Soal-soal Ikatan Kimia Kelas 10 dan 11 SMA/MA Pilihan
Summary
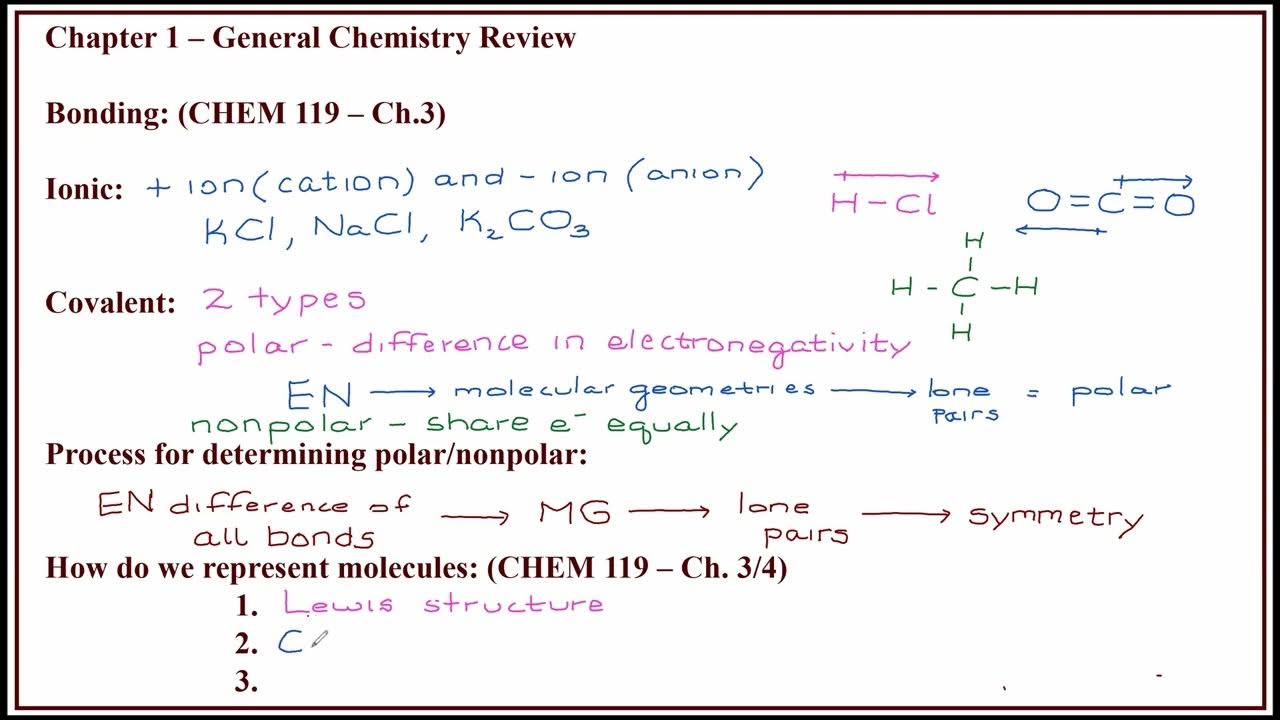
TLDRThis educational video script focuses on teaching chemical bonding, exploring ionic and covalent bonds, molecular formulas, and Lewis structures. It uses examples of specific elements and their group numbers to explain how to determine bonding types and chemical formulas. The script covers the process of identifying ionic bonds (positive and negative ions) and covalent bonds (electron sharing for octet stability), as well as how to write chemical formulas and name compounds. Key concepts like the octet rule, ion charges, and Lewis structures are highlighted, making it a comprehensive guide to understanding basic chemical bonding.
Takeaways
- 😀 The script explains how to identify ionic and covalent bonds based on the electron configuration of elements.
- 😀 Elements from Group 2 (like X) tend to form ions with a 2+ charge, while elements from Group 6 (like Y) tend to form ions with a 2- charge, leading to ionic bonds.
- 😀 Ionic bonds are characterized by positive and negative ions, whereas covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons.
- 😀 To write chemical formulas for ionic compounds, the charges of the ions are balanced by adjusting the subscripts (e.g., X2Y2 becomes XY).
- 😀 For covalent compounds, naming follows specific rules, such as indicating the number of atoms in the compound using prefixes (e.g., phosphorus tribromide).
- 😀 In naming covalent compounds, if the first element has only one atom, no prefix is used (e.g., carbon monoxide).
- 😀 The concept of octet rule and duet rule are used to determine the electron stability of elements when forming bonds.
- 😀 Lewis structures are used to visualize how atoms share electrons in both ionic and covalent compounds.
- 😀 The script provides examples of ionic compounds, like NH4SO4 and CaSO4, and how to correctly write their chemical formulas.
- 😀 Different types of covalent bonds, such as single, double, and triple bonds, are explained using examples like CH4, CO2, and HCN.
- 😀 The importance of the electron configuration and the periodic table groups in predicting bonding behavior and compound formation is emphasized.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the script?
-The script focuses on teaching students about chemical bonding, specifically ionic and covalent bonds, and how to determine chemical formulas and names based on atomic properties and electron configurations.
How do students determine whether a bond is ionic or covalent?
-Students determine the type of bond by examining the valence electrons of the atoms involved. If one atom donates electrons and the other accepts, it forms an ionic bond. If electrons are shared, the bond is covalent.
What is the significance of group numbers in the periodic table in determining bond types?
-Group numbers help identify the valence electrons of an atom. Atoms from group 2A typically form +2 ions, while atoms from group 6A tend to form -2 ions, leading to ionic bonds when combined.
What is the chemical formula for a compound formed between an atom from group 2A and group 6A?
-The chemical formula would be XY, where X represents the element from group 2A and Y represents the element from group 6A, reflecting the +2 and -2 charges, respectively.
What is the Lewis structure of an atom with 2 valence electrons, like X in the script?
-The Lewis structure would show X with 2 electrons in its outer shell, and it would typically form an ion with a +2 charge by losing these electrons to another atom.
How does the script explain the naming of ionic compounds?
-The script explains that ionic compounds are named by identifying the cation and anion, removing their charges, and combining them in a way that balances the overall charge.
What are the key differences between covalent and ionic bonds, according to the script?
-Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, while ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons, resulting in positive and negative ions attracting each other.
What does the script suggest about the naming convention for covalent compounds?
-For covalent compounds, the script emphasizes that the number of atoms of each element is indicated using prefixes (e.g., 'di-' for two, 'tri-' for three), except when there is only one atom of the first element.
What is the correct naming and formula for the compound formed by potassium and sulfur?
-The compound formed by potassium (K) and sulfur (S) is called potassium sulfide (K2S), and it is an ionic compound due to the transfer of electrons between the ions.
How does the script describe the interaction between sulfur and fluorine?
-The script explains that sulfur and fluorine form a covalent bond, as both elements need electrons to complete their octets. The resulting formula is SF2, with sulfur sharing electrons with two fluorine atoms.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

CHEMICAL BONDING Class 11 One Shot for JEE Mains 2025 | Simply Concise

6.2 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds
CHEM 257 - Fall 2024 - Lecture 1 - Video 2

¿CÓMO dibujar estructuras de LEWIS? 1º parte.

Video 6b/17- Lewis Dot Diagrams, the BVICS method- Chemistry, Regents360

Class 11 Chemistry | Chemical Bonding and Molecular Str. in 15 Minutes | Rapid Revision by BP Sir
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
