to regulate the activity of target cells.
- 😀 Most hormones are produced by endocrine glands, but other organs like kidneys, heart, and neurons also have endocrine functions.
- 😀 Endocrine glands release hormones directly into the bloodstream, unlike exocrine glands that have ducts.
- 😀 Target organs are regulated by hormones, with target cells containing specific receptors for each hormone.
- 😀 The endocrine system works alongside the nervous system, but the endocrine regulation is slower as it involves hormone production and transport, unlike the faster electrical impulses of the nervous system.
- 😀 Hormones regulate metabolism, energy balance, growth, development, and reproduction.
- 😀 Hormones can be classified into three main groups: amines (derived from amino acids), peptides (formed by amino acid chains), and steroids (derived from cholesterol).
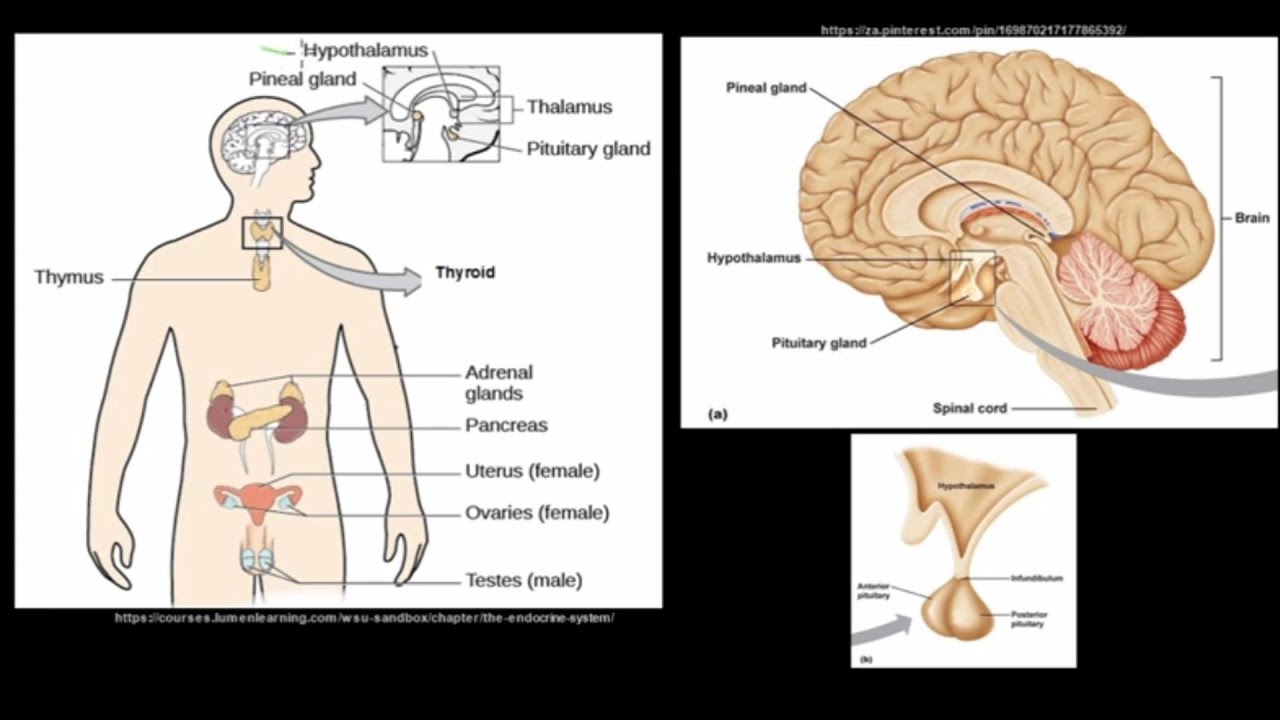
- 😀 Major endocrine glands include the pineal gland, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid, pancreas, adrenal glands, ovaries, and testes.
- 😀 The endocrine system and nervous system often collaborate to regulate bodily functions, ensuring proper coordination of various processes.
Q & A
What is the main role of the endocrine system?
-The endocrine system plays a crucial role in regulating various biological processes through the secretion of hormones, which act as chemical messengers in the body.
What are hormones and how do they function?
-Hormones are regulatory molecules that act as chemical messengers. They are released into the bloodstream by endocrine glands and travel to specific target cells, where they signal the cells on how to behave in certain situations.
What are endocrine glands, and how do they differ from exocrine glands?
-Endocrine glands are organs that release hormones directly into the bloodstream, without using ducts. This contrasts with exocrine glands, which release their secretions into ducts that lead outside the body or into body cavities.
Can you name a few organs or tissues with endocrine activity besides the endocrine glands?
-Besides the primary endocrine glands, other organs such as the kidneys, heart, and even neurons also have some endocrine activity.
What is the relationship between the endocrine system and the nervous system?
-The endocrine system often works together with the nervous system to regulate body functions. While the nervous system responds quickly through electrical impulses, the endocrine system works more slowly, using hormones transported via the bloodstream.
What are some of the key functions regulated by hormones in the body?
-Hormones regulate metabolism, energy balance, growth and development, internal chemical composition, and reproductive processes such as the formation of sperm and eggs.
What are the three main chemical groups of hormones?
-Hormones can be classified into three main groups: amines (derived from amino acids like tyrosine and tryptophan), peptides (formed from long chains of amino acids), and steroids (derived from cholesterol).
What are some examples of primary endocrine glands in the human body?
-Some of the primary endocrine glands include the pineal gland, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, pancreas, adrenal glands, ovaries in females, and testes in males.
What is the role of receptors in hormone action?
-Target cells must have specific receptors that can bind to particular hormones. This is analogous to a lock and key system, where the hormone is the key and the receptor on the cell is the lock.
How do hormones reach their target cells and what happens once they bind to receptors?
-Hormones are released into the bloodstream and travel to their target cells. Once they reach these cells, the hormones bind to specific receptors, triggering the cells to respond in a particular way depending on the hormone's function.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

SISTEMA ENDOCRINO anatomia e fisiologia: cos'è? Funzioni e da quali organi è formato? - Corpo Umano

KELENJAR HIPOFISIS - MODUL ADRENAL DAN HIPOFISIS - dr Reza Rinadhi Bramantya, SpPD-KEMD
Grade 12 Life Sciences Responding to the Environment The Endocrine System

How the Endocrine System Works

Mechanisms of Hormone Action

GCSE Biology - The Endocrine System
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)