China construyó una presa TAN GIGANTE que frenó el giro de la Tierra ¿VERDAD?
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concepts of angular momentum and moment of inertia, drawing parallels with linear motion. The key takeaway is that just as mass affects linear momentum, moment of inertia affects angular momentum. It highlights how the Earth's rotation changes with mass redistribution, such as water moving up a dam. The speaker also demonstrates this principle using examples like skaters and stars, and emphasizes the insignificance of small changes in the Earth's rotation, offering a playful reflection on human impact and the beauty of studying physics.
Takeaways
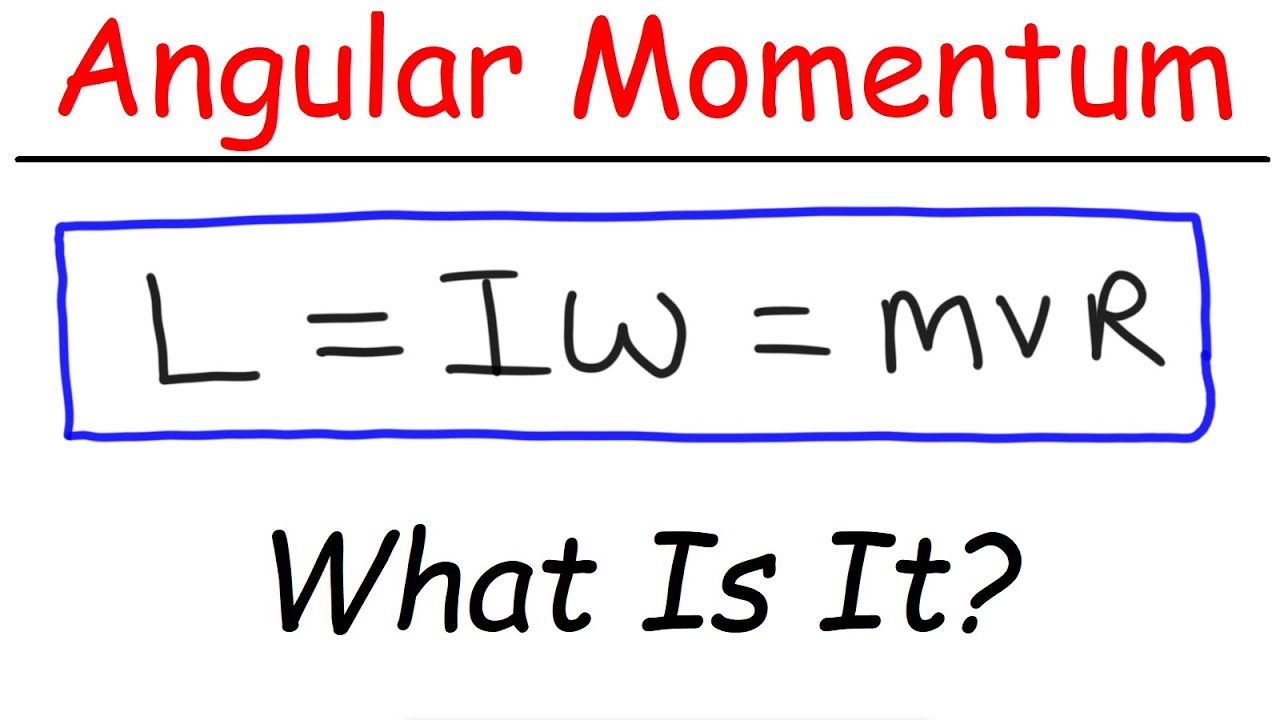
- 😀 The moment of inertia is a rotational counterpart to mass in linear motion, describing a body's resistance to rotational motion.
- 😀 Angular momentum is conserved just like linear momentum, and it depends on both the moment of inertia and angular velocity.
- 😀 Unlike mass, the moment of inertia can change depending on how the mass is distributed relative to the axis of rotation.
- 😀 The more mass an object has and the farther it is from the axis of rotation, the greater its moment of inertia.
- 😀 The Earth's rotation can slow down when the moment of inertia increases, such as when water is moved to a higher elevation.
- 😀 Conservation of angular momentum explains why the Earth's rotational speed decreases as its moment of inertia increases.
- 😀 The speed of a rotating object can change if its shape or the distribution of mass changes, as seen with skaters pulling their arms in.
- 😀 When stars form, they rotate faster as they shrink, demonstrating how angular momentum is conserved during compression.
- 😀 Neutron stars and pulsars spin incredibly fast due to their small size and the conservation of angular momentum.
- 😀 The effect of small changes in mass distribution (e.g., moving water) on the Earth's rotation speed is practically negligible and unnoticeable.
- 😀 The news about the Earth’s rotation slowing due to water being moved is exaggerated, as the change is too small to measure or notice.
Q & A
What is the moment of inertia?
-The moment of inertia is the rotational analog of mass. It measures an object's resistance to rotational motion, depending on both the amount of mass and its distribution relative to the axis of rotation.
How is the moment of inertia related to angular momentum?
-Angular momentum is the product of the moment of inertia and the angular velocity. Just as mass influences linear momentum, the moment of inertia influences angular momentum. Both quantities are conserved in rotational motion.
Why is the moment of inertia compared to mass?
-The moment of inertia is compared to mass because both are measures of inertia, but in different contexts. Mass is the resistance to linear motion, while the moment of inertia is the resistance to rotational motion.
Can the moment of inertia change? How?
-Yes, the moment of inertia can change. It is not a fixed property like mass. The distribution of mass relative to the axis of rotation affects the moment of inertia, so changing the shape or mass distribution of an object (e.g., pulling arms in or moving mass further from the axis) alters it.
What happens to an object's angular velocity if its moment of inertia increases?
-If the moment of inertia increases, the angular velocity must decrease to conserve angular momentum. This is due to the principle of conservation of angular momentum.
How does the Earth's rotation change when its moment of inertia increases?
-When the Earth's moment of inertia increases (for example, if water moves to a higher elevation), the Earth's rotation slows down to conserve angular momentum. However, this change is extremely small and imperceptible.
Why do small stars like neutron stars spin faster?
-Smaller stars, like neutron stars or pulsars, spin faster due to conservation of angular momentum. As a star contracts, its moment of inertia decreases, causing its angular velocity to increase.
What is the role of gyroscopes in phones and satellites?
-Gyroscopes use the principle of conservation of angular momentum to help devices, like phones and satellites, maintain orientation in space. They detect changes in angular velocity and allow the device to adjust accordingly.
What happens when mass is moved farther from the axis of rotation?
-When mass is moved farther from the axis of rotation, the moment of inertia increases because the mass is now further from the axis, which makes it harder to rotate the object. This results in a slower rotation if angular momentum is conserved.
How does the Earth's rotation slow down with a dam like the Three Gorges Dam?
-When water is moved to a higher elevation in a dam, the moment of inertia of the Earth increases. To conserve angular momentum, the Earth's rotation must slow down slightly. However, this effect is extremely small and not noticeable in everyday life.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)