MODEL PEMBELAJARAN - SKB GURU
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Septi Afriani explains four popular learning models: Discovery Learning, Inquiry Learning, Problem-Based Learning (PBL), and Project-Based Learning (PJBL). She outlines the goals and steps for each model, emphasizing the active role of students in discovering or solving problems. Discovery Learning focuses on students' discovery of new concepts, while Inquiry Learning aims to satisfy curiosity. PBL involves solving real-world problems with teacher guidance, and PJBL centers on hands-on projects. The video provides a comprehensive comparison of these models, highlighting their unique approaches to fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Takeaways
- 😀 Discovery learning emphasizes the process of discovering concepts or principles that were previously unknown, encouraging students to form conclusions through their own exploration.
- 😀 In discovery learning, the role of the teacher is to provide stimulating problems for students to solve, without directly offering the conclusions.
- 😀 Inquiry learning focuses on satisfying students' curiosity and does not require them to make discoveries, unlike discovery learning where discoveries are expected.
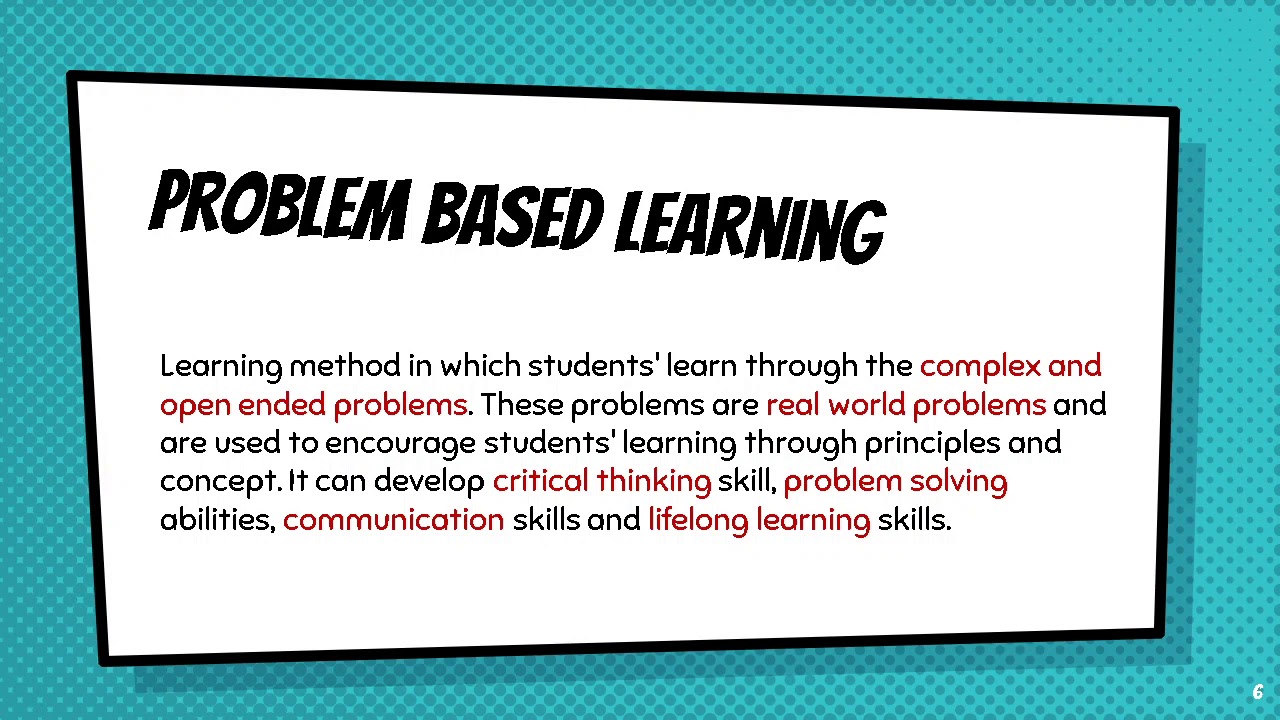
- 😀 Problem-based learning (PBL) encourages continuous guidance from the teacher, who acts as a facilitator, helping students frame questions and explore real-world problems.
- 😀 PBL emphasizes critical thinking and problem-solving skills by providing students with real-world, contextual issues to tackle.
- 😀 Steps in PBL include orienting students to the problem, organizing their tasks, guiding them through data collection, and finally analyzing the process of problem-solving.
- 😀 Project-based learning (PJBL) uses projects as the central focus of learning, where students design and implement solutions to the problems posed by the teacher.
- 😀 The teacher in PJBL helps students develop and present their projects, monitor progress, and evaluate their outcomes.
- 😀 In PJBL, students work together in groups, planning their projects, and selecting methods to solve the given problem, with the teacher providing continuous guidance and support.
- 😀 Evaluation in PJBL includes testing the outcomes of the project, as well as evaluating the learning process and experience.
- 😀 The process of organizing tasks and forming groups is an essential part of the PBL methodology, ensuring students actively collaborate and take responsibility for their learning.
Q & A
What is the main objective of Discovery Learning?
-The main objective of Discovery Learning is for students to discover concepts or principles that were previously unknown. The process emphasizes student-driven inquiry and the formulation of conclusions from exploration.
How does Discovery Learning differ from Inquiry Learning?
-Discovery Learning focuses on students making their own discoveries and formulating conclusions, while Inquiry Learning is about satisfying students' curiosity through investigation. Inquiry Learning does not necessarily require students to 'discover' something new.
