TD - Application of Isometric Circles (Example 1) @derickfrederickTD
Summary
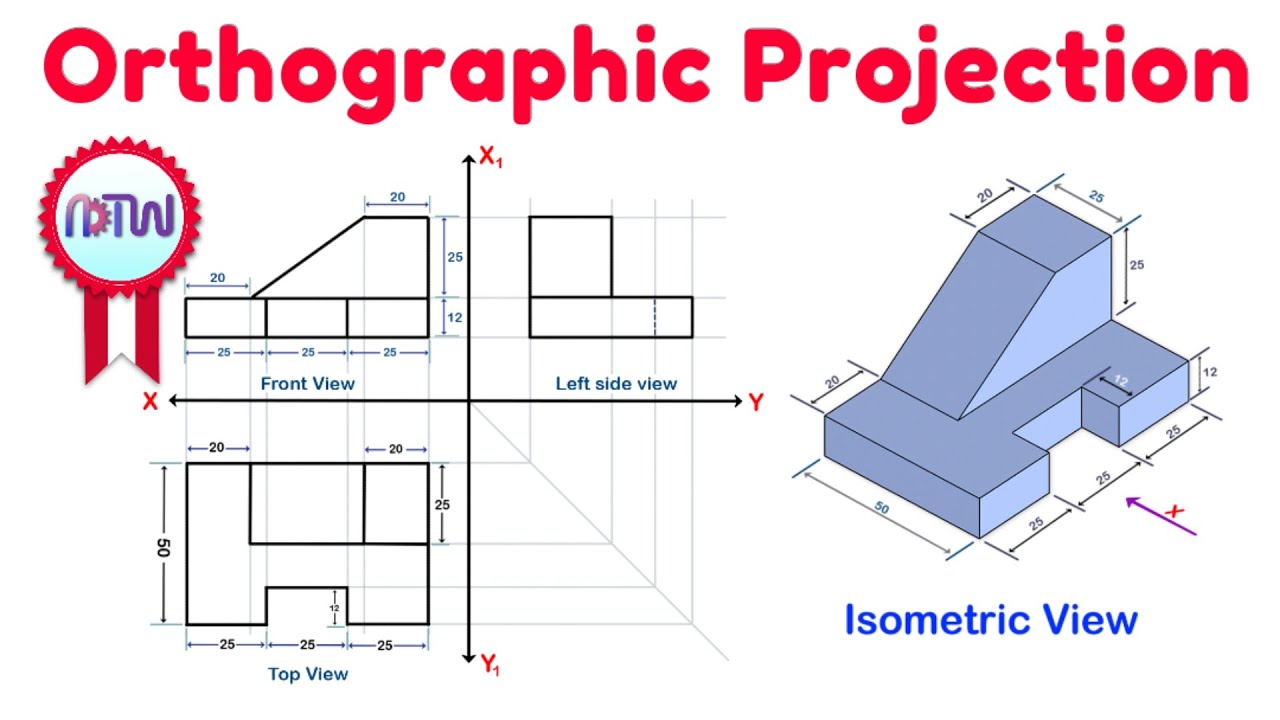
TLDRIn this tutorial, Fred explains how to apply isometric drawing techniques to real-life objects. He demonstrates how to create an isometric box by projecting the total dimensions of the object, including height, slope, and width. The process also involves drawing a rhombus to represent a circle in isometric form. Fred guides viewers step-by-step in constructing the object’s curves, transferring vertical lines, and adding thickness. He emphasizes the importance of accurate measurements and how to connect lines for precise arcs. The video concludes with a tip on dimensioning the object for clarity.
Takeaways
- 😀 Before attempting isometric drawing, ensure you have watched the video on how to draw isometric circles.
- 😀 To draw an isometric object, first project it into a box by determining its total length, width, and height.
- 😀 The total height of the object in the example is 70 units (45 + 25), with a 20-unit slope to the right and 50 units to the left.
- 😀 Use a protractor to ensure proper alignment of lines, with key angles being 90°, 30° to the right, and 30° to the left.
- 😀 Thin lines should be used to draw the isometric box and transfer measurements accurately.
- 😀 To draw a circle or arc in isometric, use a rhombus with a 50x50 dimension (diameter of 50).
- 😀 The longest diagonal of the rhombus should be drawn first to guide the placement of other lines.
- 😀 Mark the center of each side of the rhombus at the midpoint (25 units if the diameter is 50).
- 😀 To create arcs, use a needle tool to draw from the center points of the rhombus, making sure not to exceed the midpoint when drawing.
- 😀 Once the arcs are drawn, use thick lines for the edges of the object and finalize its shape by adding thickness to the back face.
- 😀 After completing the isometric drawing, dimension the object to show the scale and proportions clearly.
Q & A
What is the purpose of using an isometric box in drawing isometric objects?
-The isometric box is used to project the dimensions of an object, ensuring that it fits into a three-dimensional grid where the length, width, and height are accurately represented.
What should be done before drawing isometric objects in the tutorial?
-Before drawing isometric objects, you should watch the previous video on how to draw isometric circles, as the technique for drawing circles is crucial for creating the object in isometric form.
How do you determine the height of the isometric box?
-The height of the isometric box is determined by adding the total height dimensions of the object, such as the 45 units from the base to a midpoint and the 25 units from the midpoint to the top. The sum of these gives the total height (70 units).
Why is it important to position the protractor correctly in isometric drawing?
-Correct positioning of the protractor ensures that the lines for the isometric object are accurately projected at 30 degrees or 90 degrees, which are essential for maintaining the correct isometric angles.
How do you calculate the diameter of a circle or arc in isometric drawing?
-The diameter of the circle or arc is calculated by doubling the radius. For example, if the radius is 25 units, the diameter is 50 units.
What is the role of the rhombus in isometric circle drawing?
-The rhombus is drawn to create the framework for the isometric circle, with its diagonals helping to define the arcs and ensure the correct proportions of the circle in isometric perspective.
How do you determine the center of the rhombus?
-The center of the rhombus is located at the midpoint of its sides. For a rhombus with a side length of 50, the center would be at 25 units from each side.
What is the significance of the longest diagonal in the rhombus?
-The longest diagonal in the rhombus is important because it guides the correct positioning of the arcs, which are drawn based on the intersections of the diagonals.
Why should arcs not exceed the midpoint in isometric drawing?
-Arcs should not exceed the midpoint to avoid distorting the isometric perspective, ensuring that the arcs stay proportional and correctly positioned within the isometric view.
What is the purpose of adding thickness to the object in isometric drawing?
-Adding thickness to the object helps define its three-dimensional structure, making the object appear solid and complete in isometric view, especially when illustrating both the front and back faces of the object.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)