⚙ Lean Manufacturing | A pursuit of perfection
Summary
TLDRThis episode delves into lean manufacturing, a production management method originating from the Toyota Production System (TPS). It emphasizes maximizing customer value while eliminating waste, such as overproduction and excess inventory. Lean manufacturing, introduced by John Krafcik in 1988 and popularized by James Womack and others, employs tools like Value Stream Mapping and Kaizen for continuous improvement. TPS, with its principles of Jidoka and Just in Time, exemplifies flexibility and responsiveness, setting a benchmark for industries like Ford and Nike. Lean concepts extend beyond manufacturing to various sectors, including services, healthcare, and logistics, driving efficiency and quality improvements.
Takeaways
- 📦 Lean manufacturing is a method of production management developed from the Toyota Production System (TPS), aiming to maximize customer value while eliminating waste.
- 🔧 Waste in lean manufacturing includes overproduction, excess inventory, unnecessary processing, and more.
- 🚀 Lean production is more efficient than traditional mass production, using less human labor, production space, and engineering work.
- 📚 The term 'lean manufacturing' was coined by John Krafcik in 1988 and popularized by James Womack, Daniel Jones, and Daniel Roos in their 1990 book 'The Machine That Changed the World'.
- 🏭 Lean management extends the principles of lean manufacturing beyond production to the entire organization, emphasizing continuous cost reduction, quality improvement, and delivery time shortening.
- 📈 Key principles of lean manufacturing include defining value for the customer, determining the value stream, creating a free flow of materials, implementing a pull system, and continuous improvement (kaizen).
- 🛠️ Essential lean tools include value stream mapping (VSM), 5S (sort, set in order, shine, standardize, sustain), total productive maintenance (TPM), single-minute exchange of die (SMED), poke-yoke (error-proofing), and kaizen.
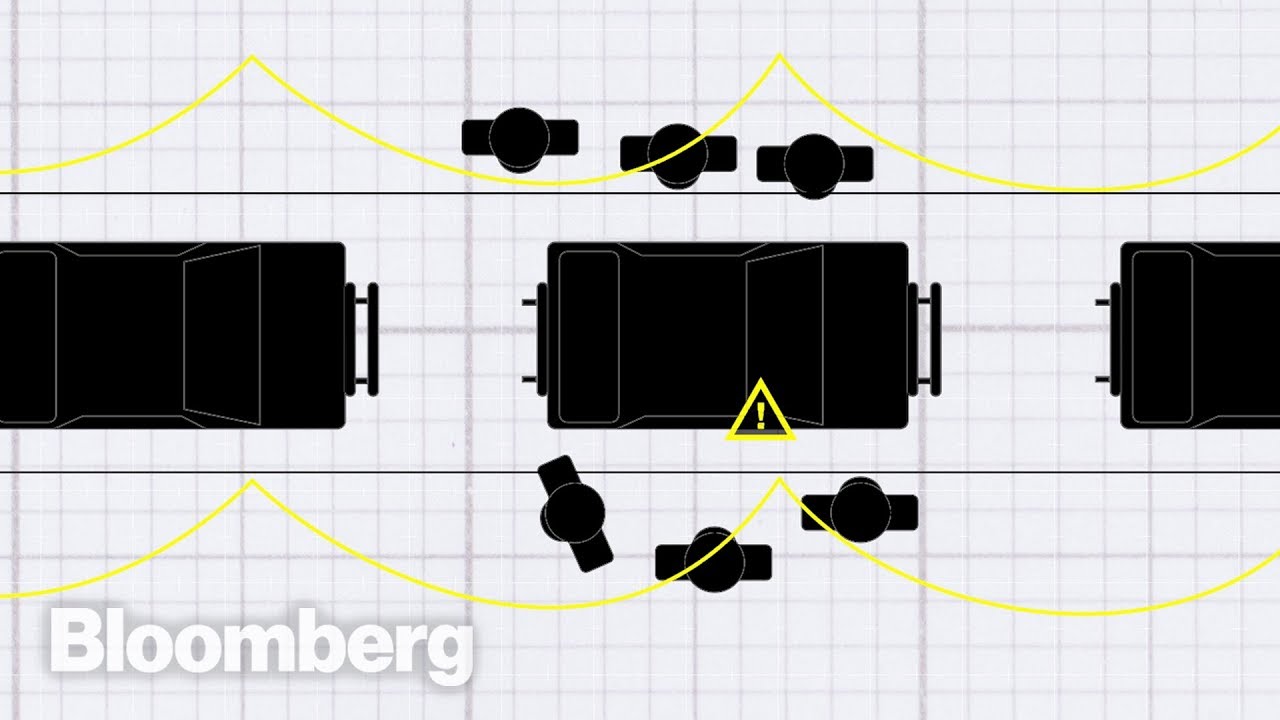
- 🔄 The Toyota Production System (TPS) is based on two main concepts: jidoka (automation with a human touch) and just-in-time production.
- 🚗 TPS optimizes production processes to produce only what the next process requires, ensuring timely and accurate delivery of parts to avoid stockpiling.
- 🌐 Lean principles are applied across various industries, including automotive, manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, IT, and more, offering benefits like improved efficiency, reduced costs, better quality, and enhanced flexibility.
Q & A
What is lean manufacturing?
-Lean manufacturing is a method of production management developed based on the principles and tools of the Toyota Production System (TPS). Its primary goal is to maximize value for the customer while eliminating waste.
What does the term 'lean' mean in the context of lean manufacturing?
-In lean manufacturing, 'lean' refers to the reduction of waste, using less human labor, production space, and engineering work compared to traditional mass production.
Who proposed the term 'lean manufacturing' and when?
-The term 'lean manufacturing' was proposed in 1988 by John Krafcik to describe an alternative system to popular mass production.
What are the basic principles of lean manufacturing?
-The basic principles of lean manufacturing include defining value for the customer, determining the value stream for each product, creating a free flow of materials and raw materials, implementing a pull system in the customer-supplier relationship, and continuously pursuing perfection.
What are some common lean manufacturing tools?
-Common lean manufacturing tools include Value Stream Mapping (VSM), 5S (Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain), Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), Single Minute Exchange of Die (SMED), Poka-yoke (error proofing), and Kaizen (continuous improvement).
How does the Toyota Production System (TPS) relate to lean manufacturing?
-Lean manufacturing concepts and tools are primarily derived from the Toyota Production System (TPS), which emphasizes automation with a human touch (Jidoka) and just-in-time production.
What is the principle of Jidoka in the Toyota Production System?
-Jidoka, or automation with a human touch, is a method in the Toyota Production System for quickly identifying and correcting problems that could lead to production defects.
What is the just-in-time (JIT) principle in the Toyota Production System?
-Just-in-time (JIT) is a principle in the Toyota Production System that involves improving and coordinating production processes to produce only what the next process requires, minimizing inventory.
Which industries commonly use the lean concept?
-Industries that commonly use the lean concept include automotive (e.g., Toyota, Ford), manufacturing (e.g., John Deere, Caterpillar), and service sectors such as banking, healthcare, logistics, construction, IT, and higher education.
What are some benefits for companies using the lean concept?
-Benefits for companies using the lean concept include increased efficiency, improved machine utilization, reduced inventory, reduced production space, shorter transition times from raw material to finished product, and improved quality.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)