What is the role of the teacher in Discovery Learning?
-In Discovery Learning, the teacher's role is to present problems that encourage exploration without providing direct solutions or conclusions. The teacher sets up the conditions for discovery but allows students to find answers on their own.
What are the key stages in the Discovery Learning process?
-The key stages in Discovery Learning are: 1) Stimulation (introducing a question), 2) Problem Statement (identifying a relevant issue), 3) Data Collection, 4) Data Processing (analyzing the collected data), 5) Verification (confirming hypotheses), and 6) Generalization (drawing conclusions).
What is the main focus of Inquiry Learning?
-Inquiry Learning focuses on investigation and satisfying students' curiosity by exploring a question or topic. Unlike Discovery Learning, the goal is not to discover new knowledge, but rather to understand and answer the questions posed.
How does Problem-Based Learning (PBL) involve students in the learning process?
-In Problem-Based Learning, students are actively involved in solving real-world problems. The teacher acts as a guide, helping students ask questions, find solutions, and work together to solve the problem through various investigative and problem-solving steps.
What are the key steps in Problem-Based Learning?
-The key steps in Problem-Based Learning are: 1) Orientation to the problem, 2) Organizing students and tasks, 3) Guiding individual investigations within groups, 4) Developing and presenting solutions, and 5) Analyzing and evaluating the problem-solving process.
What is the teacher’s role in Project-Based Learning (PJBL)?
-In Project-Based Learning, the teacher supports students by providing guidance on how to design a project, define problems, and manage tasks. The teacher helps with planning, monitoring progress, and evaluating the final project outcomes.
What are the steps involved in Project-Based Learning?
-The steps in Project-Based Learning include: 1) Defining essential questions, 2) Designing the project plan, 3) Organizing schedules and tasks, 4) Monitoring student progress, 5) Testing solutions, and 6) Evaluating the overall experience.
In Problem-Based Learning, what does the teacher do during the phase of organizing students?
-During the organizing phase of Problem-Based Learning, the teacher helps students define and organize tasks related to the problem. The teacher also forms groups to work together on solving the problem.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

PERBEDAAN DISCOVERY, INQUIRY, PBL, & PJBL (MODEL PEMBELAJARAN)

4 Model Pembelajaran Terbaik Dalam Implementasi Kurikulum Merdeka

Perbadaan Project Based Learning (PJBL) dengan Problem Based Learning (PBL) - SKB GURU -Ayu Melawati

MODEL MODEL PEMBELAJARAN 2
Metode Belajar (Learning Method)

Pembelajaran Berbasis Proyek dengan memanfaatkan Platform Teknologi #PembaTIK2023
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
